First question is why we need Normalisation/Standardisation?
=> We take a example of dataset where we have salary variable and age variable.
Age can take range from 0 to 90 where salary can be from 25,000 to 250,000.
We compare difference for 2 person then age difference will be in range of below 100 where salary difference will in range of thousands.
So if we don't want one variable to dominate other then we use either Normalisation or Standardization. Now both age and salary will be in same scale
but when we use standardiztion or normalisation, we lose original values and it is transformed to some values. So loss of interpretation but extremely important when we want to draw inference from our data.
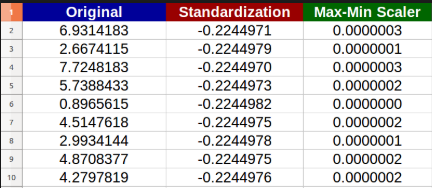
Normalization rescales the values into a range of [0,1]. also called min-max scaled.
Standardization rescales data to have a mean (μ) of 0 and standard deviation (σ) of 1.So it gives a normal graph.
![enter image description here]()
Example below:
![enter image description here]()
Another example:
![enter image description here]()
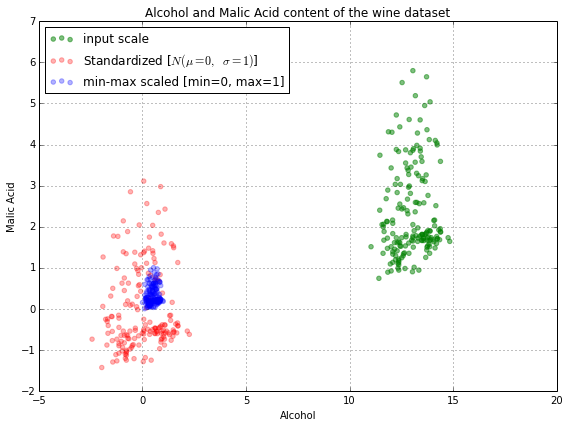
In above image, you can see that our actual data(in green) is spread b/w 1 to 6, standardised data(in red) is spread around -1 to 3 whereas normalised data(in blue) is spread around 0 to 1.
Normally many algorithm required you to first standardise/normalise data before passing as parameter. Like in PCA, where we do dimension reduction by plotting our 3D data into 1D(say).Here we required standardisation.
But in Image processing, it is required to normalise pixels before processing.
But during normalisation, we lose outliers(extreme datapoints-either too low or too high) which is slight disadvantage.
So it depends on our preference what we chose but standardisation is most recommended as it gives a normal curve.