There are a couple of CSS 3 measurement units called:
What are Viewport-Percentage Lengths?
From the linked W3 Candidate Recommendation above:
The viewport-percentage lengths are relative to the size of the initial containing block. When the height or width of the initial containing block is changed, they are scaled accordingly.
These units are vh (viewport height), vw (viewport width), vmin (viewport minimum length) and vmax (viewport maximum length).
How can this be used to make a divider fill the height of the browser?
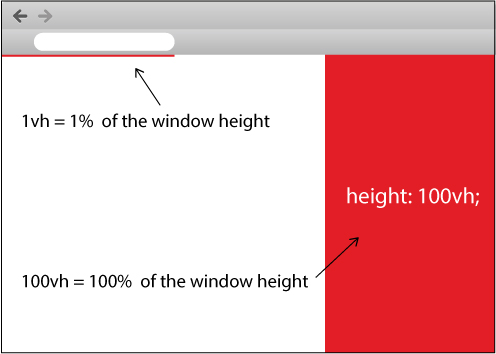
For this question, we can make use of vh: 1vh is equal to 1% of the viewport's height. That is to say, 100vh is equal to the height of the browser window, regardless of where the element is situated in the DOM tree:
HTML
<div></div>
CSS
div {
height: 100vh;
}
This is literally all that's needed. Here is a JSFiddle example of this in use.
What browsers support these new units?
This is currently supported on all up-to-date major browsers apart from Opera Mini. Check out Can I use... for further support.
How can this be used with multiple columns?
In the case of the question at hand, featuring a left and a right divider, here is a JSFiddle example showing a two-column layout involving both vh and vw.
How is 100vh different from 100%?
Take this layout for example:
<body style="height: 100%">
<div style="height: 200px">
<p style="height: 100%; display: block;">Hello, world!</p>
</div>
</body>
The p tag here is set to 100% height, but because its containing div has 200 pixels height, 100% of 200 pixels becomes 200 pixels, not 100% of the body height. Using 100vh instead means that the p tag will be 100% height of the body regardless of the div height. Take a look at this accompanying JSFiddle to easily see the difference!

heightproperty with percentage values: https://mcmap.net/q/36844/-why-is-percentage-height-not-working-on-my-div-duplicate – Oxamin-height:100vh; height:100vh; max-height:100vh;– Vanhook