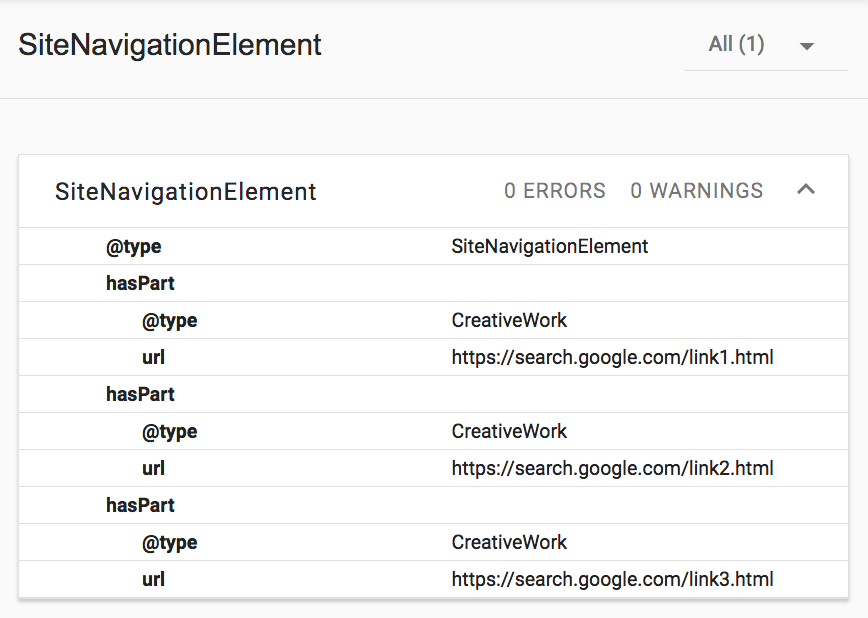
In SEO terms...
Is it best to put the scheme on the parent containing all the links?
<nav itemscope="itemscope" itemtype="http://www.schema.org/SiteNavigationElement">
<a href="#">Link 1</a>
<a href="#">Link 2</a>
<a href="#">Link 3</a>
</nav>
...or should each link be considered as it's own element?
<nav>
<span itemscope="itemscope" itemtype="http://www.schema.org/SiteNavigationElement">
<a itemprop="url" href="#">
<span itemprop="name">Link 1</span>
</a>
</span>
<span itemscope="itemscope" itemtype="http://www.schema.org/SiteNavigationElement">
<a itemprop="url" href="#">
<span itemprop="name">Link 2</span>
</a>
</span>
<span itemscope="itemscope" itemtype="http://www.schema.org/SiteNavigationElement">
<a itemprop="url" href="#">
<span itemprop="name">Link 3</span>
</a>
</span>
</nav>