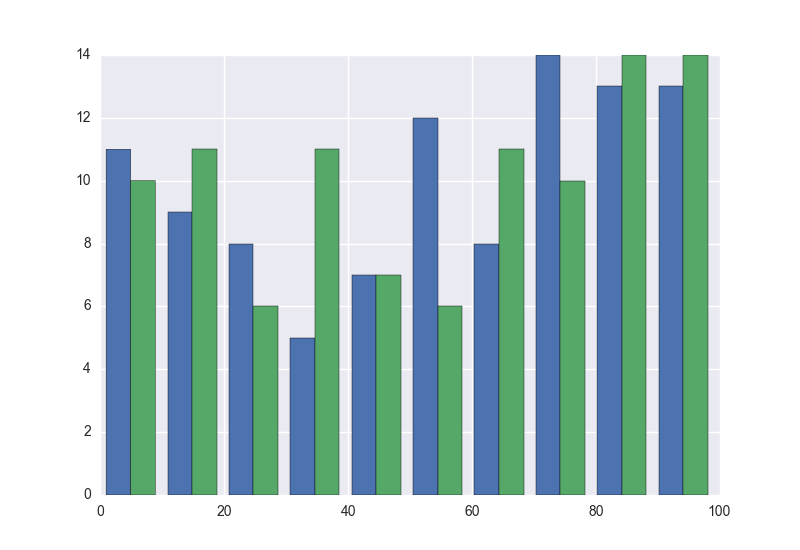
With matplotlib, I can make a histogram with two datasets on one plot (one next to the other, not overlay).
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
x = [random.randrange(100) for i in range(100)]
y = [random.randrange(100) for i in range(100)]
plt.hist([x, y])
plt.show()
This yields the following plot.
However, when I try to do this with seabron;
import seaborn as sns
sns.distplot([x, y])
I get the following error:
ValueError: color kwarg must have one color per dataset
So then I try to add some color values:
sns.distplot([x, y], color=['r', 'b'])
And I get the same error. I saw this post on how to overlay graphs, but I would like these histograms to be side by side, not overlay.
And looking at the docs it doesn't specify how to include a list of lists as the first argument 'a'.
How can I achieve this style of histogram using seaborn?