I am thinking about it and this is what I came up with:
Let's see this code below:
console.clear();
console.log("a");
setTimeout(function(){console.log("b");},1000);
console.log("c");
setTimeout(function(){console.log("d");},0);
A request comes in, and JS engine starts executing the code above step by step. The first two calls are sync calls. But when it comes to setTimeout method, it becomes an async execution. But JS immediately returns from it and continue executing, which is called Non-Blocking or Async. And it continues working on other etc.
The results of this execution is the following:
a c d b
So basically the second setTimeout got finished first and its callback function gets executed earlier than the first one and that makes sense.
We are talking about single-threaded application here. JS Engine keeps executing this and unless it finishes the first request, it won't go to second one. But the good thing is that it won't wait for blocking operations like setTimeout to resolve so it will be faster because it accepts the new incoming requests.
But my questions arise around the following items:
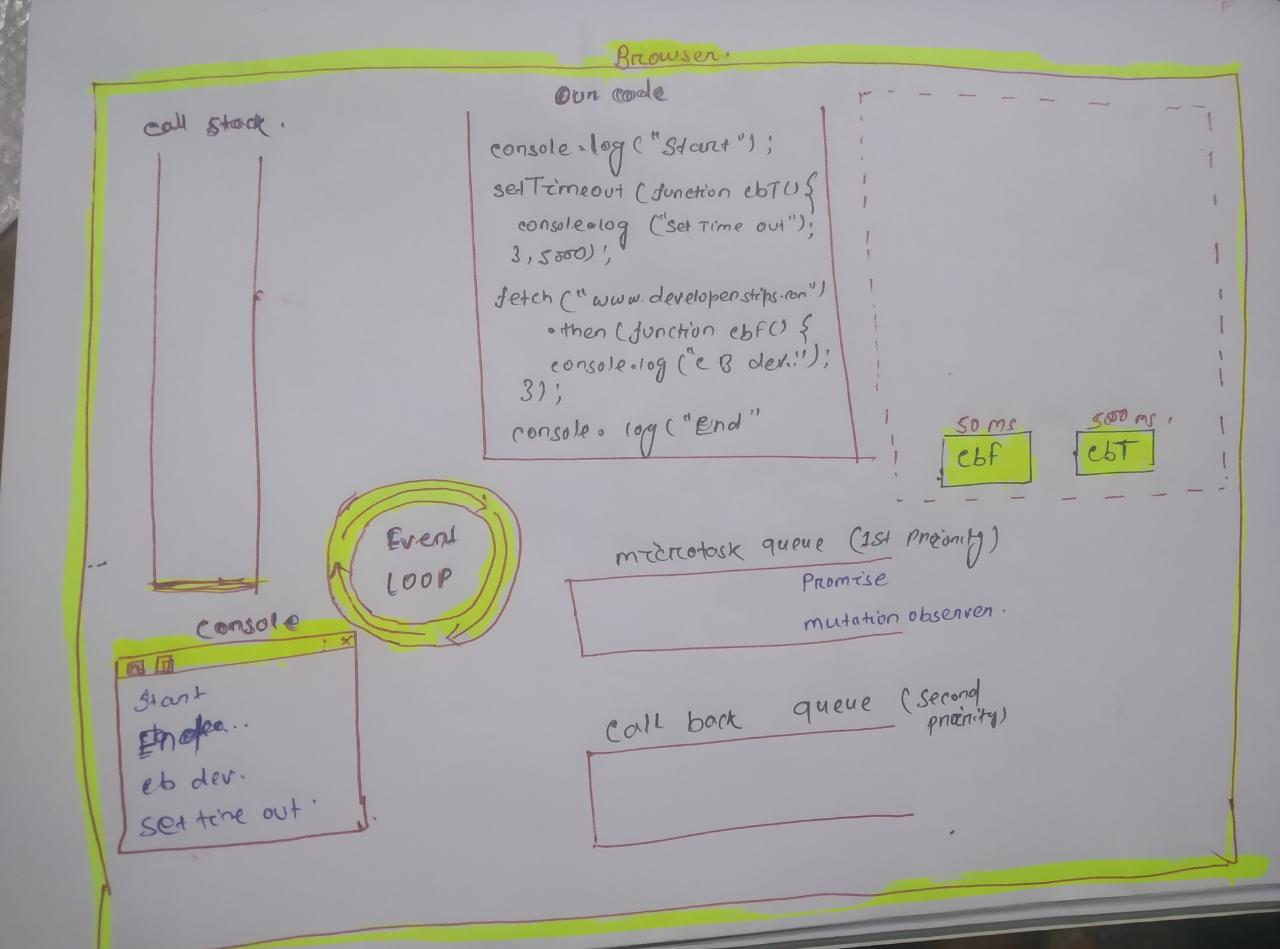
#1: If we are talking about a single-threaded application, then what mechanism processes setTimeouts while the JS engine accepts more requests and executes them? How does the single thread continue working on other requests? What works on setTimeout while other requests keep coming in and get executed.
#2: If these setTimeout functions get executed behind the scenes while more requests are coming in and being executed, what carries out the async executions behind the scenes? What is this thing that we talk about called the EventLoop?
#3: But shouldn't the whole method be put in the EventLoop so that the whole thing gets executed and the callback method gets called? This is what I understand when talking about callback functions:
function downloadFile(filePath, callback)
{
blah.downloadFile(filePath);
callback();
}
But in this case, how does the JS Engine know if it is an async function so that it can put the callback in the EventLoop? Perhaps something like the async keyword in C# or some sort of an attribute which indicates the method JS Engine will take on is an async method and should be treated accordingly.
#4: But an article says quite contrary to what I was guessing on how things might be working:
The Event Loop is a queue of callback functions. When an async function executes, the callback function is pushed into the queue. The JavaScript engine doesn't start processing the event loop until the code after an async function has executed.
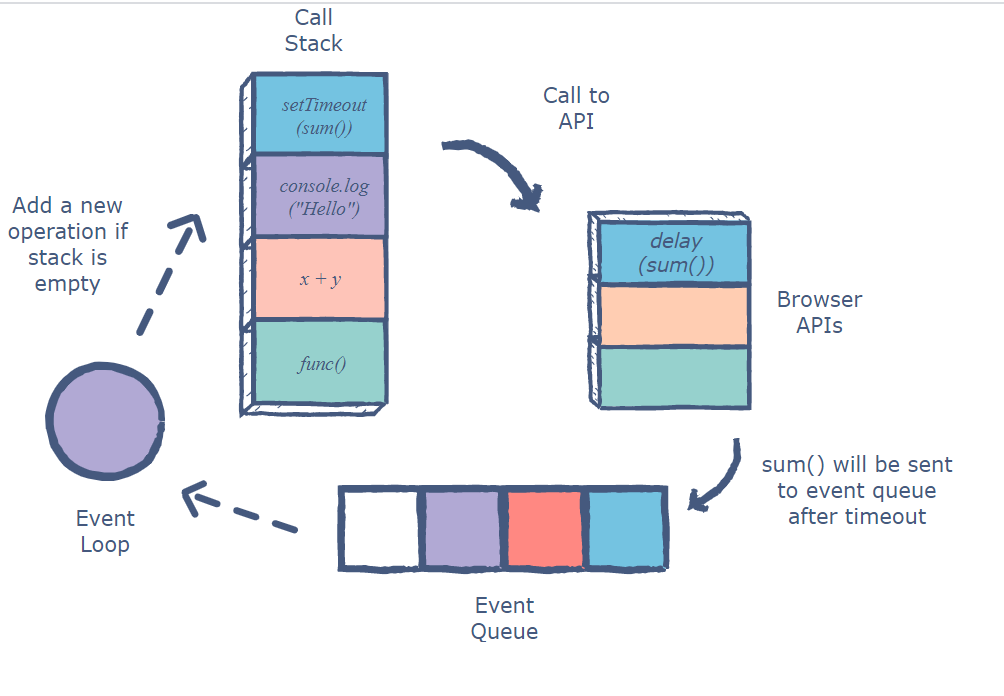
#5: And there is this image here which might be helpful but the first explanation in the image is saying exactly the same thing mentioned in question number 4:

So my question here is to get some clarifications about the items listed above?

grep -R pthread node/lib node/src, and compare it withgrep -R pthread node/deps/uv. Node.js own source code doesn't create threads. – Pianoforte