I was struggling with same question. Especially, as most of code samples are already outdated + Android Studio/SDKs is improving, so old answers sometimes are not relevant anymore.
So, first things first: you need to determine if you want to use Instrumental or simple JUnit tests.
The difference between them beautifully described by S.D. here;
In short: JUnit tests are more lightweight and not require an emulator to run, Instrumental - give you the closest to the actual device possible experience (sensors, gps, interaction with other apps etc.). Also read more about testing in Android.
1. JUnit testing of fragments
Let's say, you don't need heavy Instrumental tests and simple junit tests are enough.
I use nice framework Robolectric for this purpose.
In gradle add:
dependencies {
.....
testImplementation('junit:junit:4.12')
testImplementation('org.robolectric:robolectric:3.0')
testImplementation("org.mockito:mockito-core:1.10.8")
testImplementation('com.squareup.assertj:assertj-android:1.0.0') {
exclude module: 'support-annotations'
}
.....
}
Mockito, AsserJ are optional, but I found them very useful so I highly recommend to include them too.
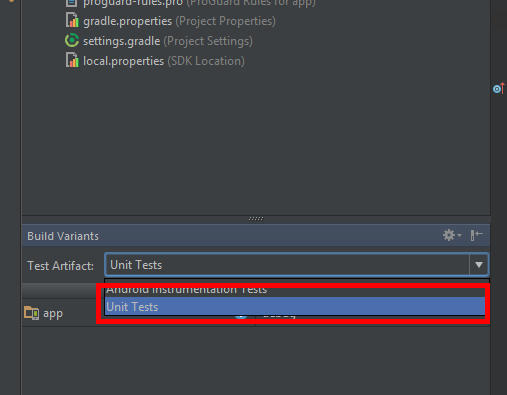
Then in Build Variants specify Unit Tests as a Test Artifact:
![enter image description here]()
Now it's time to write some real tests :-)
As an example, lets take the standard "Blank Activity with Fragment" sample project.
I added some lines of code, to have actually something to test:
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivityFragment extends Fragment {
private List<Cow> cows;
public MainActivityFragment() {}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
cows = new ArrayList<>();
cows.add(new Cow("Burka", 10));
cows.add(new Cow("Zorka", 9));
cows.add(new Cow("Kruzenshtern", 15));
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main, container, false);
}
int calculateYoungCows(int maxAge) {
if (cows == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("onCreateView hasn't been called");
}
if (getActivity() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Activity is null");
}
if (getView() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("View is null");
}
int result = 0;
for (Cow cow : cows) {
if (cow.age <= maxAge) {
result++;
}
}
return result;
}
}
And class Cow:
public class Cow {
public String name;
public int age;
public Cow(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
The Robolectic's test set would look something like:
import android.app.Application;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentManager;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.test.ApplicationTestCase;
import junit.framework.Assert;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.robolectric.Robolectric;
import org.robolectric.RobolectricGradleTestRunner;
import org.robolectric.annotation.Config;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.mock;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
@RunWith(RobolectricGradleTestRunner.class)
@Config(constants = BuildConfig.class, sdk=21)
public class MainActivityFragmentTest extends ApplicationTestCase<Application> {
public MainActivityFragmentTest() {
super(Application.class);
}
MainActivity mainActivity;
MainActivityFragment mainActivityFragment;
@Before
public void setUp() {
mainActivity = Robolectric.setupActivity(MainActivity.class);
mainActivityFragment = new MainActivityFragment();
startFragment(mainActivityFragment);
}
@Test
public void testMainActivity() {
Assert.assertNotNull(mainActivity);
}
@Test
public void testCowsCounter() {
assertThat(mainActivityFragment.calculateYoungCows(10)).isEqualTo(2);
assertThat(mainActivityFragment.calculateYoungCows(99)).isEqualTo(3);
}
private void startFragment( Fragment fragment ) {
FragmentManager fragmentManager = mainActivity.getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
fragmentTransaction.add(fragment, null );
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
}
I.e. we create activity via Robolectric.setupActivity, new fragment in the test-classes' setUp(). Optionally, you can immediately start the fragment from the setUp() or you can do it directly from the test.
NB! I haven't spent too much time on it, but it looks like it's almost impossible to tie it together with Dagger(I don't know if it's easier with Dagger2), as you can't set custom test Application with mocked injections.
2. Instrumental testing of fragments
The complexity of this approach is highly depends on if you're using Dagger/Dependency injection in the app you want to test.
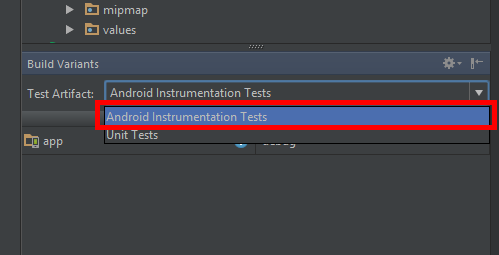
In Build Variants specify Android Instrumental Tests as a Test Artifact:
![enter image description here]()
In Gradle I add these dependencies:
dependencies {
.....
androidTestCompile "com.google.dexmaker:dexmaker:1.1"
androidTestCompile "com.google.dexmaker:dexmaker-mockito:1.1"
androidTestCompile 'com.squareup.assertj:assertj-android:1.0.0'
androidTestCompile "org.mockito:mockito-core:1.10.8"
}
.....
}
(again, pretty much all of them are optional, but they can make your life so much easier)
- If you don't have Dagger
This a happy path. The difference with Robolectric from the above would be only in small details.
Pre-step 1: If you are going to use Mockito, you have to enable it to run on the devices and emulators with this hack:
public class TestUtils {
private static final String CACHE_DIRECTORY = "/data/data/" + BuildConfig.APPLICATION_ID + "/cache";
public static final String DEXMAKER_CACHE_PROPERTY = "dexmaker.dexcache";
public static void enableMockitoOnDevicesAndEmulators() {
if (System.getProperty(DEXMAKER_CACHE_PROPERTY) == null || System.getProperty(DEXMAKER_CACHE_PROPERTY).isEmpty()) {
File file = new File(CACHE_DIRECTORY);
if (!file.exists()) {
final boolean success = file.mkdirs();
if (!success) {
fail("Unable to create cache directory required for Mockito");
}
}
System.setProperty(DEXMAKER_CACHE_PROPERTY, file.getPath());
}
}
}
The MainActivityFragment stays the same, as above. So the test-set would look like:
package com.klogi.myapplication;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentManager;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.test.ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2;
import junit.framework.Assert;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.mock;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
public class MainActivityFragmentTest extends ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2<MainActivity> {
public MainActivityFragmentTest() {
super(MainActivity.class);
}
MainActivity mainActivity;
MainActivityFragment mainActivityFragment;
@Override
protected void setUp() throws Exception {
TestUtils.enableMockitoOnDevicesAndEmulators();
mainActivity = getActivity();
mainActivityFragment = new MainActivityFragment();
}
public void testMainActivity() {
Assert.assertNotNull(mainActivity);
}
public void testCowsCounter() {
startFragment(mainActivityFragment);
assertThat(mainActivityFragment.calculateYoungCows(10)).isEqualTo(2);
assertThat(mainActivityFragment.calculateYoungCows(99)).isEqualTo(3);
}
private void startFragment( Fragment fragment ) {
FragmentManager fragmentManager = mainActivity.getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
fragmentTransaction.add(fragment, null);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
getActivity().runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
getActivity().getSupportFragmentManager().executePendingTransactions();
}
});
getInstrumentation().waitForIdleSync();
}
}
As you can see, Test class is an extension of ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2 class.
Also, it's very important to pay attention to startFragment method, that has changed comparing to JUnit example: by default, tests are not running on the UI thread and we need to explicitly call for execution pending FragmentManager's transactions.
- If you do have Dagger
Things are getting serious here :-)
First, we are getting rid of ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2 in favor of ActivityUnitTestCase class, as a base class for all fragment's test classes.
As usual, it's not that simple and there're several pitfalls (this is one of examples). So we need to pimp our AcitivityUnitTestCase to ActivityUnitTestCaseOverride
It's a bit too long to post it fully here, so I upload full version of it to github;
public abstract class ActivityUnitTestCaseOverride<T extends Activity>
extends ActivityUnitTestCase<T> {
........
private Class<T> mActivityClass;
private Context mActivityContext;
private Application mApplication;
private MockParent mMockParent;
private boolean mAttached = false;
private boolean mCreated = false;
public ActivityUnitTestCaseOverride(Class<T> activityClass) {
super(activityClass);
mActivityClass = activityClass;
}
@Override
public T getActivity() {
return (T) super.getActivity();
}
@Override
protected void setUp() throws Exception {
super.setUp();
// default value for target context, as a default
mActivityContext = getInstrumentation().getTargetContext();
}
/**
* Start the activity under test, in the same way as if it was started by
* {@link android.content.Context#startActivity Context.startActivity()}, providing the
* arguments it supplied. When you use this method to start the activity, it will automatically
* be stopped by {@link #tearDown}.
* <p/>
* <p>This method will call onCreate(), but if you wish to further exercise Activity life
* cycle methods, you must call them yourself from your test case.
* <p/>
* <p><i>Do not call from your setUp() method. You must call this method from each of your
* test methods.</i>
*
* @param intent The Intent as if supplied to {@link android.content.Context#startActivity}.
* @param savedInstanceState The instance state, if you are simulating this part of the life
* cycle. Typically null.
* @param lastNonConfigurationInstance This Object will be available to the
* Activity if it calls {@link android.app.Activity#getLastNonConfigurationInstance()}.
* Typically null.
* @return Returns the Activity that was created
*/
protected T startActivity(Intent intent, Bundle savedInstanceState,
Object lastNonConfigurationInstance) {
assertFalse("Activity already created", mCreated);
if (!mAttached) {
assertNotNull(mActivityClass);
setActivity(null);
T newActivity = null;
try {
IBinder token = null;
if (mApplication == null) {
setApplication(new MockApplication());
}
ComponentName cn = new ComponentName(getInstrumentation().getTargetContext(), mActivityClass.getName());
intent.setComponent(cn);
ActivityInfo info = new ActivityInfo();
CharSequence title = mActivityClass.getName();
mMockParent = new MockParent();
String id = null;
newActivity = (T) getInstrumentation().newActivity(mActivityClass, mActivityContext,
token, mApplication, intent, info, title, mMockParent, id,
lastNonConfigurationInstance);
} catch (Exception e) {
assertNotNull(newActivity);
}
assertNotNull(newActivity);
setActivity(newActivity);
mAttached = true;
}
T result = getActivity();
if (result != null) {
getInstrumentation().callActivityOnCreate(getActivity(), savedInstanceState);
mCreated = true;
}
return result;
}
protected Class<T> getActivityClass() {
return mActivityClass;
}
@Override
protected void tearDown() throws Exception {
setActivity(null);
// Scrub out members - protects against memory leaks in the case where someone
// creates a non-static inner class (thus referencing the test case) and gives it to
// someone else to hold onto
scrubClass(ActivityInstrumentationTestCase.class);
super.tearDown();
}
/**
* Set the application for use during the test. You must call this function before calling
* {@link #startActivity}. If your test does not call this method,
*
* @param application The Application object that will be injected into the Activity under test.
*/
public void setApplication(Application application) {
mApplication = application;
}
.......
}
Create an abstract AbstractFragmentTest for all your fragment tests:
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.ActivityInfo;
import android.content.res.Configuration;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentManager;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentTransaction;
/**
* Common base class for {@link Fragment} tests.
*/
public abstract class AbstractFragmentTest<TFragment extends Fragment, TActivity extends FragmentActivity> extends ActivityUnitTestCaseOverride<TActivity> {
private TFragment fragment;
protected MockInjectionRegistration mocks;
protected AbstractFragmentTest(TFragment fragment, Class<TActivity> activityType) {
super(activityType);
this.fragment = parameterIsNotNull(fragment);
}
@Override
protected void setActivity(Activity testActivity) {
if (testActivity != null) {
testActivity.setTheme(R.style.AppCompatTheme);
}
super.setActivity(testActivity);
}
/**
* Get the {@link Fragment} under test.
*/
protected TFragment getFragment() {
return fragment;
}
protected void setUpActivityAndFragment() {
createMockApplication();
final Intent intent = new Intent(getInstrumentation().getTargetContext(),
getActivityClass());
startActivity(intent, null, null);
startFragment(getFragment());
getInstrumentation().callActivityOnStart(getActivity());
getInstrumentation().callActivityOnResume(getActivity());
}
private void createMockApplication() {
TestUtils.enableMockitoOnDevicesAndEmulators();
mocks = new MockInjectionRegistration();
TestApplication testApplication = new TestApplication(getInstrumentation().getTargetContext());
testApplication.setModules(mocks);
testApplication.onCreate();
setApplication(testApplication);
}
private void startFragment(Fragment fragment) {
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getActivity().getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
fragmentTransaction.add(fragment, null);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
}
There're several important things here.
1) We override setActivity() method to set the AppCompact theme to the activity. Without that, test suit will crash.
2) setUpActivityAndFragment() method:
I. creates activity ( => getActivity() starts returning non-null value, in tests and in the app which is under test)
onCreate() of activity called;
onStart() of activity called;
onResume() of activity called;
II. attach and starts fragment to the activity
onAttach() of fragment called;
onCreateView() of fragment called;
onStart() of fragment called;
onResume() of fragment called;
3) createMockApplication() method:
As in the non-dagger version, in Pre-step 1, we enable mocking on the devices and on the emulators.
Then we replace the normal application with its injections with our custom, TestApplication!
MockInjectionRegistration looks like:
....
import javax.inject.Singleton;
import dagger.Module;
import dagger.Provides;
import de.greenrobot.event.EventBus;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.mock;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
@Module(
injects = {
....
MainActivity.class,
MyWorkFragment.class,
HomeFragment.class,
ProfileFragment.class,
....
},
addsTo = DelveMobileInjectionRegistration.class,
overrides = true
)
public final class MockInjectionRegistration {
.....
public DataSource dataSource;
public EventBus eventBus;
public MixpanelAPI mixpanel;
.....
public MockInjectionRegistration() {
.....
dataSource = mock(DataSource.class);
eventBus = mock(EventBus.class);
mixpanel = mock(MixpanelAPI.class);
MixpanelAPI.People mixpanelPeople = mock(MixpanelAPI.People.class);
when(mixpanel.getPeople()).thenReturn(mixpanelPeople);
.....
}
...........
@Provides
@Singleton
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
// invoked by Dagger
DataSource provideDataSource() {
Guard.valueIsNotNull(dataSource);
return dataSource;
}
@Provides
@Singleton
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
// invoked by Dagger
EventBus provideEventBus() {
Guard.valueIsNotNull(eventBus);
return eventBus;
}
@Provides
@Singleton
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
// invoked by Dagger
MixpanelAPI provideMixpanelAPI() {
Guard.valueIsNotNull(mixpanel);
return mixpanel;
}
.........
}
I.e. instead of real classes, we are providing to the fragments their mocked versions. (That are easily traceable, allows to configure results of method calls, etc.).
And the TestApplication is just your custom extension of Application, that should support setting modules and initialize the ObjectGraph.
These were pre-steps for start writing the tests :)
Now the simple part, the real tests:
public class SearchFragmentTest extends AbstractFragmentTest<SearchFragment, MainActivity> {
public SearchFragmentTest() {
super(new SearchFragment(), MainActivity.class);
}
@UiThreadTest
public void testOnCreateView() throws Exception {
setUpActivityAndFragment();
SearchFragment searchFragment = getFragment();
assertNotNull(searchFragment.adapter);
assertNotNull(SearchFragment.getSearchAdapter());
assertNotNull(SearchFragment.getSearchSignalLogger());
}
@UiThreadTest
public void testOnPause() throws Exception {
setUpActivityAndFragment();
SearchFragment searchFragment = getFragment();
assertTrue(Strings.isNullOrEmpty(SharedPreferencesTools.getString(getActivity(), SearchFragment.SEARCH_STATE_BUNDLE_ARGUMENT)));
searchFragment.searchBoxRef.setCurrentConstraint("abs");
searchFragment.onPause();
assertEquals(searchFragment.searchBoxRef.getCurrentConstraint(), SharedPreferencesTools.getString(getActivity(), SearchFragment.SEARCH_STATE_BUNDLE_ARGUMENT));
}
@UiThreadTest
public void testOnQueryTextChange() throws Exception {
setUpActivityAndFragment();
reset(mocks.eventBus);
getFragment().onQueryTextChange("Donald");
Thread.sleep(300);
// Should be one cached, one uncached event
verify(mocks.eventBus, times(2)).post(isA(SearchRequest.class));
verify(mocks.eventBus).post(isA(SearchLoadingIndicatorEvent.class));
}
@UiThreadTest
public void testOnQueryUpdateEventWithDifferentConstraint() throws Exception {
setUpActivityAndFragment();
reset(mocks.eventBus);
getFragment().onEventMainThread(new SearchResponse(new ArrayList<>(), "Donald", false));
verifyNoMoreInteractions(mocks.eventBus);
}
....
}
That's it!
Now you have Instrumental/JUnit tests enabled for your Fragments.
I sincerely hope this post helps someone.