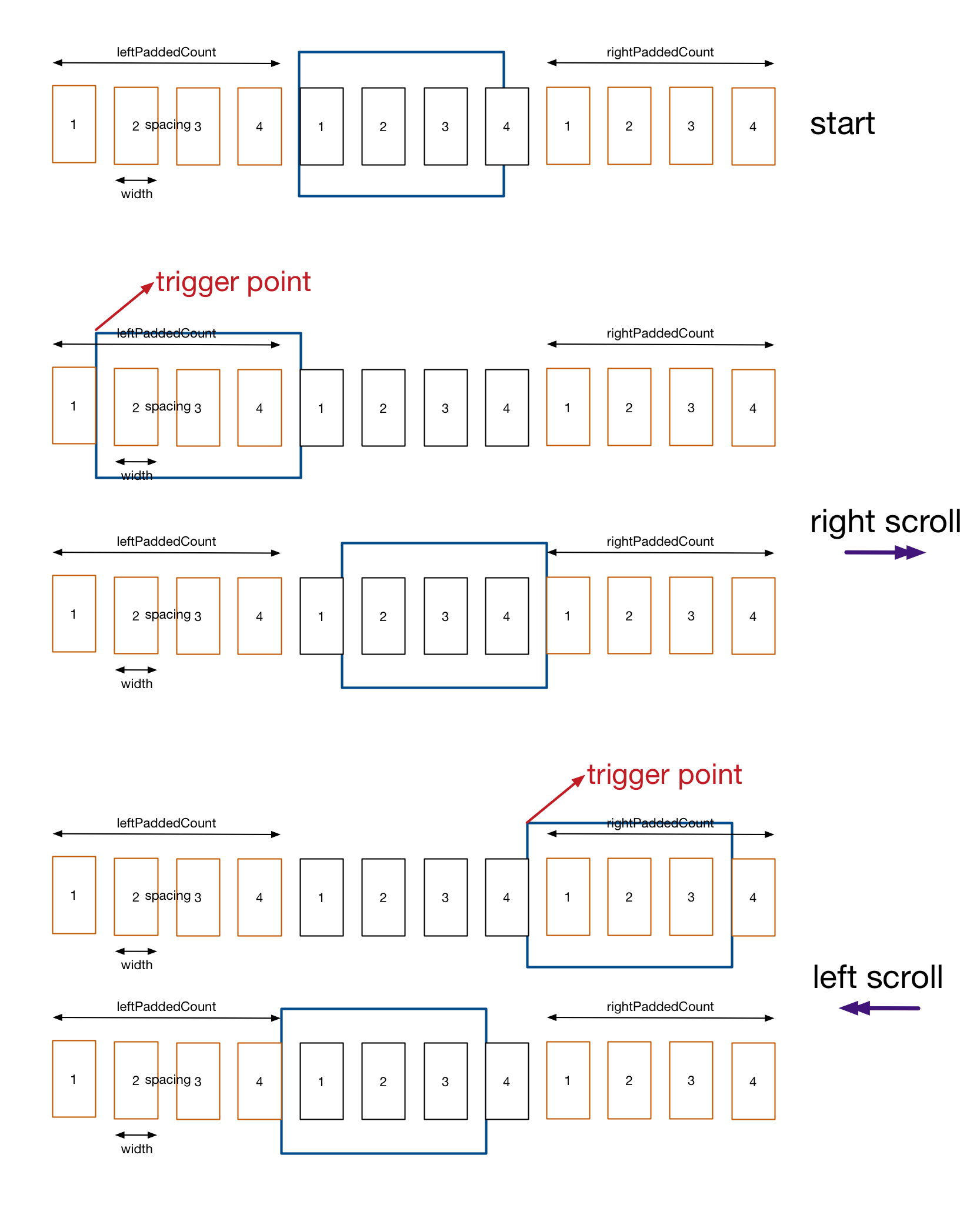
You can get infinite scrolling, by using the technique of re-centering the UIScrollView after you get a certain distance away from the center. First, you need to make the contentSize big enough that you can scroll a bit, so I return 4 times the number of items in my sections and 4 times the number of sections, and use the mod operator in the cellForItemAtIndexPath method to get the right index into my array. You then have to override layoutSubviews in a subclass of UICollectionView to do the re-centering (this is demonstrated in the WWDC 2011 video, "Advanced Scroll View Techniques"). Here is the controller class that has the collection view (set up in IB) as a subview:
#import "ViewController.h"
#import "MultpleLineLayout.h"
#import "DataCell.h"
@interface ViewController ()
@property (weak,nonatomic) IBOutlet UICollectionView *collectionView;
@property (strong,nonatomic) NSArray *theData;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
self.theData = @[@[@"1",@"2",@"3",@"4",@"5"], @[@"6",@"7",@"8",@"9",@"10"],@[@"11",@"12",@"13",@"14",@"15"],@[@"16",@"17",@"18",@"19",@"20"]];
MultpleLineLayout *layout = [[MultpleLineLayout alloc] init];
self.collectionView.collectionViewLayout = layout;
self.collectionView.showsHorizontalScrollIndicator = NO;
self.collectionView.showsVerticalScrollIndicator = NO;
layout.scrollDirection = UICollectionViewScrollDirectionHorizontal;
self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor blackColor];
[self.collectionView registerClass:[DataCell class] forCellWithReuseIdentifier:@"DataCell"];
[self.collectionView reloadData];
}
- (NSInteger)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)view numberOfItemsInSection:(NSInteger)section {
return 20;
}
- (NSInteger)numberOfSectionsInCollectionView: (UICollectionView *)collectionView {
return 16;
}
- (UICollectionViewCell *)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView cellForItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
DataCell *cell = [collectionView dequeueReusableCellWithReuseIdentifier:@"DataCell" forIndexPath:indexPath];
cell.label.text = self.theData[indexPath.section %4][indexPath.row %5];
return cell;
}
- (void)collectionView:(UICollectionView *)collectionView didSelectItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {
// UICollectionViewCell *item = [collectionView cellForItemAtIndexPath:indexPath];
NSLog(@"%@",indexPath);
}
Here is the UICollectionViewFlowLayout subclass:
#define space 5
#import "MultpleLineLayout.h"
@implementation MultpleLineLayout { // a subclass of UICollectionViewFlowLayout
NSInteger itemWidth;
NSInteger itemHeight;
}
-(id)init {
if (self = [super init]) {
itemWidth = 60;
itemHeight = 60;
}
return self;
}
-(CGSize)collectionViewContentSize {
NSInteger xSize = [self.collectionView numberOfItemsInSection:0] * (itemWidth + space); // "space" is for spacing between cells.
NSInteger ySize = [self.collectionView numberOfSections] * (itemHeight + space);
return CGSizeMake(xSize, ySize);
}
- (UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes *)layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)path {
UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes* attributes = [UICollectionViewLayoutAttributes layoutAttributesForCellWithIndexPath:path];
attributes.size = CGSizeMake(itemWidth,itemHeight);
int xValue = itemWidth/2 + path.row * (itemWidth + space);
int yValue = itemHeight + path.section * (itemHeight + space);
attributes.center = CGPointMake(xValue, yValue);
return attributes;
}
-(NSArray*)layoutAttributesForElementsInRect:(CGRect)rect {
NSInteger minRow = (rect.origin.x > 0)? rect.origin.x/(itemWidth + space) : 0; // need to check because bounce gives negative values for x.
NSInteger maxRow = rect.size.width/(itemWidth + space) + minRow;
NSMutableArray* attributes = [NSMutableArray array];
for(NSInteger i=0 ; i < self.collectionView.numberOfSections; i++) {
for (NSInteger j=minRow ; j < maxRow; j++) {
NSIndexPath* indexPath = [NSIndexPath indexPathForItem:j inSection:i];
[attributes addObject:[self layoutAttributesForItemAtIndexPath:indexPath]];
}
}
return attributes;
}
And finally, here is the subclass of UICollectionView:
-(void)layoutSubviews {
[super layoutSubviews];
CGPoint currentOffset = self.contentOffset;
CGFloat contentWidth = self.contentSize.width;
CGFloat contentHeight = self.contentSize.height;
CGFloat centerOffsetX = (contentWidth - self.bounds.size.width)/ 2.0;
CGFloat centerOffsetY = (contentHeight - self.bounds.size.height)/ 2.0;
CGFloat distanceFromCenterX = fabsf(currentOffset.x - centerOffsetX);
CGFloat distanceFromCenterY = fabsf(currentOffset.y - centerOffsetY);
if (distanceFromCenterX > contentWidth/4.0) { // this number of 4.0 is arbitrary
self.contentOffset = CGPointMake(centerOffsetX, currentOffset.y);
}
if (distanceFromCenterY > contentHeight/4.0) {
self.contentOffset = CGPointMake(currentOffset.x, centerOffsetY);
}
}



HBO GOapp. Basically it should load the tiles from an NSArray with UIViews or UIButtons or similar. It should be straightforward, however I can't seem to figure out how to do it. – Leland