To customize framework model binding error messages, you need to set custom accessors for different error message accessors of ModelBindingMessageProvider.
Example
Here you can download a full source code of what is described in this post. The repository contains example for ASP.NET Core 2.0 (VS 2017.3) and ASP.NET Core 1.1 (VS 2015):
Also here you can see the example, live:
Default Error Messages
These are default error messages which the framework shows when model binding to a property fails:
MissingBindRequiredValueAccessor A value for the '{0}' property was not provided.
MissingKeyOrValueAccessor A value is required.
ValueMustNotBeNullAccessor The value '{0}' is invalid.
AttemptedValueIsInvalidAccessor The value '{0}' is not valid for {1}.
UnknownValueIsInvalidAccessor The supplied value is invalid for {0}.
ValueIsInvalidAccessor The value '{0}' is invalid.
ValueMustBeANumberAccessor The field {0} must be a number.
In addition to above messages, ASP.NET Core 2.0 have these messages as well:
MissingRequestBodyRequiredValueAccessor A non-empty request body is required.
NonPropertyAttemptedValueIsInvalidAccessor The value '{0}' is not valid.
NonPropertyUnknownValueIsInvalidAccessor The supplied value is invalid.
NonPropertyValueMustBeANumberAccessor The field must be a number.
Localize ASP.NET Core Model Binding Error Messages
To localize ASP.NET Core model binding error messages, follow these steps:
Create Resource File - Create a resource file under Resources folder in your solution and name the file ModelBindingMessages.fa.resx. The name can be anything else but we will use it to create a localizer. In the example, I used fa (Persian) culture.
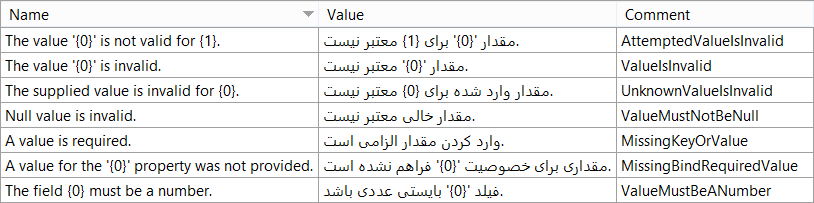
Add Resource Keys - Open the resource file and add keys and values which you want to use for localizing error messages. I used keys and values like below image:
![enter image description here]()
Keys which I used are like original messages, except the key for ValueMustNotBeNull which was the same as ValueIsInvalid, so I used Null value is invalid. for it.
Configure Options - In ConfigureServices method, when adding Mvc, configure its options to set message accessors for ModelBindingMessageProvider:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddLocalization(options => { options.ResourcesPath = "Resources"; });
services.AddMvc(options =>
{
var F = services.BuildServiceProvider().GetService<IStringLocalizerFactory>();
var L = F.Create("ModelBindingMessages", "AspNetCoreLocalizationSample");
options.ModelBindingMessageProvider.ValueIsInvalidAccessor =
(x) => L["The value '{0}' is invalid.", x];
options.ModelBindingMessageProvider.ValueMustBeANumberAccessor =
(x) => L["The field {0} must be a number.", x];
options.ModelBindingMessageProvider.MissingBindRequiredValueAccessor =
(x) => L["A value for the '{0}' property was not provided.", x];
options.ModelBindingMessageProvider.AttemptedValueIsInvalidAccessor =
(x, y) => L["The value '{0}' is not valid for {1}.", x, y];
options.ModelBindingMessageProvider.MissingKeyOrValueAccessor =
() => L["A value is required."];
options.ModelBindingMessageProvider.UnknownValueIsInvalidAccessor =
(x) => L["The supplied value is invalid for {0}.", x];
options.ModelBindingMessageProvider.ValueMustNotBeNullAccessor =
(x) => L["Null value is invalid.", x];
})
.AddDataAnnotationsLocalization()
.AddViewLocalization();
services.Configure<RequestLocalizationOptions>(options =>
{
var supportedCultures = new[]{new CultureInfo("en"), new CultureInfo("fa")};
options.DefaultRequestCulture = new RequestCulture("en", "en");
options.SupportedCultures = supportedCultures;
options.SupportedUICultures = supportedCultures;
});
}
Also add this code at beginning of Configure method:
var supportedCultures = new[] { new CultureInfo("en"), new CultureInfo("fa") };
app.UseRequestLocalization(new RequestLocalizationOptions()
{
DefaultRequestCulture = new RequestCulture(new CultureInfo("en")),
SupportedCultures = supportedCultures,
SupportedUICultures = supportedCultures
});
Important Note for ASP.NET Core 2.0
In ASP.NET Core 2.0, model binding message provider properties has got
read only, but a setter method for each property has been added.
For example, to set
ValueIsInvalidAccessor, you should use SetValueIsInvalidAccessor()
method this way:
options.ModelBindingMessageProvider.SetValueIsInvalidAccessor (
(x) => L["The value '{0}' is invalid.", x]);

Testproperty as it do not contain any validation attributes at all – An