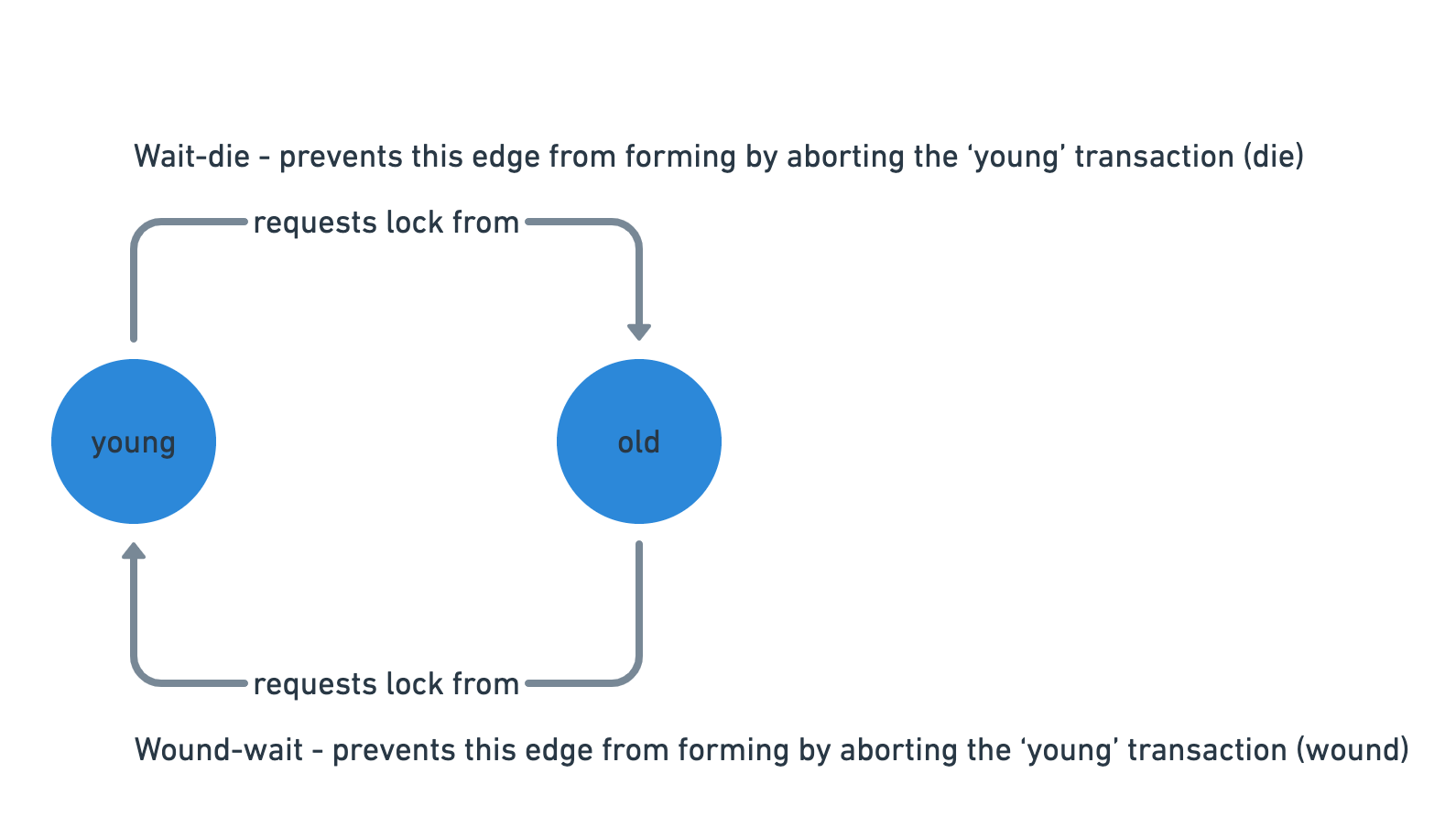
Wait-Die scheme
It is a non-preemptive technique for deadlock prevention.
When transaction Tn requests a data item currently held by Tk,
Tn is allowed to wait only if it has a timestamp smaller than that of Tk
(That is Tn is older than Tk), otherwise Tn is killed ("die").
In this scheme, if a transaction requests to lock a resource (data item),
which is already held with a conflicting lock by another transaction, then one of the two possibilities may occur:
Timestamp(Tn) < Timestamp(Tk) −
that is Tn, which is requesting a conflicting lock, is older than Tk −
then Tn is allowed to "wait" until the data-item is available.
Timestamp(Tn) > Timestamp(Tk) −
that is Tn is younger than Tk −
then Tn is killed ("dies").
Tn is restarted later with a random delay but with the same timestamp(n).
This scheme allows the older transaction to "wait" but kills the younger one ("die").
Example
Suppose that transaction T5, T10, T15 have time-stamps 5, 10 and 15 respectively.
If T5 requests a data item held by T10 then T5 will "wait".
If T15 requests a data item held by T10, then T15 will be killed ("die").
Wound-Wait scheme
It is a preemptive technique for deadlock prevention.
It is a counterpart to the wait-die scheme.
When Transaction Tn requests a data item currently held by Tk,
Tn is allowed to wait only if it has a timestamp larger than that of Tk,
otherwise Tk is killed
(i.e. Tk is wounded by Tn).
In this scheme, if a transaction requests to lock a resource (data item),
which is already held with conflicting lock by some another transaction, one of the two possibilities may occur:
Timestamp(Tn) < Timestamp(Tk),
then Tn forces Tk to be killed − that is Tn "wounds" Tk.
Tk is restarted later with a random delay but with the same timestamp(k).
Timestamp(Tn) > Timestamp(Tk),
then Tn is forced to "wait" until the resource is available.
This scheme allows the younger transaction requesting a lock to "wait" if the older transaction already holds a lock, but forces the younger one to be suspended ("wound") if the older transaction requests a lock on an item already held by the younger one.
Example
Again, suppose that Transactions T5, T10, T15 have time-stamps 5, 10 and 15 respectively.
If T5 requests a data item held by T10,
then data item will be preempted from T10 and T10 will be suspended. ("wounded")
If T15 requests a data item held by T10, then T15 will "wait".
Summary
In both the cases, only the transaction that enters the system at a later timestamp (i.e. the younger transaction) might be killed and restarted.