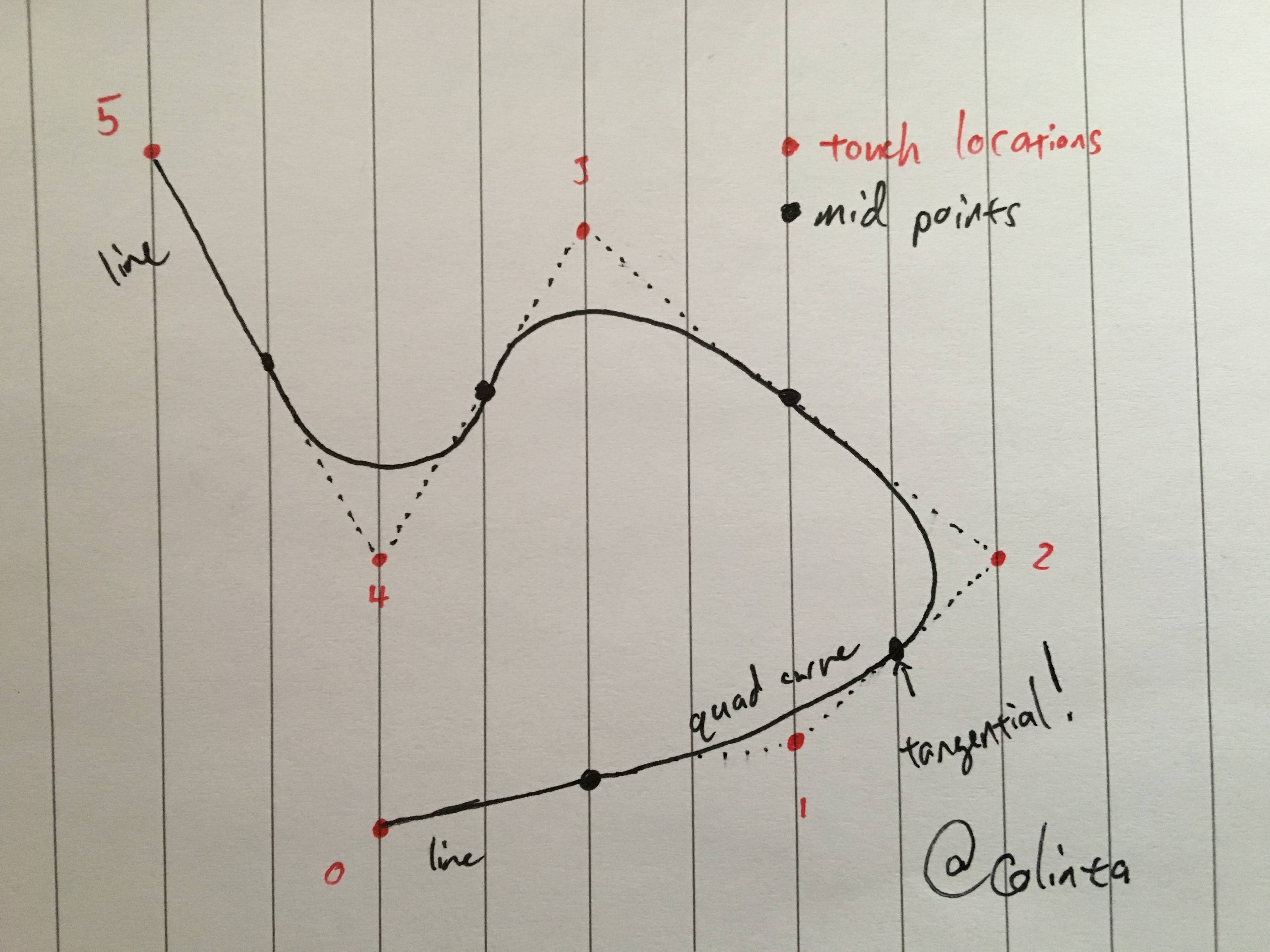
How do you smooth a set of points in an iOS drawing app WHILE MOVING? I have tried UIBezierpaths but all I get are jagged ends where they intersect, when I just shift the points 1,2,3,4 - 2,3,4,5. I have heard of spline curves and all the other types. I am quite new to iPhone programming and do not understand how to program it in my quartz drawing app. A solid example would be greatly appreciated, I have spent weeks running in circles and I can never seem to find any iOS code for this task. Most of the posts just link to a java simulation or pages on wikipedia about curve fitting which does nothing for me. Also I do not want to switch to openGL ES. I hope someone can finally provide code to answer this circulating question.
This was my code for the UIBezierPath which left edges at intersection///
UPDATED TO AN ANSWER BELOW
#define VALUE(_INDEX_) [NSValue valueWithCGPoint:points[_INDEX_]]
#define POINT(_INDEX_) [(NSValue *)[points objectAtIndex:_INDEX_] CGPointValue]
- (UIBezierPath*)smoothedPathWithGranularity:(NSInteger)granularity
{
NSMutableArray *points = [(NSMutableArray*)[self pointsOrdered] mutableCopy];
if (points.count < 4) return [self bezierPath];
// Add control points to make the math make sense
[points insertObject:[points objectAtIndex:0] atIndex:0];
[points addObject:[points lastObject]];
UIBezierPath *smoothedPath = [self bezierPath];
[smoothedPath removeAllPoints];
[smoothedPath moveToPoint:POINT(0)];
for (NSUInteger index = 1; index < points.count - 2; index++)
{
CGPoint p0 = POINT(index - 1);
CGPoint p1 = POINT(index);
CGPoint p2 = POINT(index + 1);
CGPoint p3 = POINT(index + 2);
// now add n points starting at p1 + dx/dy up until p2 using Catmull-Rom splines
for (int i = 1; i < granularity; i++)
{
float t = (float) i * (1.0f / (float) granularity);
float tt = t * t;
float ttt = tt * t;
CGPoint pi; // intermediate point
pi.x = 0.5 * (2*p1.x+(p2.x-p0.x)*t + (2*p0.x-5*p1.x+4*p2.x-p3.x)*tt + (3*p1.x-p0.x-3*p2.x+p3.x)*ttt);
pi.y = 0.5 * (2*p1.y+(p2.y-p0.y)*t + (2*p0.y-5*p1.y+4*p2.y-p3.y)*tt + (3*p1.y-p0.y-3*p2.y+p3.y)*ttt);
[smoothedPath addLineToPoint:pi];
}
// Now add p2
[smoothedPath addLineToPoint:p2];
}
// finish by adding the last point
[smoothedPath addLineToPoint:POINT(points.count - 1)];
return smoothedPath;
}
- (PVPoint *)pointAppendingCGPoint:(CGPoint)CGPoint
{
PVPoint *newPoint = [[PVPoint alloc] initInsertingIntoManagedObjectContext:[self managedObjectContext]];
[newPoint setCGPoint:CGPoint];
[newPoint setOrder:[NSNumber numberWithUnsignedInteger:[[self points] count]]];
[[self mutableSetValueForKey:@"points"] addObject:newPoint];
[(NSMutableArray *)[self pointsOrdered] addObject:newPoint];
[[self bezierPath] addLineToPoint:CGPoint];
return [newPoint autorelease];
if ([self bezierPath] && [pointsOrdered count] > 3)
{
PVPoint *control1 = [pointsOrdered objectAtIndex:[pointsOrdered count] - 2];
PVPoint *control2 = [pointsOrdered objectAtIndex:[pointsOrdered count] - 1];
[bezierPath moveToPoint:[[pointsOrdered objectAtIndex:[pointsOrdered count] - 3] CGPoint]];
[[self bezierPath] addCurveToPoint:CGPoint controlPoint1:[control1 CGPoint] controlPoint2:[control2 CGPoint]];
}
}
- (BOOL)isComplete { return [[self points] count] > 1; }
- (UIBezierPath *)bezierPath
{
if (!bezierPath)
{
bezierPath = [UIBezierPath bezierPath];
for (NSUInteger p = 0; p < [[self points] count]; p++)
{
if (!p) [bezierPath moveToPoint:[(PVPoint *)[[self pointsOrdered] objectAtIndex:p] CGPoint]];
else [bezierPath addLineToPoint:[(PVPoint *)[[self pointsOrdered] objectAtIndex:p] CGPoint]];
}
[bezierPath retain];
}
return bezierPath;
}
- (CGPathRef)CGPath
{
return [[self bezierPath] CGPath];
}