Setup: Entity framework code first to new database.
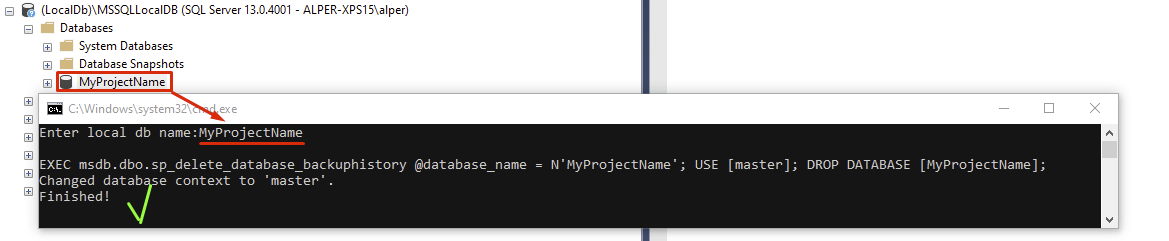
Scenario: I'm playing around with EF and I add a bunch of elements to my database. I then change the entity model, and while I know that I could do migrations, I just want to start from scratch and basically wipe the database from the earth.
The database used by default was (localdb)\v11.0.
My question is:
Can I go somewhere and just delete a file, or start some kind of manager to delete that database and start from scratch?