I am currently using a normal java project (gradle project) and want to convert this into a JavaFx project without having to reimport the existing sources into a new Javafx project. Is there any way to achieve this?
There is nothing to convert.
I don't believe there is any difference in Idea between a "normal" Java project and a JavaFX project.
Sure, in Idea 12.x+ there is a wizard you can use to create a new JavaFX project. But I think that all it does is create a sample hello world application - after initial creation, the way the project works is not any different than any other Java project.
And this is how it should be, JavaFX is just Java. Oracle doesn't differentiate between JavaFX and Java in their distribution, and neither should IDEs in their project types.
I believe, in this case, even if I'm wrong, that I am right enough that it doesn't really matter if I'm wrong.
Update
So I was wrong enough that it matters :-)
Using Idea 13.1.4, if I create a new project using File | New Project | Java, there are the following resource settings (File | Settings | Compiler):
?*.properties;?*.xml;?*.gif;?*.png;?*.jpeg;?*.jpg;?*.html;?*.dtd;?*.tld;?*.ftl
That is, the resources for the project are just set to copy only specific file types. So you could modify it to get the additional file types required in some JavaFX projects by adding resource copying support for fxml and css; i.e, appending ;?*.fxml;?*.css.
The interesting part is that if you create a new project using File | New Project | JavaFX, there are the following resource settings:
!?*.java;!?*.form;!?*.class;!?*.groovy;!?*.scala;!?*.flex;!?*.kt;!?*.clj
Essentially, it's copying everything which not a source file, a kind of file blacklist set rather than a file whitelist set as is used by other project creation templates. Really weird... Anyway, the resource sets are user configurable, so you can modify them as you see fit and once you do so, you shouldn't have any issues (I believe, but I've been wrong before ;-)
Suggestion - Use 3rd party build tools in conjunction with your IDE
You might be better off basing your build off of a 3rd party tool such as Gradle or Maven. Idea works really well with both these external build tools (and others). The advantages of using a 3rd party tool is:
- Projects with those tools follow a convention where resources are placed in a specific resource folder and everything in that folder is treated as a resource to be packaged in your build output. So there is less confusion there.
- The resultant projects are more portable and easier to use by other developers who may not be using Idea.
- The projects can be built easily by continuous integration build systems like Jenkins.
- Both Gradle and Maven have JavaFX specific plugins which provide additional support for packaging JavaFX applications.
Of course, the disadvantage of using a 3rd party build tool, is the complexity (and many quirks) of learning them as sometimes they can be quite the beast. So I think it's a bit of a tradeoff - small, personal exploratory projects don't need them, larger projects or projects you intend to share with others benefit from using such tools.
!?*.java;!?*.form;!?*.class;!?*.groovy;!?*.scala;!?*.flex;!?*.kt;!?*.clj;!?*.aj, even if it's just a regular Java project. –
Dunlop One solution is to generate your code using Scene Builder, and then integrate it into your existing IntelliJ project. While it should be possible to import this as a module, you can also simply move the code to where it needs to be (making appropriate corrections to package statements, etc). If you notice that the javafx imports aren't recognized within your project, try this solution:
First ensure that you've set up IntelliJ in general for JavaFX by following the intial steps in this tutorial. Note: Below I mention 1.8, but this should work with 1.7+. I recommend 1.8+.
Second ensure that the existing project settings allow for javaFX use
- Open Project Structure
- Click on Project under the project settings pane
- Ensure that the Project SDK is 1.8+.
Third Ensure that the modules are configured for a JDK supporting JavaFX
- Open Project Structure
- Click on Modules under the project settings pane
- Ensure that the module SDK being used supports javaFX, Again I use JDK 1.8 but it should work with 1.7.
Also, please be aware that if you have a maven project, you may need to put your fxml in a particular location, "/main/resources/". Take a look at this.
That worked for me, and I hope it helps you.
I followed those steps
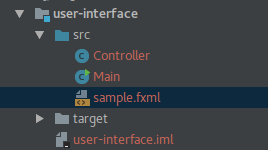
- Create a new module in your existing intellij project (A)
- Create a new JavaFx project elsewhere
- Copy the code from the JavaFx project, namely
Controller.java,Main.java and sample.fxmlinto your module in the (A) project under the src directory as inA/user-interface/src
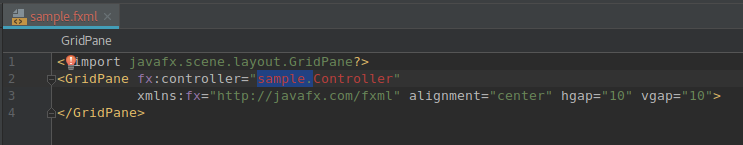
- You'll find an error in
sample.fxmlsince it references the controller class assample.Controllerchange it to 'Controller' only. it worked this way (as I removed thesamplepackage folder
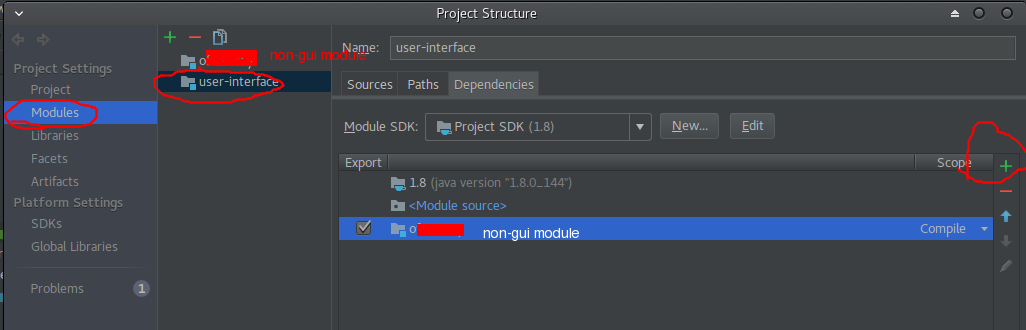
- In (A) open the settings menu
File | Project Structure | Modules - Select the
user-interfacemodule from the list on the left side of the settings window - Switch to the
dependenciestab - Add your old non-gui module as a module dependency using the green
+mark on the right-hand side - Now you can use the classes in the non-gui module, enjoy!
note: you can skip the add module dependency and let intellij do it for you, just type a name of a class in the old module, alt+enter (the light bulb magic) -> add module depenency
So after lots of googling I finally found it out myself!
If you can create new Javafx projects in IntelliJ and it works perfectly, but when you open a normal java application that happens to use javafx doesn't work, (because java just doesn't want to resolve the javafx references)
what works for me is this:
You must add the "jre/lib/ext/jfxrt.jar" file to the module classpath that is located inside IDEA on my windows machine this is C:\Program Files\JetBrains\IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition 2018.3.3\jre64\lib\ext\jfxrt.jar.
And now it finally builds!
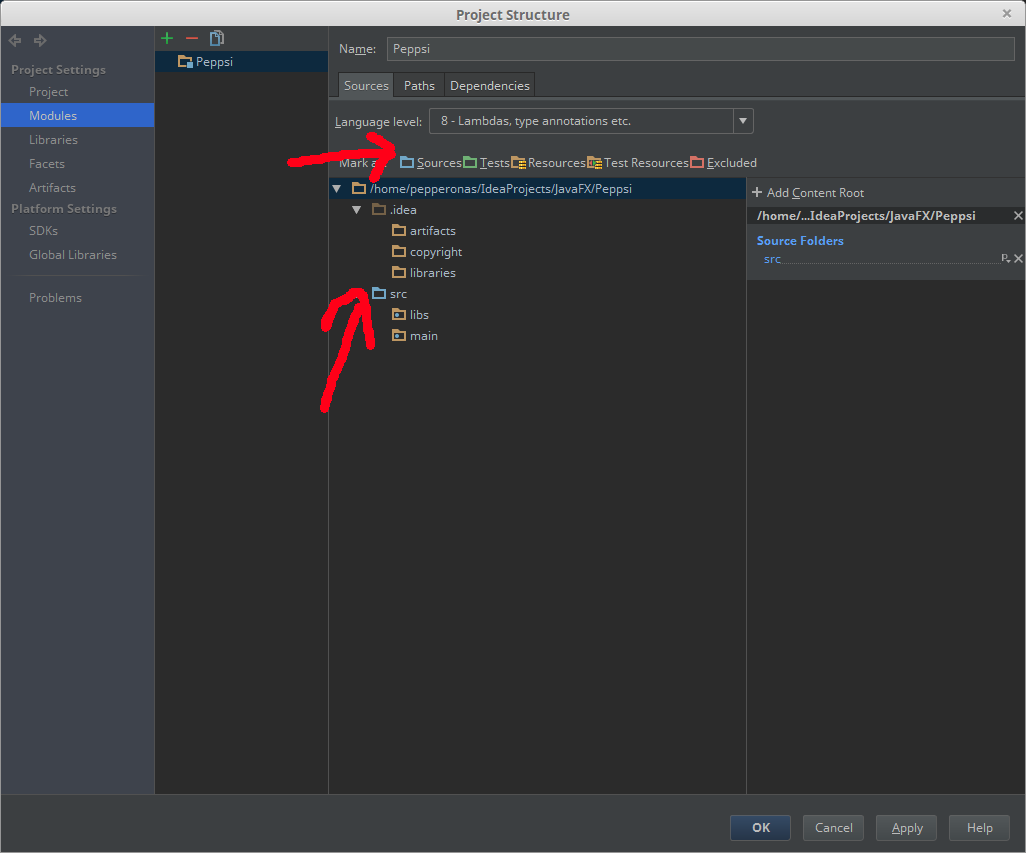
Please keep in mind that your source(s) folder(s) has to be set correctly. See screenshot to get an idea what I mean..
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.