I'd like to create a stacked histogram. If I have a single 2-D array, made of three equal length data sets, this is simple. Code and image below:
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# create 3 data sets with 1,000 samples
mu, sigma = 200, 25
x = mu + sigma*np.random.randn(1000,3)
#Stack the data
plt.figure()
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(x, 30, stacked=True, density = True)
plt.show()

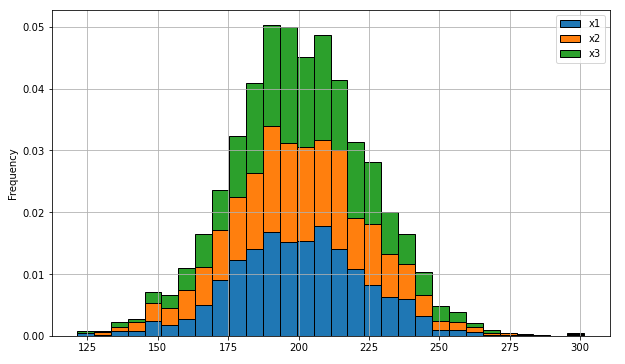
However, if I try similar code with three data sets of a different length the results are that one histogram covers up another. Is there any way I can do the stacked histogram with mixed length data sets?
##Continued from above
###Now as three separate arrays
x1 = mu + sigma*np.random.randn(990,1)
x2 = mu + sigma*np.random.randn(980,1)
x3 = mu + sigma*np.random.randn(1000,1)
#Stack the data
plt.figure()
plt.hist(x1, bins, stacked=True, density = True)
plt.hist(x2, bins, stacked=True, density = True)
plt.hist(x3, bins, stacked=True, density = True)
plt.show()


x1,x2, andx3separately? – Firedog