When this is true
#1: https://<my-domain>.auth.us-east-1.amazoncognito.com/login?response_type=code&client_id=<MY_POOL_CLIENT_ID>&redirect_uri=https://localhost:8080
The AWS Cognito Redirect will be
https://localhost:8080?code=8023253d-1c76-4c70-be3d-c8c29cc18c95
Then from your web client, use the returned code in the following app request.
NOTE: Post Header Content-Type MUST BE 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'; Code is a one time use; redirect_uri from #1 and #2 requests must match.
#2: POST https://<my-domain>.auth.us-east-1.amazoncognito.com/oauth2/token?grant_type=authorization_code&code=8023253d-1c76-4c70-be3d-c8c29cc18c95&client_id=<MY_POOL_CLIENT_ID>&redirect_uri=https://localhost:8080
And will then get a response payload as follows
{
"id_token": "...",
"access_token": "...",
"refresh_token": "...",
"expires_in": 3600,
"token_type": "Bearer"
}
NOTE: If you instead have a Custom Domain setup, then the two above calls would change to
#1: https://my.custom.auth.domain.com/login?...
#2: https://my.custom.auth.domain.com/oauth2/token?...
UPDATE
In regards to comment to extend answer.
I use this library: https://github.com/awslabs/cognito-at-edge on a cloudfront edge.
I actually opened the lib use it locally in a file so that I could change the names of each cookie.
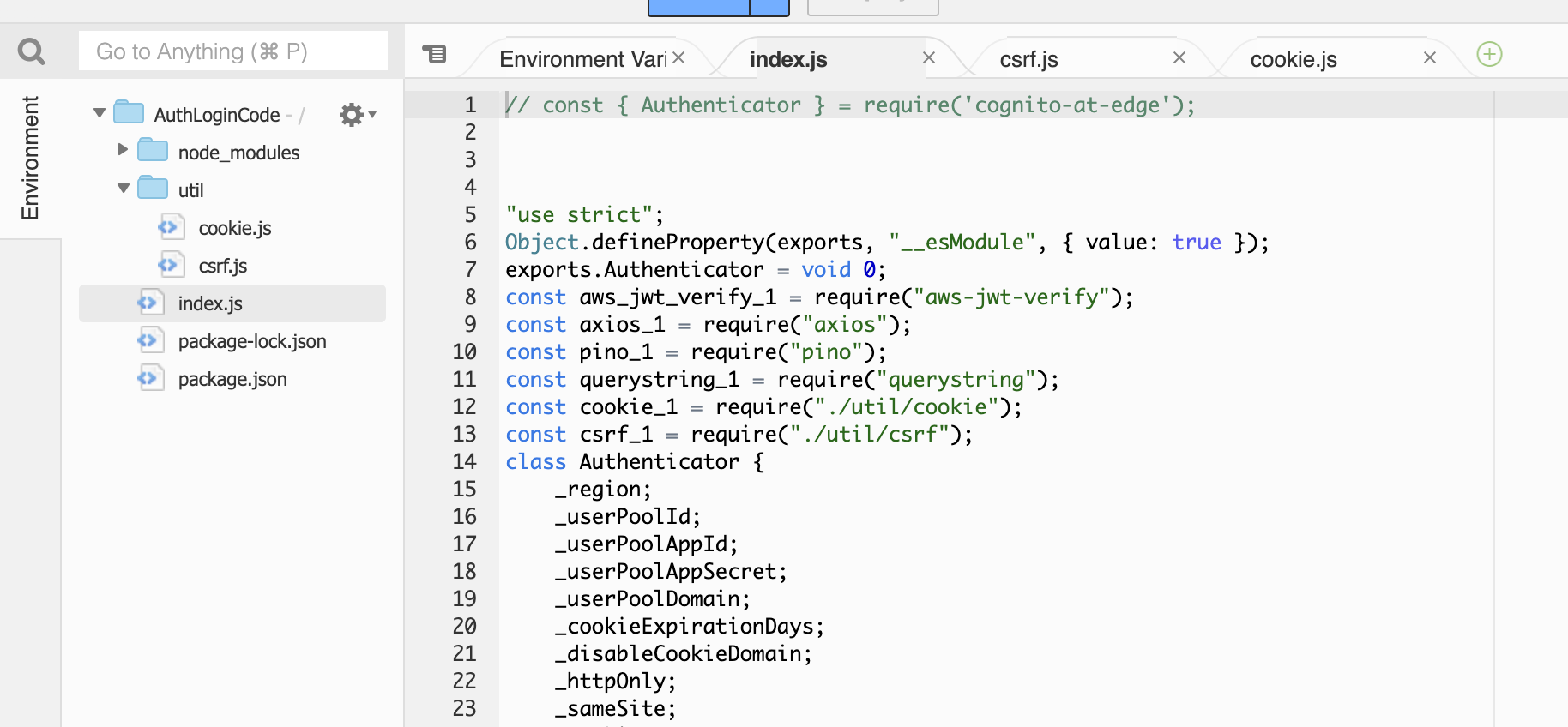
Create a Lambda and add the library to the index.js like this.
There may be a few more steps as I have a utilities folder with csrf.js and cookie.js libs locally. I don't recall why I had to do that. Probably something with using the main lib locally instead of npm installing it.
![enter image description here]()
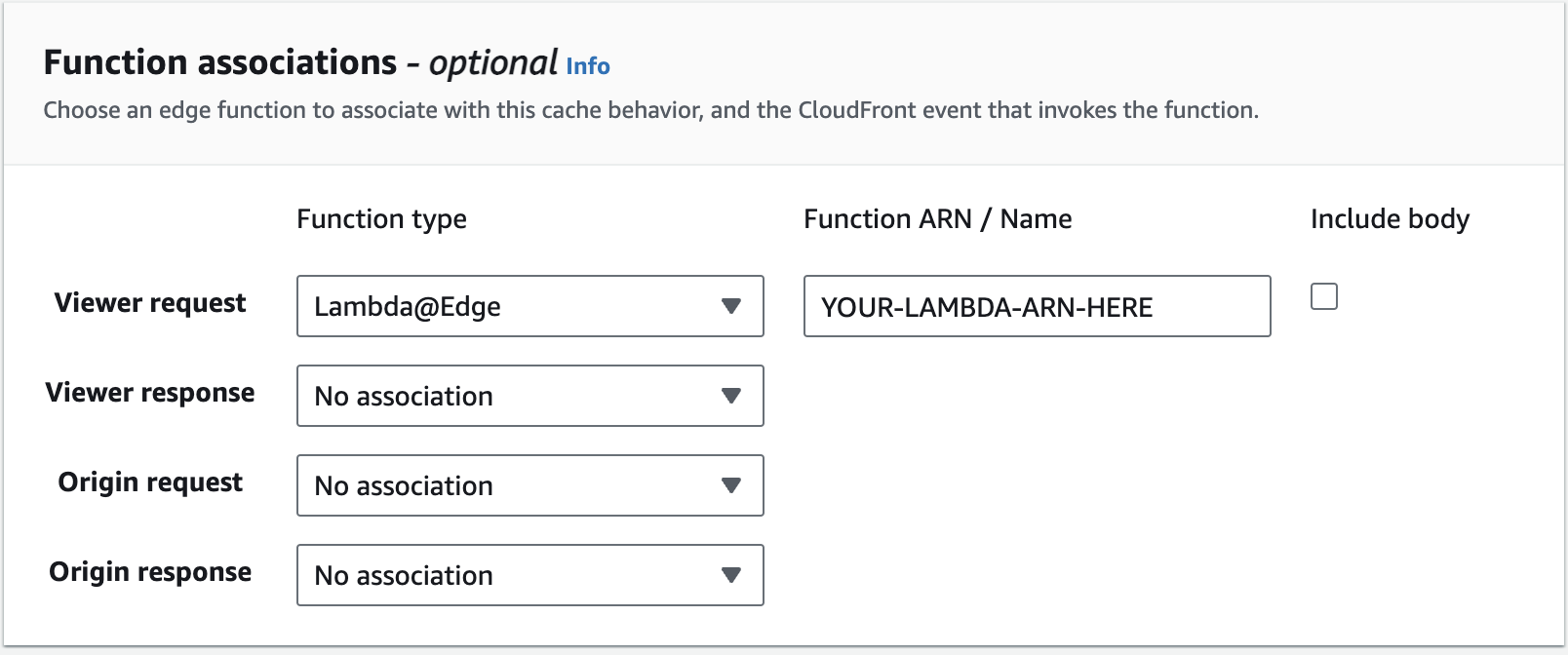
Then in your cloudfront add this lambda as the "Viewer Request" with the ARN from the above lambda like this.
![enter image description here]()
This should solve all your cookie issues as I think the lib attempts a refresh when needed. It's been awhile since I worked on this so memory is a bit lost.
Then for your api gateway, I think there is a setting on any route your add verification, where you say to accept a boolean so that you can return false from your verification lamba.
So make another lambda for API Gateway and attach it. In it just add the following code.
Verify cookie token on API Gateway route.
import { CognitoJwtVerifier } from 'aws-jwt-verify';
import { parseCookies } from './utilities/parse-cookie.mjs';
const verifier = CognitoJwtVerifier.create({
userPoolId: process.env.COGNITO_POOL_ID,
tokenUse: "access",
clientId: process.env.COGNITO_CLIENT_ID
});
const TOKEN_NAME = process.env.COGNITO_TOKEN_NAME;
export const handler = async (event) =>
{
if (event.cookies === null)
{
return {
isAuthorized: false,
};
}
const TOKEN = parseCookies(event.cookies, TOKEN_NAME);
if (TOKEN === null)
{
return {
isAuthorized: false,
};
}
try
{
await verifier.verify(TOKEN);
return {
isAuthorized: true,
};
}
catch(e)
{
return {
isAuthorized: false,
};
}
};
This will still take you a bit of time as there are many things going on and I could not include it all, but this is the bulk. Working with Edge is cumbersome as the changes don't propagate quickly. I found using the lambda_@_edge lib to be very easy to use and exactly what I was looking for.
Have patience and keep trying a little of the flow at a time until it works, then move on to the API gateway lambda.
You can get the cognito and cloudfront working just using postman requests.

https://localhost:3000/#id_token={id_token}– Binford