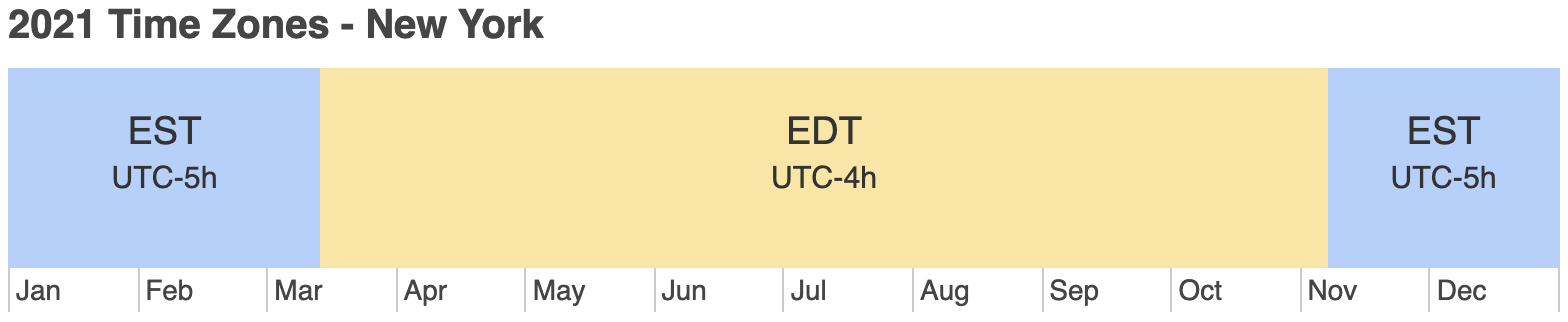
The timezone, America/New_York observes two different timezone offsets:
- EST (winter time): has a timezone offset of
-05:00 hours
- EDT (summer time): has a timezone offset of
-04:00 hours
![enter image description here]()
java.time
The java.util Date-Time API and their formatting API, SimpleDateFormat are outdated and error-prone. It is recommended to stop using them completely and switch to the modern Date-Time API*.
Also, quoted below is a notice from the home page of Joda-Time:
Note that from Java SE 8 onwards, users are asked to migrate to java.time (JSR-310) - a core part of the JDK which replaces this project.
What Date-Time object should I use to adjust the offset automatically?
Use ZonedDateTime which has been designed to adjust the timezone offset automatically.
Demo:
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.Month;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("America/New_York");
// Custom times
ZonedDateTime zdtDstOn = ZonedDateTime.of(LocalDate.of(2020, Month.OCTOBER, 22), LocalTime.MIN, zoneId);
ZonedDateTime zdtDstOff = ZonedDateTime.of(LocalDate.of(2020, Month.NOVEMBER, 22), LocalTime.MIN, zoneId);
System.out.println(zdtDstOn);
System.out.println(zdtDstOff);
// Current time
ZonedDateTime zdtNow = ZonedDateTime.now(zoneId);
System.out.println(zdtNow);
}
}
Output:
2020-10-22T00:00-04:00[America/New_York]
2020-11-22T00:00-05:00[America/New_York]
2021-08-17T12:19:41.854781-04:00[America/New_York]
ONLINE DEMO
Avoid using the abbreviated timezone names
The following quote from the documentation states the problem clearly:
Three-letter time zone IDs
For compatibility with JDK 1.1.x, some
other three-letter time zone IDs (such as "PST", "CTT", "AST") are
also supported. However, their use is deprecated because the same
abbreviation is often used for multiple time zones (for example, "CST"
could be U.S. "Central Standard Time" and "China Standard Time"), and
the Java platform can then only recognize one of them.
Then, what Date-Time object should I use for a fixed timezone offset?
Use OffsetDateTime for a fixed timezone offset.
Demo:
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.Month;
import java.time.OffsetDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneOffset;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZoneOffset zoneOffset = ZoneOffset.of("-04:00");
// A custom time
OffsetDateTime odt = OffsetDateTime.of(LocalDate.of(2020, Month.OCTOBER, 22), LocalTime.MIN, zoneOffset);
System.out.println(odt);
// Current time
OffsetDateTime odtNow = OffsetDateTime.now(zoneOffset);
System.out.println(odtNow);
}
}
Output:
2020-10-22T00:00-04:00
2021-08-17T12:36:09.123599-04:00
ONLINE DEMO
Note: For any reason, if you need to convert an object of OffsetDateTime or ZonedDateTime to an object of java.util.Date, you can do so as follows:
Date date = Date.from(odtNow.toInstant());
or
Date date = Date.from(zdtNow.toInstant());
Learn more about the modern Date-Time API* from Trail: Date Time.
Check this answer and this answer to learn how to use java.time API with JDBC.
* For any reason, if you have to stick to Java 6 or Java 7, you can use ThreeTen-Backport which backports most of the java.time functionality to Java 6 & 7. If you are working for an Android project and your Android API level is still not compliant with Java-8, check Java 8+ APIs available through desugaring and How to use ThreeTenABP in Android Project.