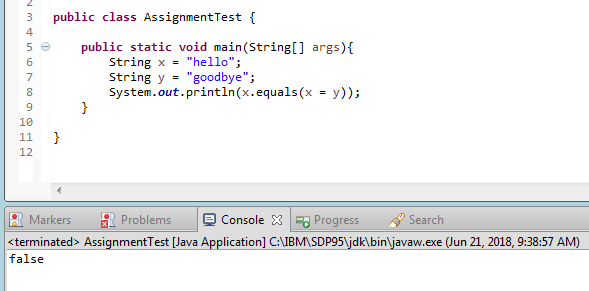
In Java, I understand that assignment evaluates to the value of the right operand, so statements like x == (y = x) evaluate to true.
This code, however, outputs false.
public static void main(String[]args){
String x = "hello";
String y = "goodbye";
System.out.println(x.equals(x = y));
}
Why is this? In my understanding, it first evaluates (x = y), which assigns x the value of y, and then returns the value of y. Then x.equals(y) is evaluated, which should be true since x and y should share the same references now, but instead, I get false.
What is happening here?

x.equals( y = x )– Boehmenismxandy? – Corderox = yon the right hand side is executed before thexon the left hand side is evaluated? – Pierianx == (y = x)evaluates to true. The behavior of what you suggest would then be obvious... – Circumstantiality