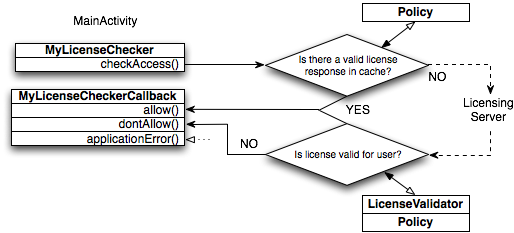
To ensure that my paid android application was legally installed from store, I write this:
String installer = getPackageManager().getInstallerPackageName(
"com.example.myapp");
if (installer == null) {
// app was illegally downloaded from unknown source.
// dear user, please re-install it from market
}
else {
// app was probably installed legally
// (also it's good to check actual installer name)
}
Is it ok? Is there a chance that application that is legally purchased and installed from market will get empty installer package name and fail this test?
I understand that user can run adb -i com.fake.installer myapp.apk and pass this check, but it's more important if legal users will get potential problems or not.