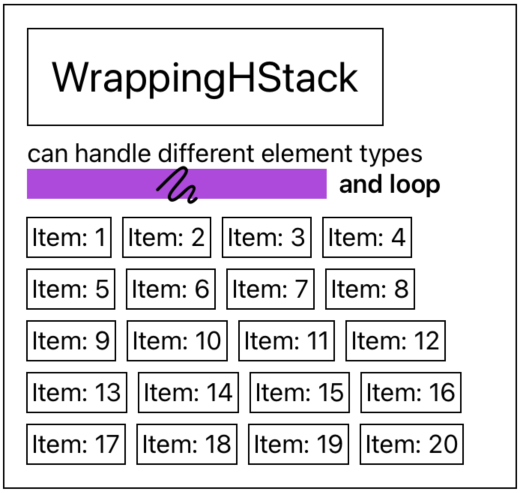
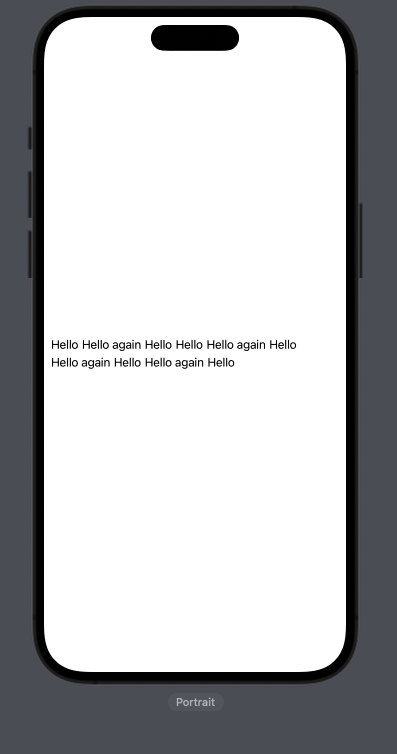
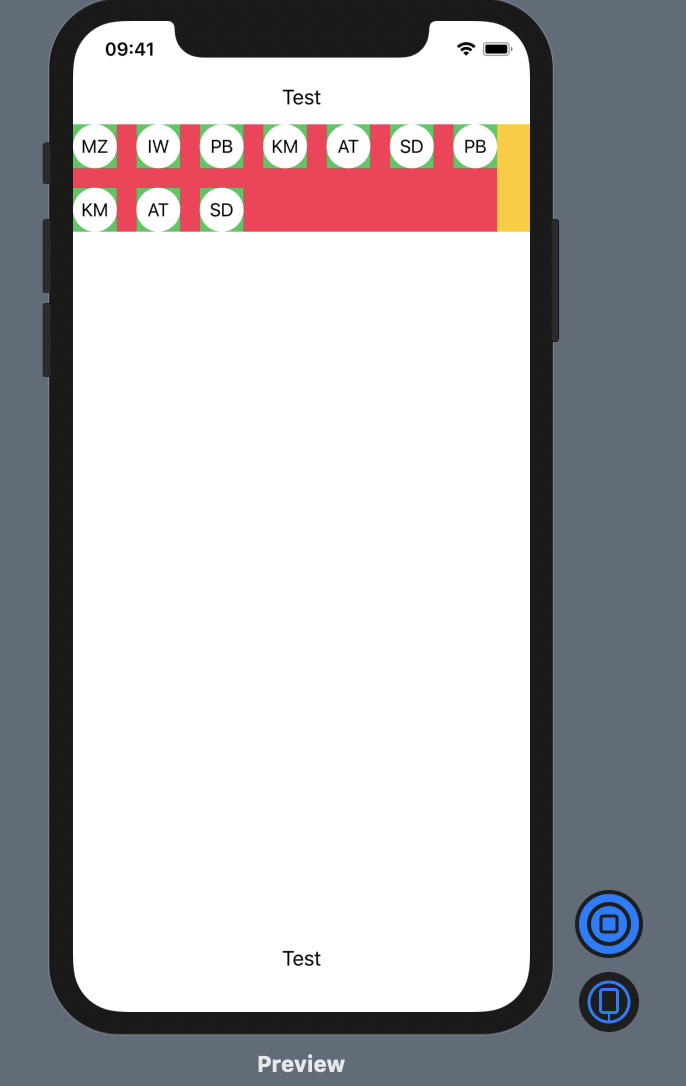
I've had ago at creating what you need.
Ive used HStack's in a VStack.
You pass in a geometryProxy which is used for determining the maximum row width.
I went with passing this in so it would be usable within a scrollView
I wrapped the SwiftUI Views in a UIHostingController to get a size for each child.
I then loop through the views adding them to the row until it reaches the maximum width, in which case I start adding to a new row.
This is just the init and final stage combining and outputting the rows in the VStack
struct WrappedHStack<Content: View>: View {
private let content: [Content]
private let spacing: CGFloat = 8
private let geometry: GeometryProxy
init(geometry: GeometryProxy, content: [Content]) {
self.content = content
self.geometry = geometry
}
var body: some View {
let rowBuilder = RowBuilder(spacing: spacing,
containerWidth: geometry.size.width)
let rowViews = rowBuilder.generateRows(views: content)
let finalView = ForEach(rowViews.indices) { rowViews[$0] }
VStack(alignment: .center, spacing: 8) {
finalView
}.frame(width: geometry.size.width)
}
}
extension WrappedHStack {
init<Data, ID: Hashable>(geometry: GeometryProxy, @ViewBuilder content: () -> ForEach<Data, ID, Content>) {
let views = content()
self.geometry = geometry
self.content = views.data.map(views.content)
}
init(geometry: GeometryProxy, content: () -> [Content]) {
self.geometry = geometry
self.content = content()
}
}
The magic happens in here
extension WrappedHStack {
struct RowBuilder {
private var spacing: CGFloat
private var containerWidth: CGFloat
init(spacing: CGFloat, containerWidth: CGFloat) {
self.spacing = spacing
self.containerWidth = containerWidth
}
func generateRows<Content: View>(views: [Content]) -> [AnyView] {
var rows = [AnyView]()
var currentRowViews = [AnyView]()
var currentRowWidth: CGFloat = 0
for (view) in views {
let viewWidth = view.getSize().width
if currentRowWidth + viewWidth > containerWidth {
rows.append(createRow(for: currentRowViews))
currentRowViews = []
currentRowWidth = 0
}
currentRowViews.append(view.erasedToAnyView())
currentRowWidth += viewWidth + spacing
}
rows.append(createRow(for: currentRowViews))
return rows
}
private func createRow(for views: [AnyView]) -> AnyView {
HStack(alignment: .center, spacing: spacing) {
ForEach(views.indices) { views[$0] }
}
.erasedToAnyView()
}
}
}
and here's extensions I used
extension View {
func erasedToAnyView() -> AnyView {
AnyView(self)
}
func getSize() -> CGSize {
UIHostingController(rootView: self).view.intrinsicContentSize
}
}
You can see the full code with some examples here:
https://gist.github.com/kanesbetas/63e719cb96e644d31bf027194bf4ccdb