I was using readLine of BufferedReader to get input/new password from user, but wanted to mask the password so I am trying to use java.io.Console class. Problem is that System.console() returns null when an application is debugged in Eclipse. I am new to Java and Eclipse not sure is this the best way to achieve? I am right clicking on the source file and selecting "Debug As" > "Java Application". Is there any workaround?
This code snippet should do the trick:
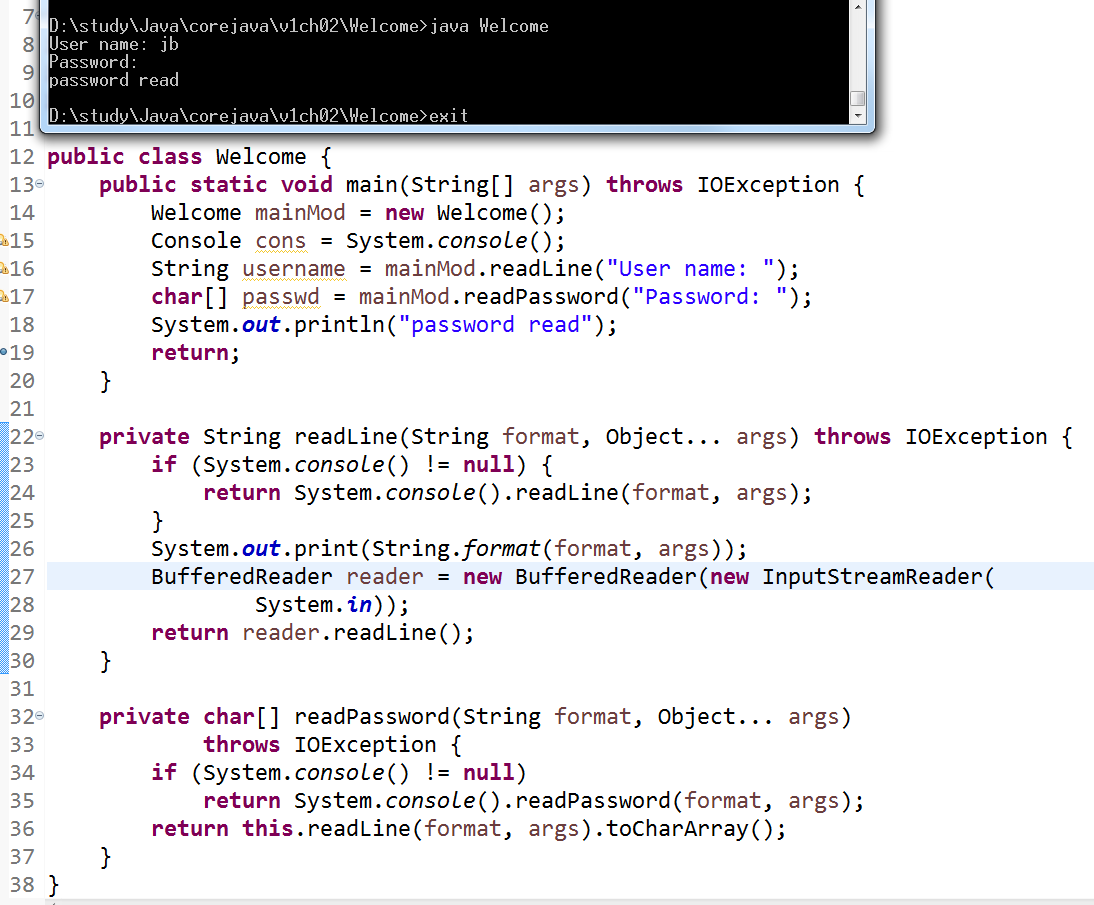
private String readLine(String format, Object... args) throws IOException {
if (System.console() != null) {
return System.console().readLine(format, args);
}
System.out.print(String.format(format, args));
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
System.in));
return reader.readLine();
}
private char[] readPassword(String format, Object... args)
throws IOException {
if (System.console() != null)
return System.console().readPassword(format, args);
return this.readLine(format, args).toCharArray();
}
While testing in Eclipse, your password input will be shown in clear. At least, you will be able to test. Just don't type in your real password while testing. Keep that for production use ;).
readLine method close the BufferedReader in a finally (or try-with-resources) block? –
Revocable System.in stream and no further reading could be made afterward. –
Operose System.console() returns null if there is no console.
You can work round this either by adding a layer of indirection to your code or by running the code in an external console and attaching a remote debugger.
java -cp ... Class | tee out. –
Littlefield I also ran into this problem when trying to write a simple command line application.
Another alternative to creating your own BufferedReader object from System.in is to use java.util.Scanner like this:
import java.util.Scanner;
Scanner in;
in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = in.nextLine();
Of course this will not be a drop-in replacement to Console, but will give you access to a variety of different input functions.
According to the API:
"If the virtual machine is started from an interactive command line without redirecting the standard input and output streams then its console will exist and will typically be connected to the keyboard and display from which the virtual machine was launched. If the virtual machine is started automatically, for example by a background job scheduler, then it will typically not have a console."
According to the docs:
If the virtual machine is started automatically, for example by a background job scheduler, then it will typically not have a console.
Got this error message when running the application from Netbeans. Judging from the other answers, it seems this happens when running your application from an IDE. If you take a look at this question: Trying to read from the console in Java, it is because
Most IDEs are using javaw.exe instead of java.exe to run Java code
The solution is to use the command line/terminal to get the Console.
I refered&used formixian's answer shown above. The point is use (black) cmd console to run your Java program as "ojonugwa ochalifu" suggested.
If your IDE uses javaw instead of java, then this issue is bound to happen as javaw is essentially java without console window.
That is right.
You will have to run the application outside of Eclipse. Look at the launcher configuration panels within Eclipse and see if you can spot the option that says to run the command in a separate JVM.
I believe that in the run configurations for Eclipse, you can configure whether to assign a console or not - ensure this is checked. (It's been a while since I used Eclipse so I can't give specific instructions I'm afraid).
If that doesn't work, then something that will definitely do this job is starting your application in debug mode, then connect to the process with Eclipse. Search for "eclipse remote debugging" if you're not sure how to do this.
Furthermore, in general it is a bad idea to require a console to be assigned as this very much impacts the flexibility of your application - as you've just discovered. Many ways of invoking Java will not assign a console, and your application is unusable in these instances (which is bad). Perhaps you could alternatively allow arguments to be specified on the command line. (If you're testing the console input specifically then fair enough, but it would potentially be useful for people to be able to invoke your application from scripts and/or on headless servers, so this sort of flexible design is almost always a good idea. It often leads to better-organised code, too.)
-Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=8000 to the VM's arguments (on Sun JVMs at least). Using the console can be OK, but as pointed out means that your code simply won't work when launched without one. Instead, consider passing in values directly sourced from command-line arguments, system properties, property files etc. At the very least provide some alternative - e.g. only go to the console if a value wasn't provided as a command-line argument. –
Musa Try to compile your class and run it in terminal. It works.
add -console in your program arguments to start OSGi console
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.

System.outandSystem.into be sufficient for my use case and abondaned usingSystem.console(). – Moravia