I tried researching the web for a good explanation on 5 tier architecture. However, I didn't find any good articles. I understand 3- and 4 tier architecture, however 5 tier won't go in my head. Can someone explain it and maybe provide an example? Thanks!
I think you mean 5-layer architecture. First of all we should define 5-layer architecture before moving on 5-tier.
5-layer Architecture
Layering is logical separation that you implement in your application. It has a relation with N-Tier but we will move onto it later:
1) Presentation This is how your application is shown to the user. You can think about it is a look and feel of the application. But it is very similar to the UI layer, todays world with the improvement of JavaScript (client-side-rendering solutions like React, Angular, etc.) this separation may not be seem exact but still makes sense, let me continue:
2) UI This is where user interactions are interpreted. What happens when user clicks submit button, how the data is sent to the server and retrieved? If you think about server-side rendering which we used older times, we were all interpreting those and returning user fully ready HTML page but today with client-side-rendering all of those works are done in the user's browser with the help of JavaScript. So you can think about now Presentation + UI is done in users server (phone, pc etc.) if client-side-rendering is used. If the user's server is only responsible for showing the data, now the Presentation layer takes place there while UI layer takes place in our server.
3) Business Logic This is the place where we are responsible for data validation (even if you did it in client-side, we should do in server-side too because we never trust to clients), manipulation, security, processing, database lookups, etc. takes place. Those responsibilities can be shared between UI side and Data Access depending on the action's security scope
4) Data Access This is where you abstract to insert, delete, etc. actions that you need to do on the DataBase (Data Storage level). It kinda interfaces between DataBases and your application
5) Data Storage This is were database servers belong. This is the implementation of the Data Access layer which psychically inserts, deletes, etc. data on the server.
5-Tier Architecture
Now depending on your application's needs, you should define your trade-offs:
- What do you want to achieve?
- How much do you want to scale?
- What is your acceptable latency?
If you achieve low latency and you don't aim to be used by too many users, you can start with 1-tier. In the below demonstrations keep in mind that the business logic layer can be done in any layers as long as you keep security reasons, you can have some general/simple business logic in client-side (Presentation/UI layers) too which may increase your servers performance. Also, you can put UI layer in higher/lower tiers depend on using server-side or client-side rendering but we talked about general idea above:
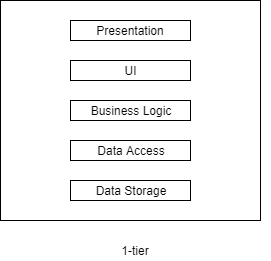
1-tier
All layers belong to one physical location. Like a game that installed on the user's database and doesn't request any other external system, it has own database on the user's server and all logics implemented there.
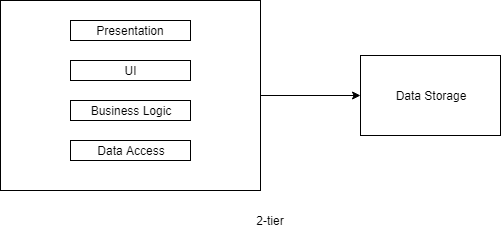
2-tier
Lets say you want to central database management and all other parts can remain still user's server, like hes is playing a game on mobile-phone but data is stored in our servers.
Up to now, you have a performance advantage. If you need to support more users and need more security than you need scalability.
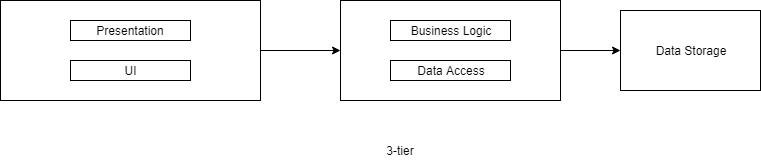
3-tier
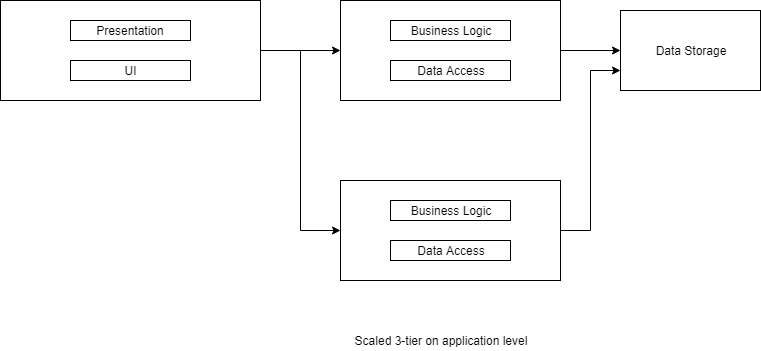
Beside microservices (maybe another discussion topic), this is one of the most used architecture. Presentation and UI is on the user's server (client), business logic and data access belongs to application server, and data storage is in another server.
But now your user's request is jumping more tier's which will increase your network latency. As talked before it is about trade-offs. Also now you started to have benefit of scaling like:
So depending on your application needs, security levels, latency limits, user counts etc. You can split it up to more tiers which is it the reason why its name is N-Tier.
References
Expert C#3006 Business Objects - Rockford Lhotka
Software Architecture Patterns - Mark Richards
- Presentation Layer (Browser or other Presentation application)
- Layer Tier (View Model)
- Business Logic / Domain Logic (Services/Domain Layer)
- Data Access Layer (Database access logic, etc)
- Data Storage Layer (Database Engine or similar)
Some of these things can be physically separated much easier than others. Presentation and Data Storage are often separated, Business logic is sometimes separated, but less often. Data Access and View Model would be difficult and largely pointless to separate from the Business Logic layer.
I'm currently studying the book Fundamentals of Database Systems (Seventh edition published by Pearson, good availability as free pdf e-book through search engine.) There's a written chapter about DBMS Client-Server, 2/3/n-tier -architecture. Take a look down the book and you can get some more information about differences between single/multilayered architechture.
3/n -tier architecture model have been more popular since telecommunications network usage has grown rapidly. For Distrubted cloud-service-platform solutions (for those companies who have to make a deal with handling Big Data) have arised popularity of the 4- and 5-tier Architechutre solutions.
The Large companies (For ie. Social Media company Facebook) may use decentralized solution oppositing of old-fashioned centralized-dbms -solution and they can tune up the security on each level behalf of them that they are more in safe for the end users (Parametric or naive Facebook users).
If I would be the president, or CEO of large technology company, I would say it's not good idea to put all the balls in the same basket. Oppsiting the more layers there's in the solution, the more security-related issues and problems it arises on the table to get solved and more IT-professionals you have to hire if you're not an A-graded Oxford University mastermind -graduated in Everything. And nobody really isn't at all!
I'm not sure if the best and biggest web hosting companies are using distrbuted de-centralized database servers for their clients but in early days of World Wide Web they were as weak as the WWW was Wild West on the later part in 1990-decade with no laws and weak security (Equalled to early tor-network and darknet nowdays in the 2020).
Conclusion to the original question: Nicname "cmlonder" gave good answer, read the book chapter referred in my answer, and make your company IT-architechure high-level secured using de-centarilez multitier solution. If you can't do that, don't start your own Tech-Business.
5 Tier container Technology architecture -
Tier-1: Developer machines - image creation, testing and accreditation
Tier-2: Testing and accreditation systems - verification and validation of image contents, signing images and sending them to the registries.
Tier-3: Registries - storing images and disseminating images to the orchestrators based on requests.
Tier-4: Orchestrators - transforming images into containers and deploying containers to hosts.
Tier-5: Hosts - operating and managing containers as instructed by the orchestrator.
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.