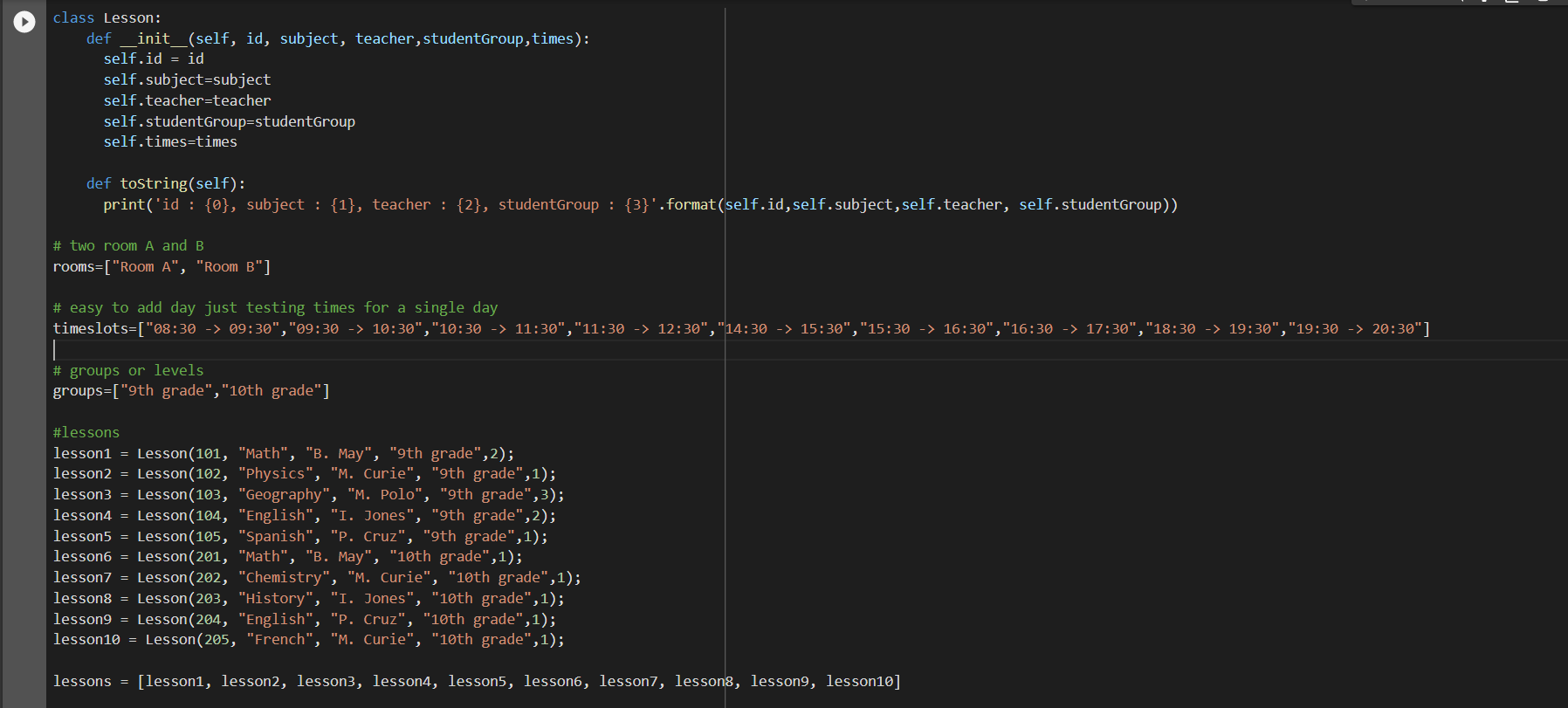
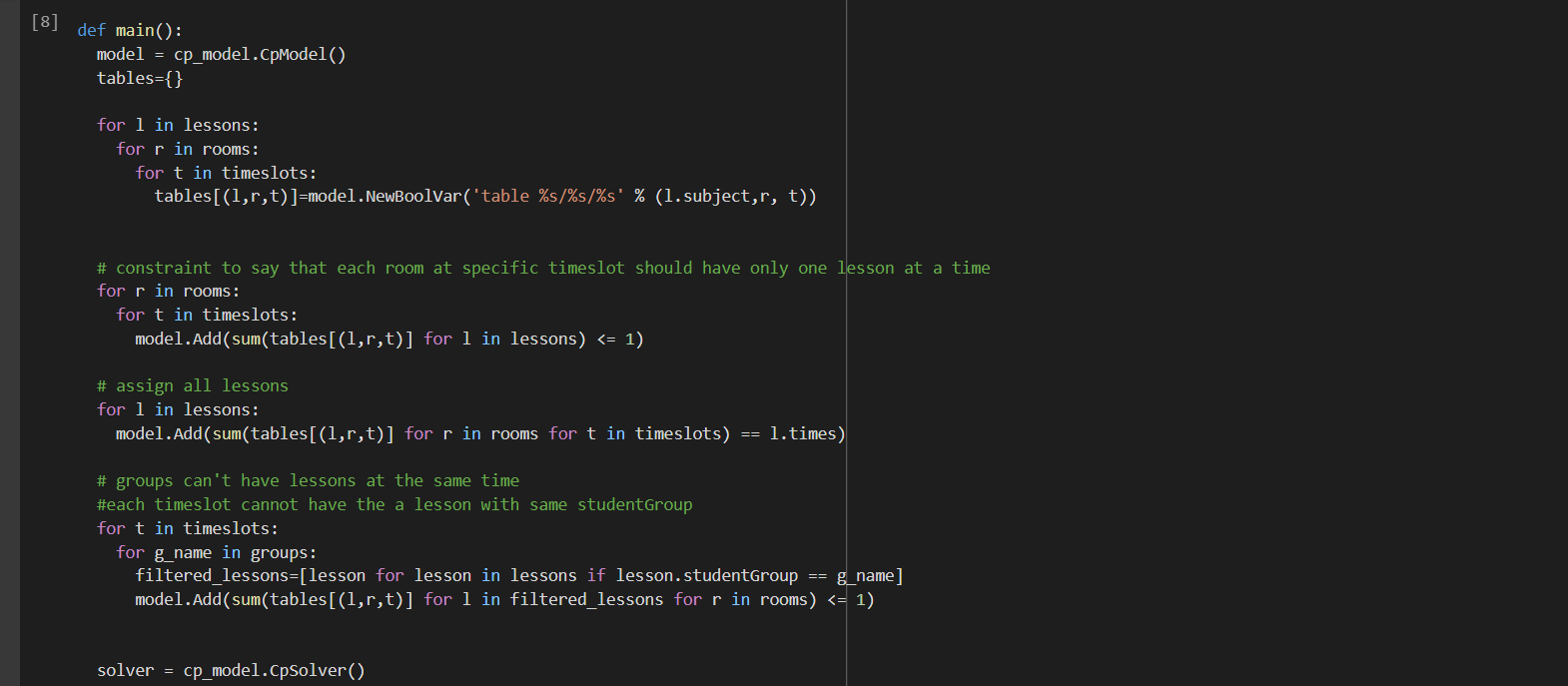
Probably a duplicate of Do Google Optimization Tools support Soft Constraints?, but I'll add some examples with CP-SAT.
Here's a simple soft limit example:
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
model = cp_model.CpModel()
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
x = [model.NewBoolVar("") for i in range(10)]
# hard constraint: number of 1's >= 4
model.Add(sum(x) >= 4)
# soft constraint: number of 1's <= 5
delta = model.NewIntVar(-5, 5, "")
excess = model.NewIntVar(0, 5, "")
model.Add(delta == sum(x) - 5)
model.AddMaxEquality(excess, [delta, 0])
model.Minimize(excess)
solver.Solve(model)
print([solver.Value(i) for i in x])
print(solver.Value(excess))
See a more complex example here
And here's one concerning fullfiled requests:
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
model = cp_model.CpModel()
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
x = [model.NewIntVar(0, 10, "") for i in range(10)]
# request: sum() <= 10
req1 = model.NewBoolVar("")
model.Add(sum(x) <= 10).OnlyEnforceIf(req1)
# request: sum() >= 5
req2 = model.NewBoolVar("")
model.Add(sum(x) >= 5).OnlyEnforceIf(req2)
# request: sum() >= 100
req3 = model.NewBoolVar("")
model.Add(sum(x) >= 100).OnlyEnforceIf(req3)
model.Maximize(req1 + req2 + req3)
solver.Solve(model)
print(solver.Value(sum(x)))
print(solver.ObjectiveValue())