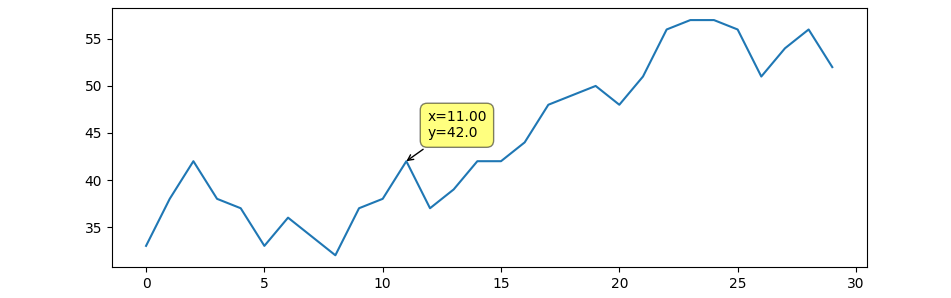
One approach is to create an invisible scatterplot for the same points, and attach the mplcursor to it.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import mplcursors
x = np.arange(30)
y = 30 + np.random.randint(-5, 6, x.size).cumsum()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y)
dots = ax.scatter(x, y, color='none')
mplcursors.cursor(dots, hover=True)
plt.show()
![example plot]()
The functionality could be wrapped into a helper function:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import mplcursors
def create_mplcursor_for_points_on_line(lines, ax=None, annotation_func=None, **kwargs):
ax = ax or plt.gca()
scats = [ax.scatter(x=line.get_xdata(), y=line.get_ydata(), color='none') for line in lines]
cursor = mplcursors.cursor(scats, **kwargs)
if annotation_func is not None:
cursor.connect('add', annotation_func)
return cursor
x = np.arange(10, 301, 10)
y = 30 + np.random.randint(-5, 6, x.size).cumsum()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
lines = ax.plot(x, y)
cursor = create_mplcursor_for_points_on_line(lines, ax=ax, hover=True)
plt.show()