Instead of depending on a socket from outside of the session, I'd depend on your program logic to implement the session.
That's because the session (connection) will govern its own lifetime, arriving spontaneously and potentially disconnecting spontaneously. Your hardware, most likely, doesn't.
So, borrowing the concept of "Dependency Injection" tell your listener about your application logic, and then call into that from the session. (The listener will "inject" the dependency into each newly created session).
Let's start from a simplified/modernized version of your linked example.
Now, where we prepare a response, you want your own logic injected, so let's write it how we would imagine it:
void on_read(beast::error_code ec, std::size_t /*bytes_transferred*/) {
if (ec == websocket::error::closed) return;
if (ec.failed()) return fail(ec, "read");
// Process the message
response_ = logic_->Process(beast::buffers_to_string(buffer_));
ws_.async_write(
net::buffer(response_),
beast::bind_front_handler(&session::on_write, shared_from_this()));
}
Here we declare the members and initialize them from the constructor:
std::string response_;
std::shared_ptr<AppDomain::Logic> logic_;
public:
explicit session(tcp::socket&& socket,
std::shared_ptr<AppDomain::Logic> logic)
: ws_(std::move(socket))
, logic_(logic) {}
Now, we need to inject the listener with the logic so we can pass it along:
class listener : public std::enable_shared_from_this<listener> {
net::any_io_executor ex_;
tcp::acceptor acceptor_;
std::shared_ptr<AppDomain::Logic> logic_;
public:
listener(net::any_io_executor ex, tcp::endpoint endpoint,
std::shared_ptr<AppDomain::Logic> logic)
: ex_(ex)
, acceptor_(ex)
, logic_(logic) {
So that we can pass it along:
void on_accept(beast::error_code ec, tcp::socket socket) {
if (ec) {
fail(ec, "accept");
} else {
std::make_shared<session>(std::move(socket), logic_)->run();
}
// Accept another connection
do_accept();
}
Now making the real logic in main:
auto logic = std::make_shared<AppDomain::Logic>("StackOverflow Demo/");
try {
// The io_context is required for all I/O
net::thread_pool ioc(threads);
std::make_shared<listener>(ioc.get_executor(),
tcp::endpoint{address, port}, logic)
->run();
ioc.join();
} catch (beast::system_error const& se) {
fail(se.code(), "listener");
}
Demo Logic
Just for fun, let's implement some random logic, that might be implemented in hardware in the future:
namespace AppDomain {
struct Logic {
std::string banner;
Logic(std::string msg) : banner(std::move(msg)) {}
std::string Process(std::string request) {
std::cout << "Processing: " << std::quoted(request) << std::endl;
std::string result;
auto fold = [&result](auto op, double initial) {
return [=, &result](auto& ctx) {
auto& args = _attr(ctx);
auto v = accumulate(args.begin(), args.end(), initial, op);
result = "Fold:" + std::to_string(v);
};
};
auto invalid = [&result](auto& ctx) {
result = "Invalid Command: " + _attr(ctx);
};
using namespace boost::spirit::x3;
auto args = rule<void, std::vector<double>>{} = '(' >> double_ % ',' >> ')';
auto add = "adding" >> args[fold(std::plus<>{}, 0)];
auto mul = "multiplying" >> args[fold(std::multiplies<>{}, 1)];
auto err = lexeme[+char_][invalid];
phrase_parse(begin(request), end(request), add | mul | err, blank);
return banner + result;
}
};
} // namespace AppDomain
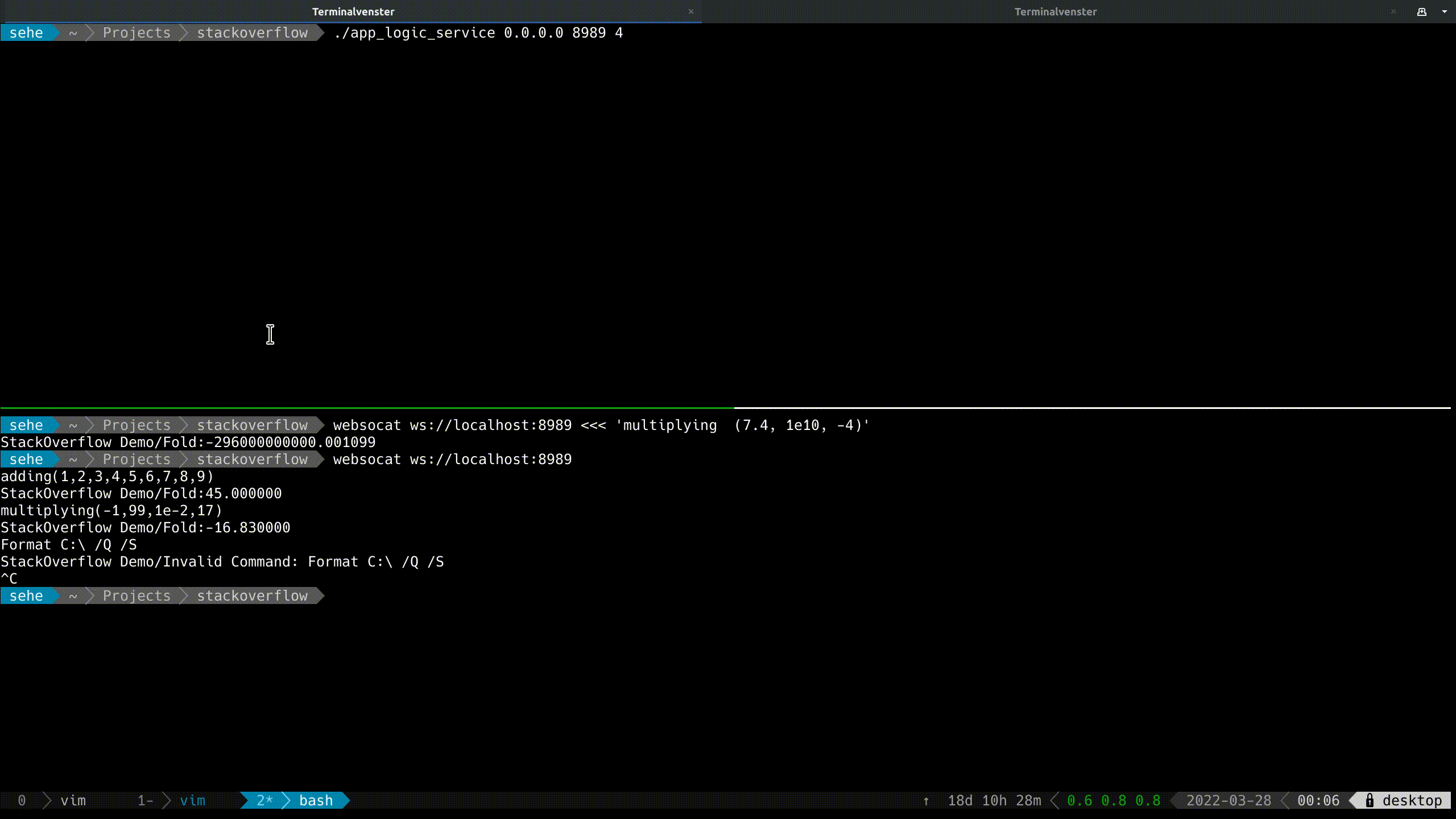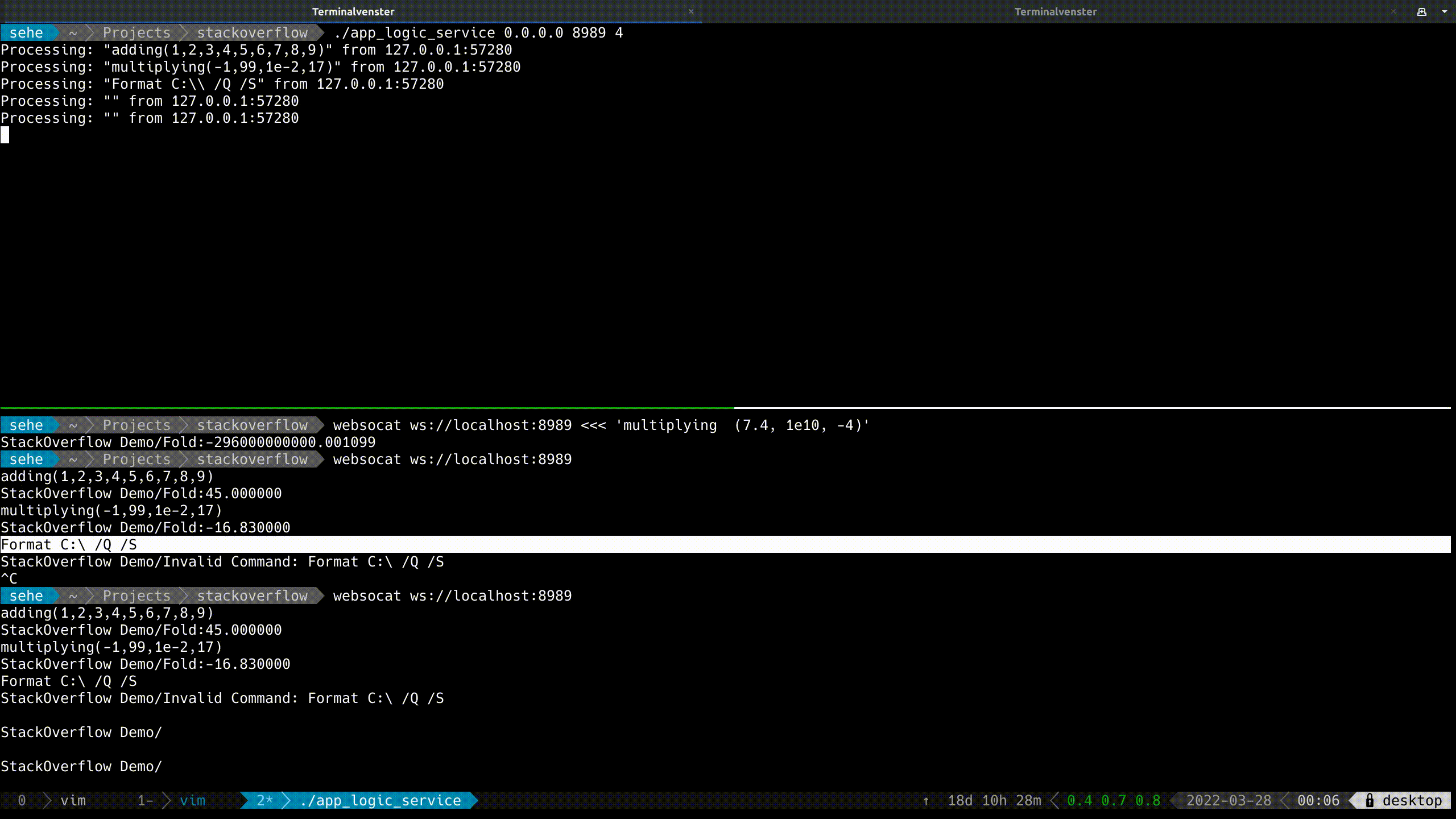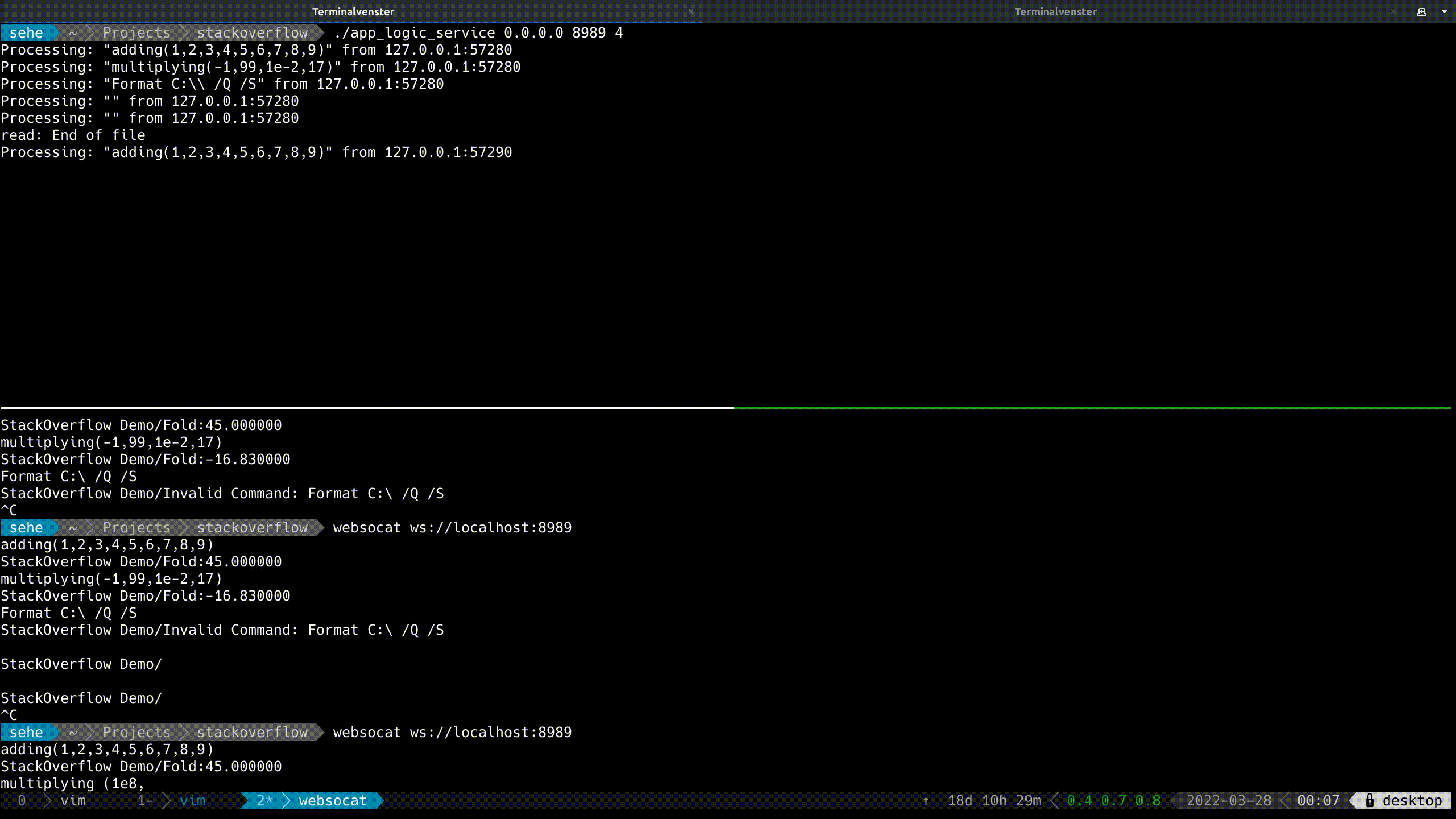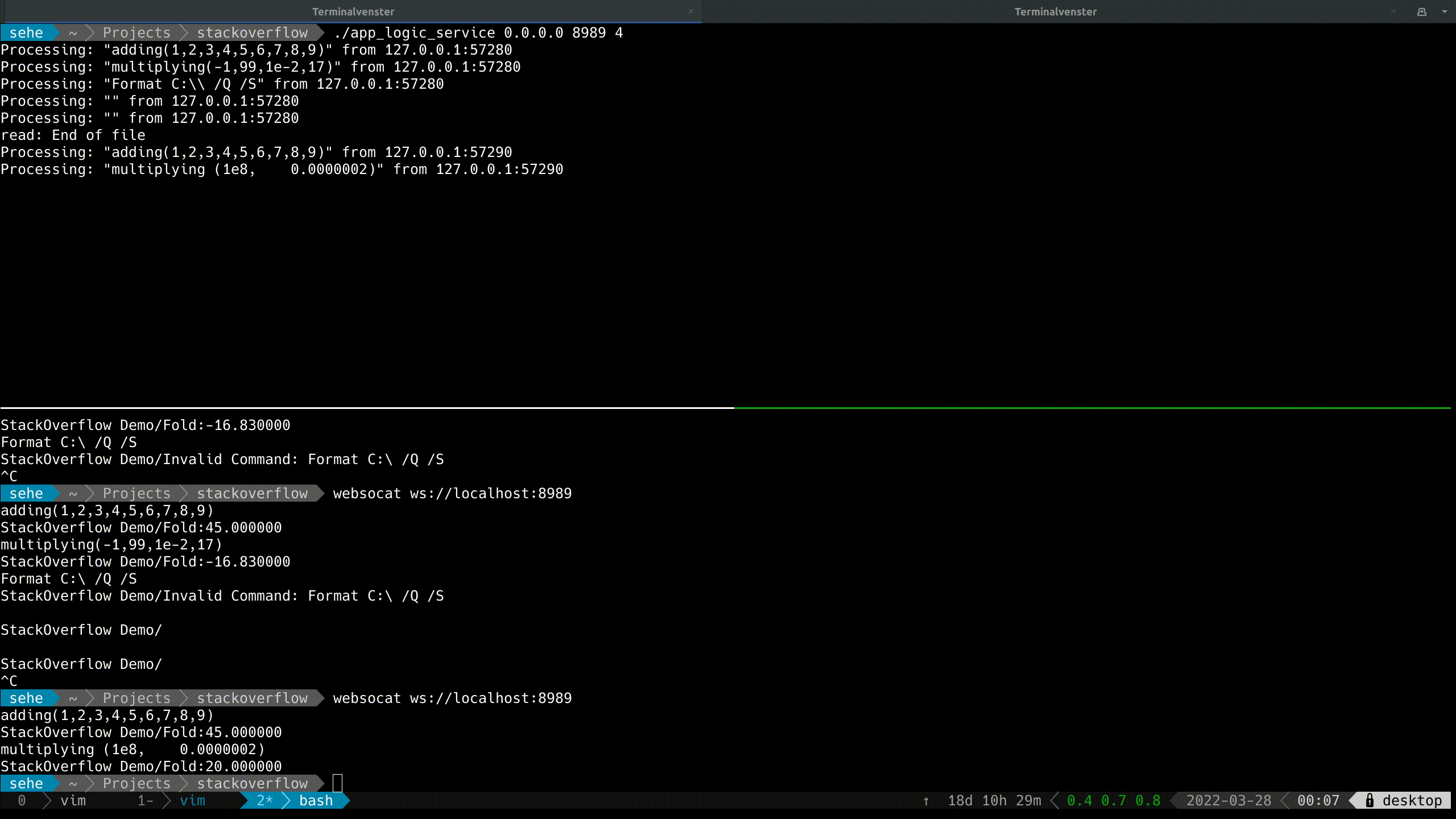
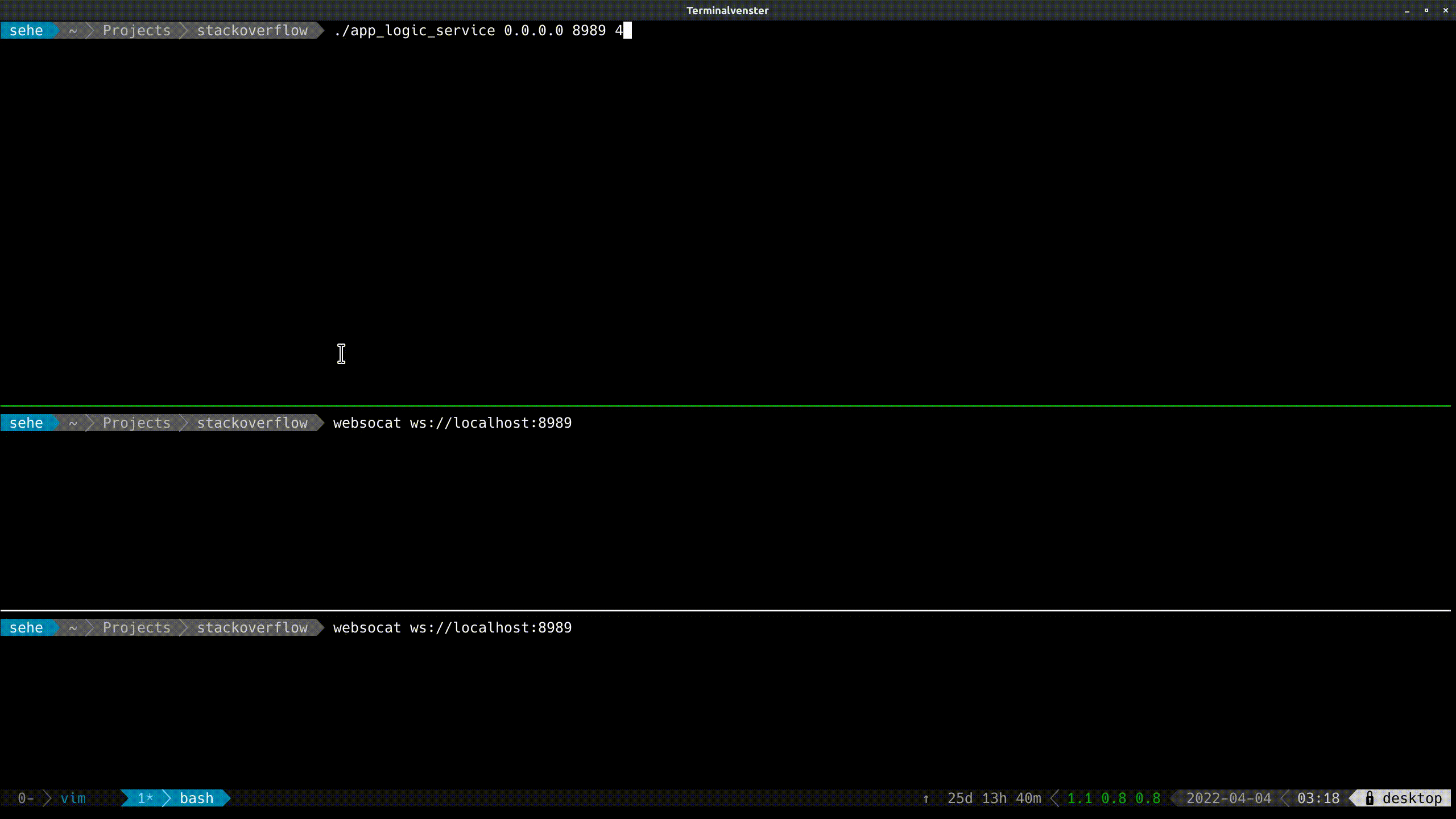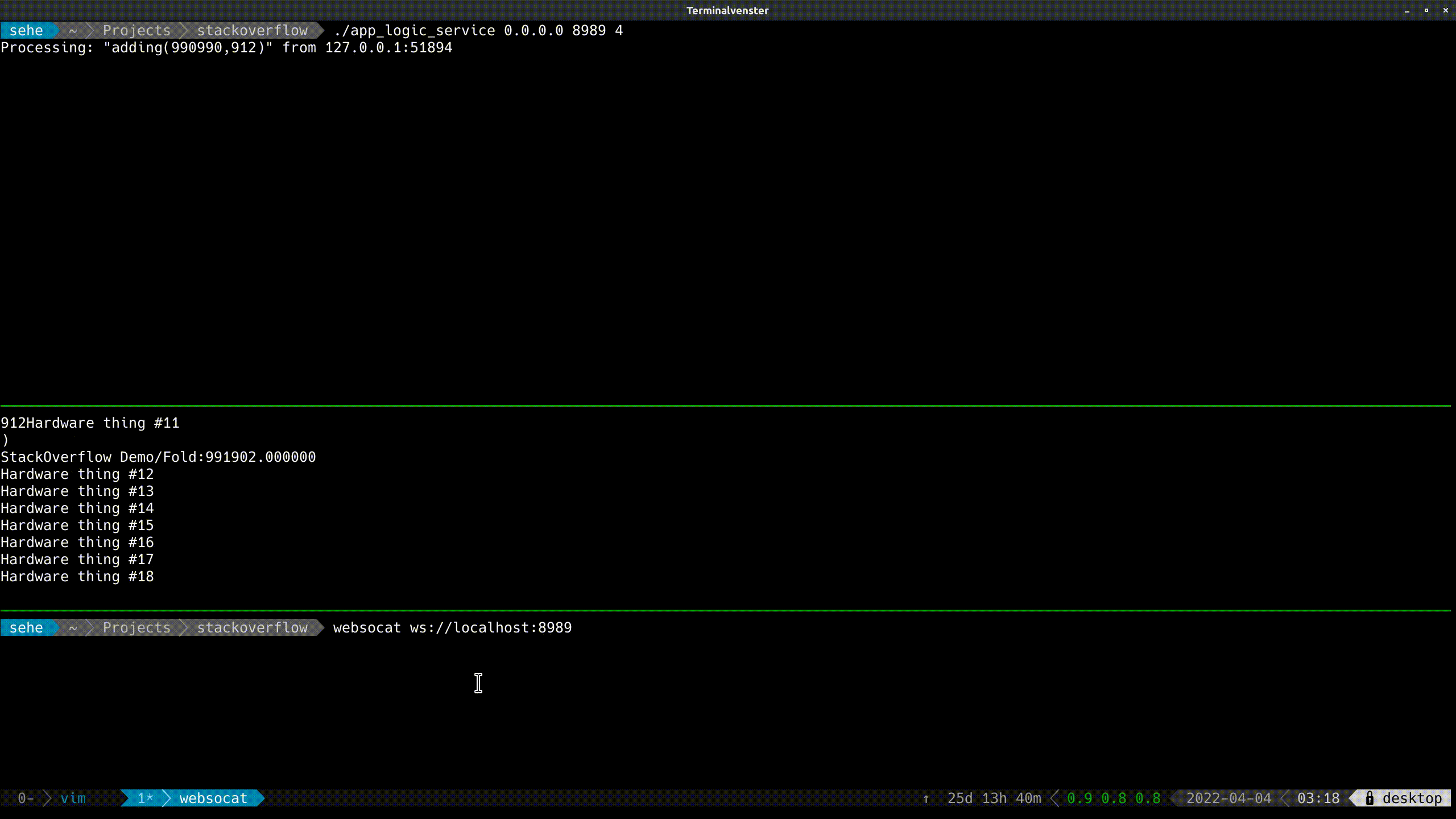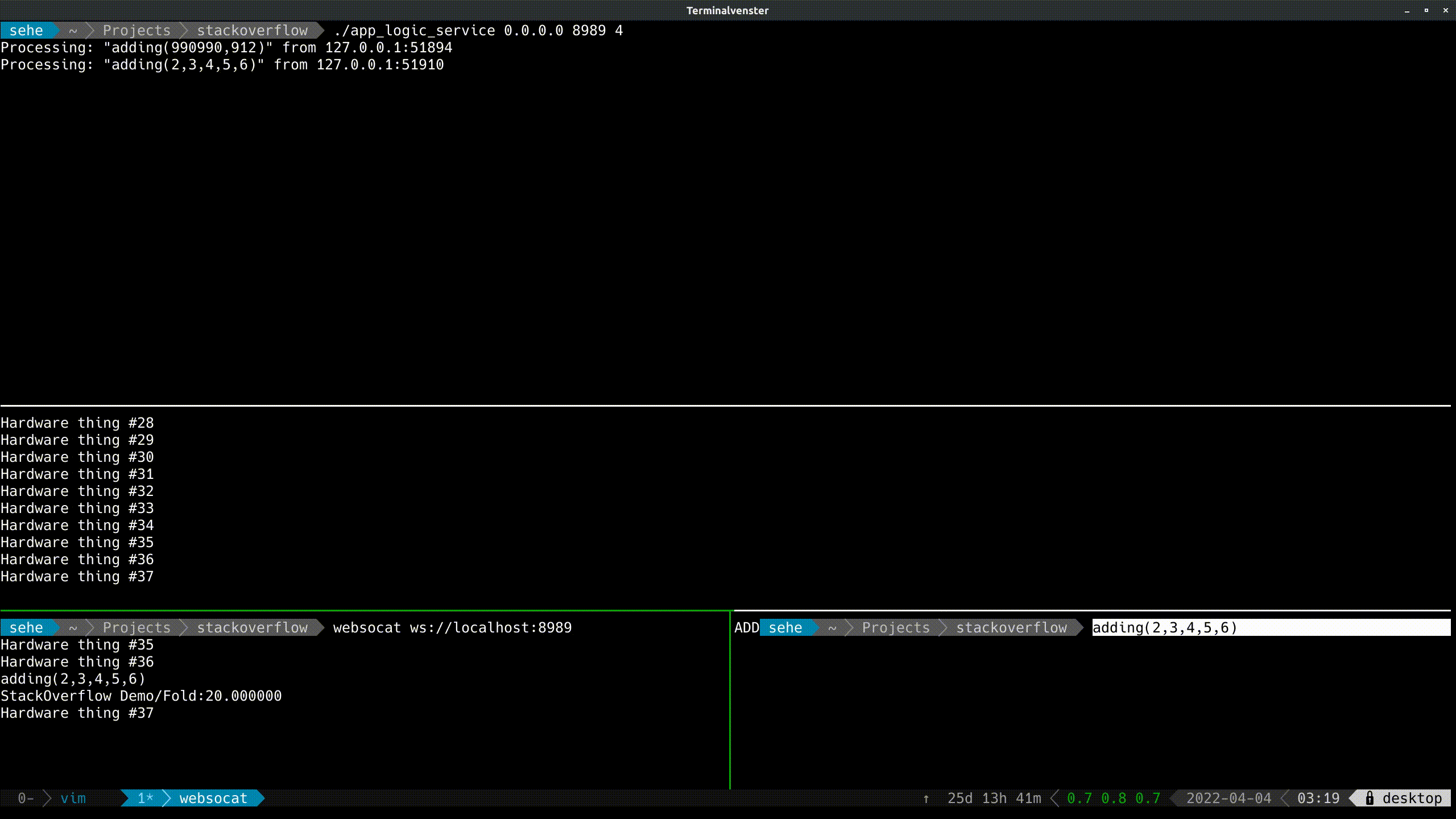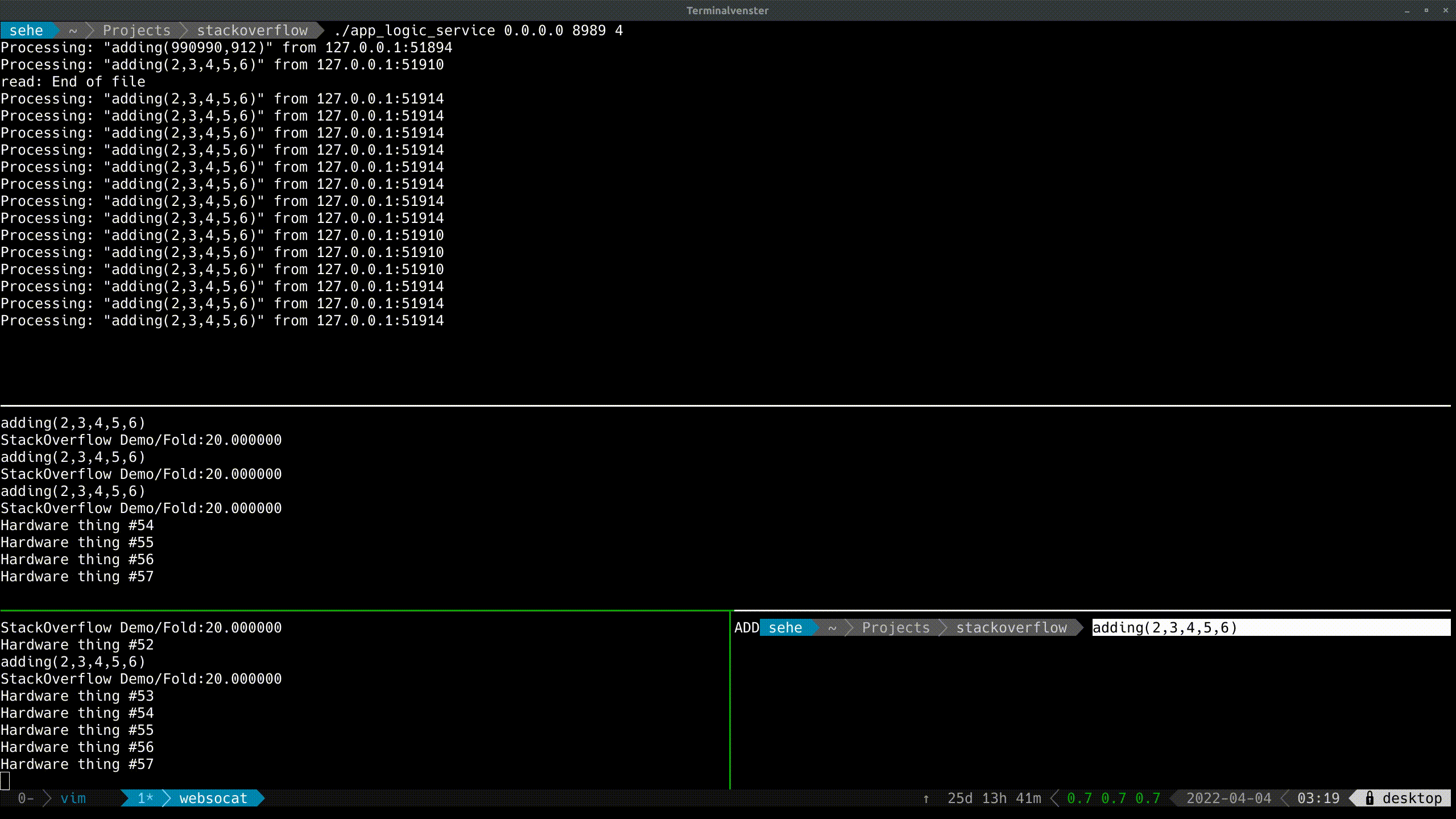
Now you can see it in action: Full Listing
![enter image description here]()
Where To Go From Here
What if you need multiple responses for one request?
You need a queue. I usually call those outbox so searching for outbox_, _outbox etc will give lots of examples.
Those examples will also show how to deal with other situations where writes can be "externally initiated", and how to safely enqueue those. Perhaps a very engaging example is here How to batch send unsent messages in asio
Listing For Reference
In case the links go dead in the future:
#include <boost/algorithm/string/trim.hpp>
#include <boost/asio.hpp>
#include <boost/beast.hpp>
#include <filesystem>
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
static std::string g_app_name = "app-logic-service";
#include <boost/core/demangle.hpp> // just for our demo logic
#include <boost/spirit/home/x3.hpp> // idem
#include <numeric> // idem
namespace AppDomain {
struct Logic {
std::string banner;
Logic(std::string msg) : banner(std::move(msg)) {}
std::string Process(std::string request) {
std::string result;
auto fold = [&result](auto op, double initial) {
return [=, &result](auto& ctx) {
auto& args = _attr(ctx);
auto v = accumulate(args.begin(), args.end(), initial, op);
result = "Fold:" + std::to_string(v);
};
};
auto invalid = [&result](auto& ctx) {
result = "Invalid Command: " + _attr(ctx);
};
using namespace boost::spirit::x3;
auto args = rule<void, std::vector<double>>{} = '(' >> double_ % ',' >> ')';
auto add = "adding" >> args[fold(std::plus<>{}, 0)];
auto mul = "multiplying" >> args[fold(std::multiplies<>{}, 1)];
auto err = lexeme[+char_][invalid];
phrase_parse(begin(request), end(request), add | mul | err, blank);
return banner + result;
}
};
} // namespace AppDomain
namespace beast = boost::beast; // from <boost/beast.hpp>
namespace http = beast::http; // from <boost/beast/http.hpp>
namespace websocket = beast::websocket; // from <boost/beast/websocket.hpp>
namespace net = boost::asio; // from <boost/asio.hpp>
using tcp = boost::asio::ip::tcp; // from <boost/asio/ip/tcp.hpp>
// Report a failure
void fail(beast::error_code ec, char const* what) {
std::cerr << what << ": " << ec.message() << "\n";
}
class session : public std::enable_shared_from_this<session> {
websocket::stream<beast::tcp_stream> ws_;
beast::flat_buffer buffer_;
std::string response_;
std::shared_ptr<AppDomain::Logic> logic_;
public:
explicit session(tcp::socket&& socket,
std::shared_ptr<AppDomain::Logic> logic)
: ws_(std::move(socket))
, logic_(logic) {}
void run() {
// Get on the correct executor
// strand for thread safety
dispatch(
ws_.get_executor(),
beast::bind_front_handler(&session::on_run, shared_from_this()));
}
private:
void on_run() {
// Set suggested timeout settings for the websocket
ws_.set_option(websocket::stream_base::timeout::suggested(
beast::role_type::server));
// Set a decorator to change the Server of the handshake
ws_.set_option(websocket::stream_base::decorator(
[](websocket::response_type& res) {
res.set(http::field::server,
std::string(BOOST_BEAST_VERSION_STRING) + " " +
g_app_name);
}));
// Accept the websocket handshake
ws_.async_accept(
beast::bind_front_handler(&session::on_accept, shared_from_this()));
}
void on_accept(beast::error_code ec) {
if (ec)
return fail(ec, "accept");
do_read();
}
void do_read() {
ws_.async_read(
buffer_,
beast::bind_front_handler(&session::on_read, shared_from_this()));
}
void on_read(beast::error_code ec, std::size_t /*bytes_transferred*/) {
if (ec == websocket::error::closed) return;
if (ec.failed()) return fail(ec, "read");
// Process the message
auto request = boost::algorithm::trim_copy(
beast::buffers_to_string(buffer_.data()));
std::cout << "Processing: " << std::quoted(request) << " from "
<< beast::get_lowest_layer(ws_).socket().remote_endpoint()
<< std::endl;
response_ = logic_->Process(request);
ws_.async_write(
net::buffer(response_),
beast::bind_front_handler(&session::on_write, shared_from_this()));
}
void on_write(beast::error_code ec, std::size_t bytes_transferred) {
boost::ignore_unused(bytes_transferred);
if (ec)
return fail(ec, "write");
// Clear the buffer
buffer_.consume(buffer_.size());
// Do another read
do_read();
}
};
// Accepts incoming connections and launches the sessions
class listener : public std::enable_shared_from_this<listener> {
net::any_io_executor ex_;
tcp::acceptor acceptor_;
std::shared_ptr<AppDomain::Logic> logic_;
public:
listener(net::any_io_executor ex, tcp::endpoint endpoint,
std::shared_ptr<AppDomain::Logic> logic)
: ex_(ex)
, acceptor_(ex)
, logic_(logic) {
acceptor_.open(endpoint.protocol());
acceptor_.set_option(tcp::acceptor::reuse_address(true));
acceptor_.bind(endpoint);
acceptor_.listen(tcp::acceptor::max_listen_connections);
}
// Start accepting incoming connections
void run() { do_accept(); }
private:
void do_accept() {
// The new connection gets its own strand
acceptor_.async_accept(make_strand(ex_),
beast::bind_front_handler(&listener::on_accept,
shared_from_this()));
}
void on_accept(beast::error_code ec, tcp::socket socket) {
if (ec) {
fail(ec, "accept");
} else {
std::make_shared<session>(std::move(socket), logic_)->run();
}
// Accept another connection
do_accept();
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
g_app_name = std::filesystem::path(argv[0]).filename();
if (argc != 4) {
std::cerr << "Usage: " << g_app_name << " <address> <port> <threads>\n"
<< "Example:\n"
<< " " << g_app_name << " 0.0.0.0 8080 1\n";
return 1;
}
auto const address = net::ip::make_address(argv[1]);
auto const port = static_cast<uint16_t>(std::atoi(argv[2]));
auto const threads = std::max<int>(1, std::atoi(argv[3]));
auto logic = std::make_shared<AppDomain::Logic>("StackOverflow Demo/");
try {
// The io_context is required for all I/O
net::thread_pool ioc(threads);
std::make_shared<listener>(ioc.get_executor(),
tcp::endpoint{address, port}, logic)
->run();
ioc.join();
} catch (beast::system_error const& se) {
fail(se.code(), "listener");
}
}
UPDATE
In response to the comments I reified the outbox pattern again. Note some of the comments in the code.
Compiler Explorer
#include <boost/algorithm/string/trim.hpp>
#include <boost/asio.hpp>
#include <boost/beast.hpp>
#include <deque>
#include <filesystem>
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
static std::string g_app_name = "app-logic-service";
#include <boost/core/demangle.hpp> // just for our demo logic
#include <boost/spirit/home/x3.hpp> // idem
#include <numeric> // idem
namespace AppDomain {
struct Logic {
std::string banner;
Logic(std::string msg) : banner(std::move(msg)) {}
std::string Process(std::string request) {
std::string result;
auto fold = [&result](auto op, double initial) {
return [=, &result](auto& ctx) {
auto& args = _attr(ctx);
auto v = accumulate(args.begin(), args.end(), initial, op);
result = "Fold:" + std::to_string(v);
};
};
auto invalid = [&result](auto& ctx) {
result = "Invalid Command: " + _attr(ctx);
};
using namespace boost::spirit::x3;
auto args = rule<void, std::vector<double>>{} = '(' >> double_ % ',' >> ')';
auto add = "adding" >> args[fold(std::plus<>{}, 0)];
auto mul = "multiplying" >> args[fold(std::multiplies<>{}, 1)];
auto err = lexeme[+char_][invalid];
phrase_parse(begin(request), end(request), add | mul | err, blank);
return banner + result;
}
};
} // namespace AppDomain
namespace beast = boost::beast; // from <boost/beast.hpp>
namespace http = beast::http; // from <boost/beast/http.hpp>
namespace websocket = beast::websocket; // from <boost/beast/websocket.hpp>
namespace net = boost::asio; // from <boost/asio.hpp>
using tcp = boost::asio::ip::tcp; // from <boost/asio/ip/tcp.hpp>
// Report a failure
void fail(beast::error_code ec, char const* what) {
std::cerr << what << ": " << ec.message() << "\n";
}
class session : public std::enable_shared_from_this<session> {
websocket::stream<beast::tcp_stream> ws_;
beast::flat_buffer buffer_;
std::shared_ptr<AppDomain::Logic> logic_;
public:
explicit session(tcp::socket&& socket,
std::shared_ptr<AppDomain::Logic> logic)
: ws_(std::move(socket))
, logic_(logic) {}
void run() {
// Get on the correct executor
// strand for thread safety
dispatch(
ws_.get_executor(),
beast::bind_front_handler(&session::on_run, shared_from_this()));
}
void post_message(std::string msg) {
post(ws_.get_executor(),
[self = shared_from_this(), this, msg = std::move(msg)] {
do_post_message(std::move(msg));
});
}
private:
void on_run() {
// on the strand
// Set suggested timeout settings for the websocket
ws_.set_option(websocket::stream_base::timeout::suggested(
beast::role_type::server));
// Set a decorator to change the Server of the handshake
ws_.set_option(websocket::stream_base::decorator(
[](websocket::response_type& res) {
res.set(http::field::server,
std::string(BOOST_BEAST_VERSION_STRING) + " " +
g_app_name);
}));
// Accept the websocket handshake
ws_.async_accept(
beast::bind_front_handler(&session::on_accept, shared_from_this()));
}
void on_accept(beast::error_code ec) {
// on the strand
if (ec)
return fail(ec, "accept");
do_read();
}
void do_read() {
// on the strand
buffer_.clear();
ws_.async_read(
buffer_,
beast::bind_front_handler(&session::on_read, shared_from_this()));
}
void on_read(beast::error_code ec, std::size_t /*bytes_transferred*/) {
// on the strand
if (ec == websocket::error::closed) return;
if (ec.failed()) return fail(ec, "read");
// Process the message
auto request = boost::algorithm::trim_copy(
beast::buffers_to_string(buffer_.data()));
std::cout << "Processing: " << std::quoted(request) << " from "
<< beast::get_lowest_layer(ws_).socket().remote_endpoint()
<< std::endl;
do_post_message(logic_->Process(request)); // already on the strand
do_read();
}
std::deque<std::string> _outbox;
void do_post_message(std::string msg) {
// on the strand
_outbox.push_back(std::move(msg));
if (_outbox.size() == 1)
do_write_loop();
}
void do_write_loop() {
// on the strand
if (_outbox.empty())
return;
ws_.async_write( //
net::buffer(_outbox.front()),
[self = shared_from_this(), this] //
(beast::error_code ec, size_t bytes_transferred) {
// on the strand
boost::ignore_unused(bytes_transferred);
if (ec)
return fail(ec, "write");
_outbox.pop_front();
do_write_loop();
});
}
};
// Accepts incoming connections and launches the sessions
class listener : public std::enable_shared_from_this<listener> {
net::any_io_executor ex_;
tcp::acceptor acceptor_;
std::shared_ptr<AppDomain::Logic> logic_;
public:
listener(net::any_io_executor ex, tcp::endpoint endpoint,
std::shared_ptr<AppDomain::Logic> logic)
: ex_(ex)
, acceptor_(make_strand(ex)) // NOTE to guard sessions_
, logic_(logic) {
acceptor_.open(endpoint.protocol());
acceptor_.set_option(tcp::acceptor::reuse_address(true));
acceptor_.bind(endpoint);
acceptor_.listen(tcp::acceptor::max_listen_connections);
}
// Start accepting incoming connections
void run() { do_accept(); }
void broadcast(std::string msg) {
post(acceptor_.get_executor(),
beast::bind_front_handler(&listener::do_broadcast,
shared_from_this(), std::move(msg)));
}
private:
using handle_t = std::weak_ptr<session>;
std::list<handle_t> sessions_;
void do_broadcast(std::string const& msg) {
for (auto handle : sessions_)
if (auto sess = handle.lock())
sess->post_message(msg);
}
void do_accept() {
// The new connection gets its own strand
acceptor_.async_accept(make_strand(ex_),
beast::bind_front_handler(&listener::on_accept,
shared_from_this()));
}
void on_accept(beast::error_code ec, tcp::socket socket) {
// on the strand
if (ec) {
fail(ec, "accept");
} else {
auto sess = std::make_shared<session>(std::move(socket), logic_);
sessions_.emplace_back(sess);
// optionally:
sessions_.remove_if(std::mem_fn(&handle_t::expired));
sess->run();
}
// Accept another connection
do_accept();
}
};
static void emulate_hardware_stuff(std::shared_ptr<listener> srv) {
using std::this_thread::sleep_for;
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
// Extremely simplistic. Instead I'd recommend `steady_timer` with
// `_async_wait` here, but since I'm just making a sketch...
unsigned i = 0;
while (true) {
sleep_for(1s);
srv->broadcast("Hardware thing #" + std::to_string(++i));
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
g_app_name = std::filesystem::path(argv[0]).filename();
if (argc != 4) {
std::cerr << "Usage: " << g_app_name << " <address> <port> <threads>\n"
<< "Example:\n"
<< " " << g_app_name << " 0.0.0.0 8080 1\n";
return 1;
}
auto const address = net::ip::make_address(argv[1]);
auto const port = static_cast<uint16_t>(std::atoi(argv[2]));
auto const threads = std::max<int>(1, std::atoi(argv[3]));
auto logic = std::make_shared<AppDomain::Logic>("StackOverflow Demo/");
try {
// The io_context is required for all I/O
net::thread_pool ioc(threads);
auto srv = std::make_shared<listener>( //
ioc.get_executor(), //
tcp::endpoint{address, port}, //
logic);
srv->run();
std::thread something_hardware(emulate_hardware_stuff, srv);
ioc.join();
something_hardware.join();
} catch (beast::system_error const& se) {
fail(se.code(), "listener");
}
}
With Live Demo:
![enter image description here]()