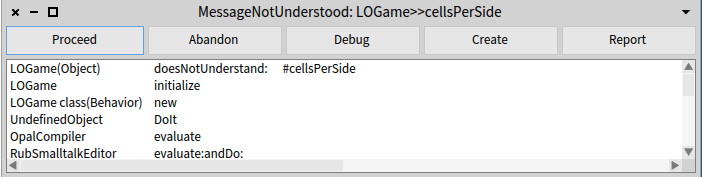
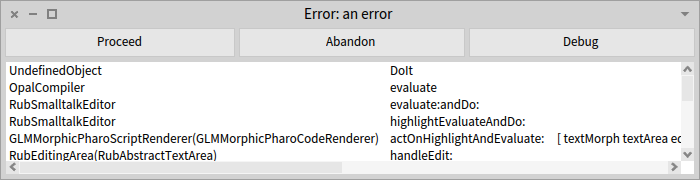
The debugger is opened as a response to an unhandled exception. To better explain we can start from triggering an exception that is not caught anywhere in the system. For example, we can execute in a Playground Error signal: 'an error'. (signal is throwing an error in Pharo). This opens the following debugger:
![enter image description here]()
When an exception happens the system first tries to find an exception handler for that exception. If no exception handler is found then the system sends the message defaultAction to the exception. This is implemented in the class Error as:
Error>>#defaultAction
"No one has handled this error, but now give them a chance to decide how
to debug it. If none handle this either then open debugger
(see UnhandedError-defaultAction)"
UnhandledError signalForException: self
So the system responds to an unhandled exception by throwing another exception, UnhandledError. Again if no exception handlers are found for the new exception the system sends the message defaultAction to the exception object. In this case the exception is an instance of UnhandledError and this class overriders defaultAction with the following implementation:
UnhandledError>>#defaultAction
<reflective: #unhandledErrorDefaultAction:message:>
^ UIManager default unhandledErrorDefaultAction: self exception
The method unhandledErrorDefaultAction: is quite simple and just sends the exception object the message debug.
MorphicUIManager>>#unhandledErrorDefaultAction: anException
anException debug
The method debug is implemented in Exception, the root class of all exceptions in Pharo as:
Exception>>#debug
"open a debugger on myself"
Processor activeProcess
debug: self signalerContext
title: self description
So this is what opens the debugger.
In the case of sending an unknown message to an object an exception of type MessageNotUnderstood is thrown by the method Object>>#doesNotUnderstand:. This exception follows the same chain as before and the system ends up sending the debug message to the MessageNotUnderstood exception which opens the debugger.
So in short:
- when an unknown message is sent to an object the system sends the object the message
#doesNotUnderstand:;
doesNotUnderstand: raises an exception of type MessageNotUnderstood;- if this exception is not caught another exception of type
UnhandledError is raised;
- if this new
UnhandledError is not caught it asks the UI manager to handle this case;
- the UI manager sends the message
debug to the initial exception, in this case the MessageNotUnderstood exception (only MorphicUIManager does this; other UI managers like CommandLineUIManager do other actions like existing the image);
- the
debug message opens the debugger
The handler for non existent variables has a totally different implementation that is in the actual compiler. When code is compiled in a class that has unknown variables the compiler detects that and asks the user what to do: create a new instance variable or a local parameter.
If you try to execute code containing an unknown class, like UnnknowsClass new. the compiler also detects this and asks the user what to do. There is no exception raised in this case.
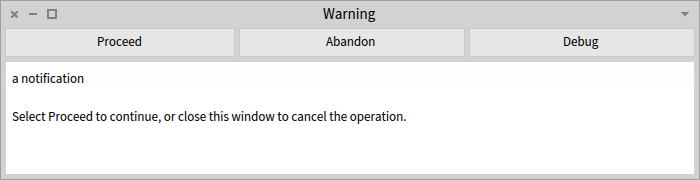
There are other helpers that use the same mechanism as doesNotUnderstand: for example raising notifications. If you execute Object new notify: 'a notification' the method notify: throws a Warning exception that ends up opening the debugger.
![enter image description here]()