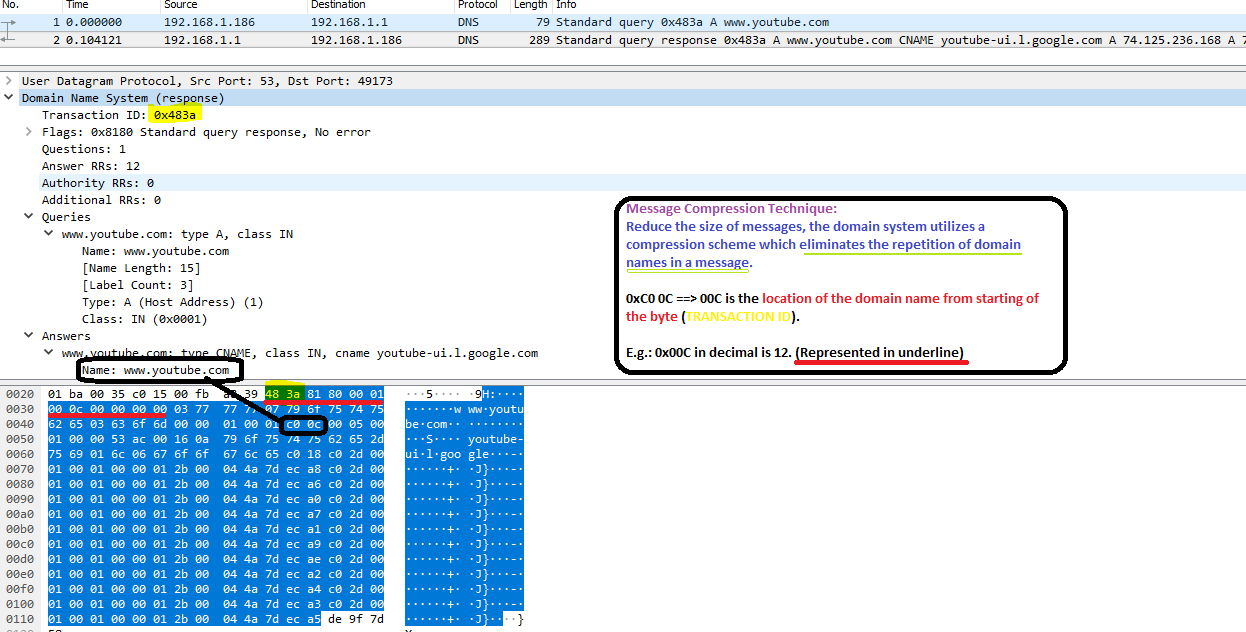
I have been looking at DNS response packets in Wireshark, and am not able to understand hex coding for the answer and authoritative sections.
Considering DNS query for: mail.abcd.com
The answer section contains name field, and the hex coding for this varies among:
0xc00c
0xc012
Both of them lead to the entire name being populated in the field.
The authoritative section also contains the name field, but the hex coding for this is usually:
0xc010
This leads to abcd.com being populated in the field.
Can anyone tell what is the convention followed to populate these fields, as its pretty confusing.
Thanks