Right now i have a large data set with temperature going up and down all the time. I want to smoothen my data and plot the best fit line with all the temperature,
Here is the data:
weather.data
date mtemp
1 2008-01-01 12.9
2 2008-01-02 12.9
3 2008-01-03 14.5
4 2008-01-04 15.7
5 2008-01-05 17.0
6 2008-01-06 17.8
7 2008-01-07 20.2
8 2008-01-08 20.8
9 2008-01-09 21.4
10 2008-01-10 20.8
11 2008-01-11 21.4
12 2008-01-12 22.0
and so on............... til 2009 Dec 31
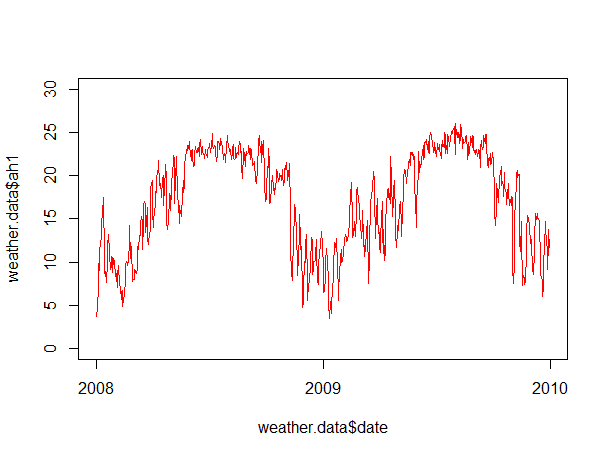
My current graph looks like this and my data fit a regression like either the running average or loess:
However, when I tried to fit it with the running average, it became like this:
Here is my code.
plot(weather.data$date,weather.data$mtemp,ylim=c(0,30),type='l',col="orange")
par(new=TRUE)
Could anyone give me a hand?