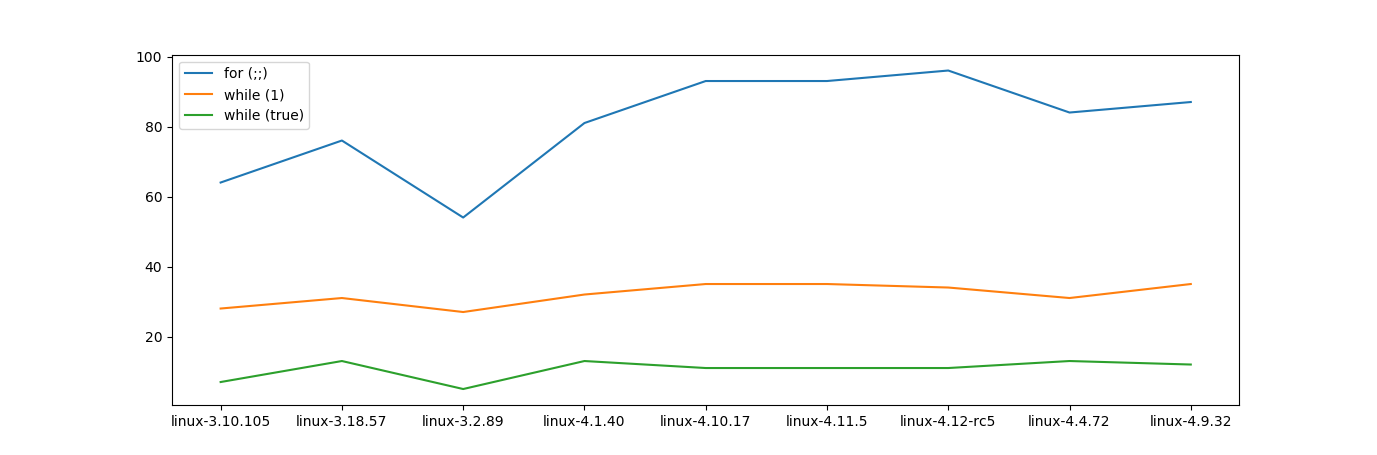
Everyone seems to like while (true):
https://mcmap.net/q/18776/-infinite-loops-top-or-bottom-closed
https://mcmap.net/q/18778/-which-is-the-correct-c-infinite-loop-for-or-while-true-closed
https://mcmap.net/q/18778/-which-is-the-correct-c-infinite-loop-for-or-while-true-closed
https://mcmap.net/q/18778/-which-is-the-correct-c-infinite-loop-for-or-while-true-closed
https://mcmap.net/q/18778/-which-is-the-correct-c-infinite-loop-for-or-while-true-closed
According to SLaks, they compile identically.
Ben Zotto also says it doesn't matter:
It's not faster.
If you really care, compile with assembler output for your platform and look to see.
It doesn't matter. This never matters. Write your infinite loops however you like.
In response to user1216838, here's my attempt to reproduce his results.
Here's my machine:
cat /etc/*-release
CentOS release 6.4 (Final)
gcc version:
Target: x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu
Thread model: posix
gcc version 4.8.2 (GCC)
And test files:
// testing.cpp
#include <iostream>
int main() {
do { break; } while(1);
}
// testing2.cpp
#include <iostream>
int main() {
while(1) { break; }
}
// testing3.cpp
#include <iostream>
int main() {
while(true) { break; }
}
The commands:
gcc -S -o test1.asm testing.cpp
gcc -S -o test2.asm testing2.cpp
gcc -S -o test3.asm testing3.cpp
cmp test1.asm test2.asm
The only difference is the first line, aka the filename.
test1.asm test2.asm differ: byte 16, line 1
Output:
.file "testing2.cpp"
.local _ZStL8__ioinit
.comm _ZStL8__ioinit,1,1
.text
.globl main
.type main, @function
main:
.LFB969:
.cfi_startproc
pushq %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa_offset 16
.cfi_offset 6, -16
movq %rsp, %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa_register 6
nop
movl $0, %eax
popq %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa 7, 8
ret
.cfi_endproc
.LFE969:
.size main, .-main
.type _Z41__static_initialization_and_destruction_0ii, @function
_Z41__static_initialization_and_destruction_0ii:
.LFB970:
.cfi_startproc
pushq %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa_offset 16
.cfi_offset 6, -16
movq %rsp, %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa_register 6
subq $16, %rsp
movl %edi, -4(%rbp)
movl %esi, -8(%rbp)
cmpl $1, -4(%rbp)
jne .L3
cmpl $65535, -8(%rbp)
jne .L3
movl $_ZStL8__ioinit, %edi
call _ZNSt8ios_base4InitC1Ev
movl $__dso_handle, %edx
movl $_ZStL8__ioinit, %esi
movl $_ZNSt8ios_base4InitD1Ev, %edi
call __cxa_atexit
.L3:
leave
.cfi_def_cfa 7, 8
ret
.cfi_endproc
.LFE970:
.size _Z41__static_initialization_and_destruction_0ii, .-_Z41__static_initialization_and_destruction_0ii
.type _GLOBAL__sub_I_main, @function
_GLOBAL__sub_I_main:
.LFB971:
.cfi_startproc
pushq %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa_offset 16
.cfi_offset 6, -16
movq %rsp, %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa_register 6
movl $65535, %esi
movl $1, %edi
call _Z41__static_initialization_and_destruction_0ii
popq %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa 7, 8
ret
.cfi_endproc
.LFE971:
.size _GLOBAL__sub_I_main, .-_GLOBAL__sub_I_main
.section .ctors,"aw",@progbits
.align 8
.quad _GLOBAL__sub_I_main
.hidden __dso_handle
.ident "GCC: (GNU) 4.8.2"
.section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits
With -O3, the output is considerably smaller of course, but still no difference.

endless: GOTO endless;– Incretionvoid loop() { ...; loop(); }. – Civilitywhile(true)though. – Twelve