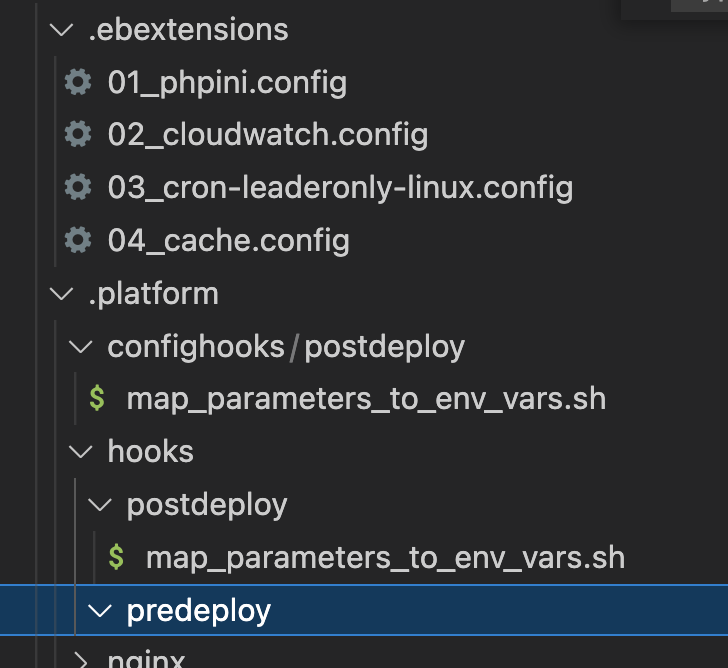
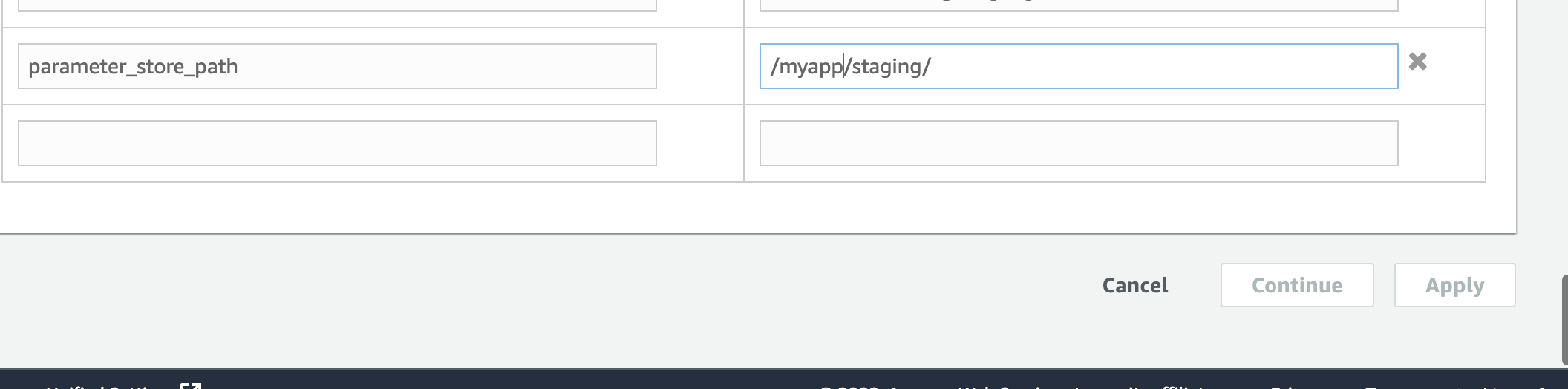
I am using AWS Elastic beanstalk and want to configure different ENV var for different environment. The only way which I found was using ebextensions but ENVIRONMENT variables once set in ebextension cannot be overridden if I am deploying the same packet to multiple environments. Heard about SSM Parameter store but was not able to find a way to use is with Elastic Beanstalk.
From what I found was that SSM Parameter store can do it for EC2 instances. I don't want to restart the EC2 instance every time I update one environment variable. Also thought of writing a script which takes the value from SSM and updates environment variables in ebextentsions. But that only seems to be a hack and not the proper solution and will take to check the scenarios where it might fail