First, let's set the above existing json data to a constants.dart
const response = {
"food": [
{
"id": "0001",
"name": "Cake",
"description": [
{"id": "instruction_1002", "type": "Chocolate"},
{"id": "instruction_1003", "type": "fruits"},
{"id": "instruction_1004", "type": "Corn"}
]
},
{
"id": "0002",
"name": "Raised",
"description": [
{"id": "instruction_2002", "type": "Grape"},
{"id": "instruction_2003", "type": "Wheat"}
]
}
],
"instruction": [
{"category": "instruction_1002", "content": "abc1234"},
{"category": "instruction_1003", "content": "def56789"}
]
};
From this data we'll get to create 3 collections and one of them will be an embedded object
Create a folder called collections.
Inside the collections folder create a dart file called food.dart
This file will contain a collection called Food and another collection called Description that will be embedded to the Food collection. The properties are also defined by the keys provided in the existing json data in constants.dart
import 'package:isar/isar.dart';
part 'food.g.dart';
@Collection()
class Food {
Food({this.foodId, this.name, this.description});
Id? foodId = Isar.autoIncrement;
String? id;
String? name;
List<Description>? description;
}
@embedded
class Description {
Description({this.id, this.type});
String? id;
String? type;
}
Inside the collections folder create another dart file called instruction.dart
import 'package:isar/isar.dart';
part 'instruction.g.dart';
@Collection()
class Instruction {
Instruction({this.category, this.content});
Id? id = Isar.autoIncrement;
String? category;
String? content;
}
Next, we need to create generated files for these two files by using build_runner.
Import the build_runner flutter package.
Run the command below to generate the files:
flutter pub run build_runner build
You'll find 2 files created in the collections folder: food.g.dart & instruction.g.dart
Next, we'll go to the necessary class, to import the existing json data to isar database. In my case I'll use the skeleton below to proceed.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() async {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
final Isar isar;
const MyApp({super(key: key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text("Isar Database"),
),
body: Center(
child: TextButton(
onPressed: () {
//IMPORT LOGIC HERE
},
child: const Text("Import JSON"),
),
),
));
}
}
Now let's add the import json logic.
Ensure you have these packages installed.
isar: ^3.0.5
isar_generator: ^3.0.5
isar_flutter_libs: ^3.0.5
path_provider: ^2.0.13
Let's initialize isar to the application in the main function. It will look like this:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:import_to_isar/collections/food.dart';
import 'package:import_to_isar/collections/instruction.dart';
import 'package:import_to_isar/constant.dart';
import 'package:isar/isar.dart';
import 'package:path_provider/path_provider.dart';
void main() async {
//INITIALIZE ISAR TO THE APPLICATION
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
final dir = await getApplicationSupportDirectory();
if (dir.existsSync()) {
final isar = await Isar.open([FoodSchema, InstructionSchema]);
runApp(MyApp(isar: isar));
}
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
final Isar isar;
const MyApp({Key? key, required this.isar}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text("Isar Database"),
),
body: Center(
child: TextButton(
onPressed: () {
//IMPORT LOGIC HERE
},
child: const Text("Import JSON"),
),
),
));
}
}
Now, we create a function that will use the importJson() method by Isar database as shown below.
importjson() async {
//We first clear the database - not a must!
await isar.writeTxn(() async {
await isar.clear();
});
importFood(); //This function imports the data in the key 'food' from the existing json data
importInstructions(); //This function imports the data in the key 'instruction' from the existing json data
}
importFood() async {
await isar.writeTxn(() async {
await isar.foods.importJson(response['food']!);
});
}
importInstructions() async {
await isar.writeTxn(() async {
await isar.instructions.importJson(response['instruction']!);
});
}
Full code:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:import_to_isar/collections/food.dart';
import 'package:import_to_isar/collections/instruction.dart';
import 'package:import_to_isar/constant.dart';
import 'package:isar/isar.dart';
import 'package:path_provider/path_provider.dart';
void main() async {
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
final dir = await getApplicationSupportDirectory();
if (dir.existsSync()) {
final isar = await Isar.open([FoodSchema, InstructionSchema]);
runApp(MyApp(isar: isar));
}
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
final Isar isar;
const MyApp({Key? key, required this.isar}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text("Isar Database"),
),
body: Center(
child: TextButton(
onPressed: () {
importjson();
},
child: const Text("Import JSON"),
),
),
));
}
importjson() async {
await isar.writeTxn(() async {
await isar.clear();
});
importFood();
importInstructions();
}
importFood() async {
await isar.writeTxn(() async {
await isar.foods.importJson(response['food']!);
});
}
importInstructions() async {
await isar.writeTxn(() async {
await isar.instructions.importJson(response['instruction']!);
});
}
}
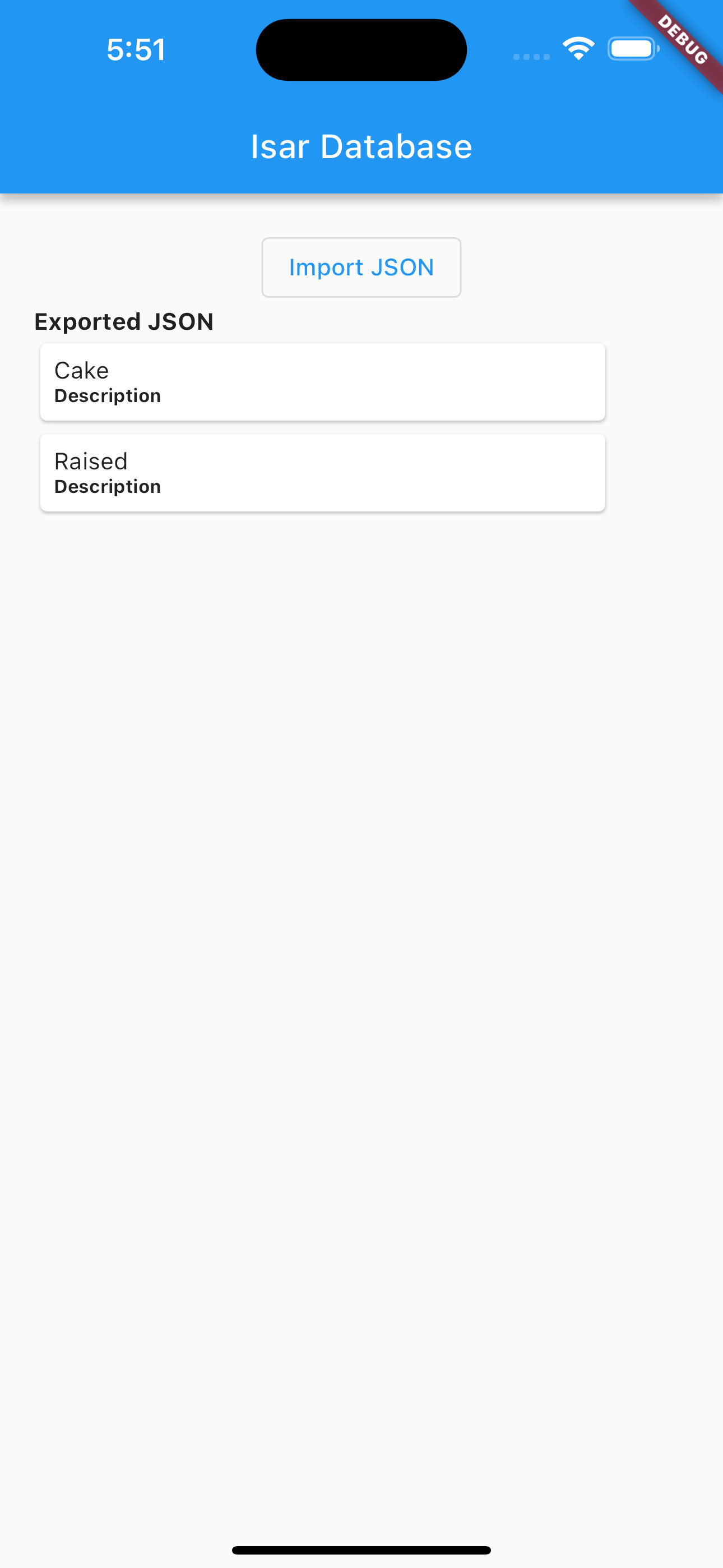
The UI looks like this:
![enter image description here]()
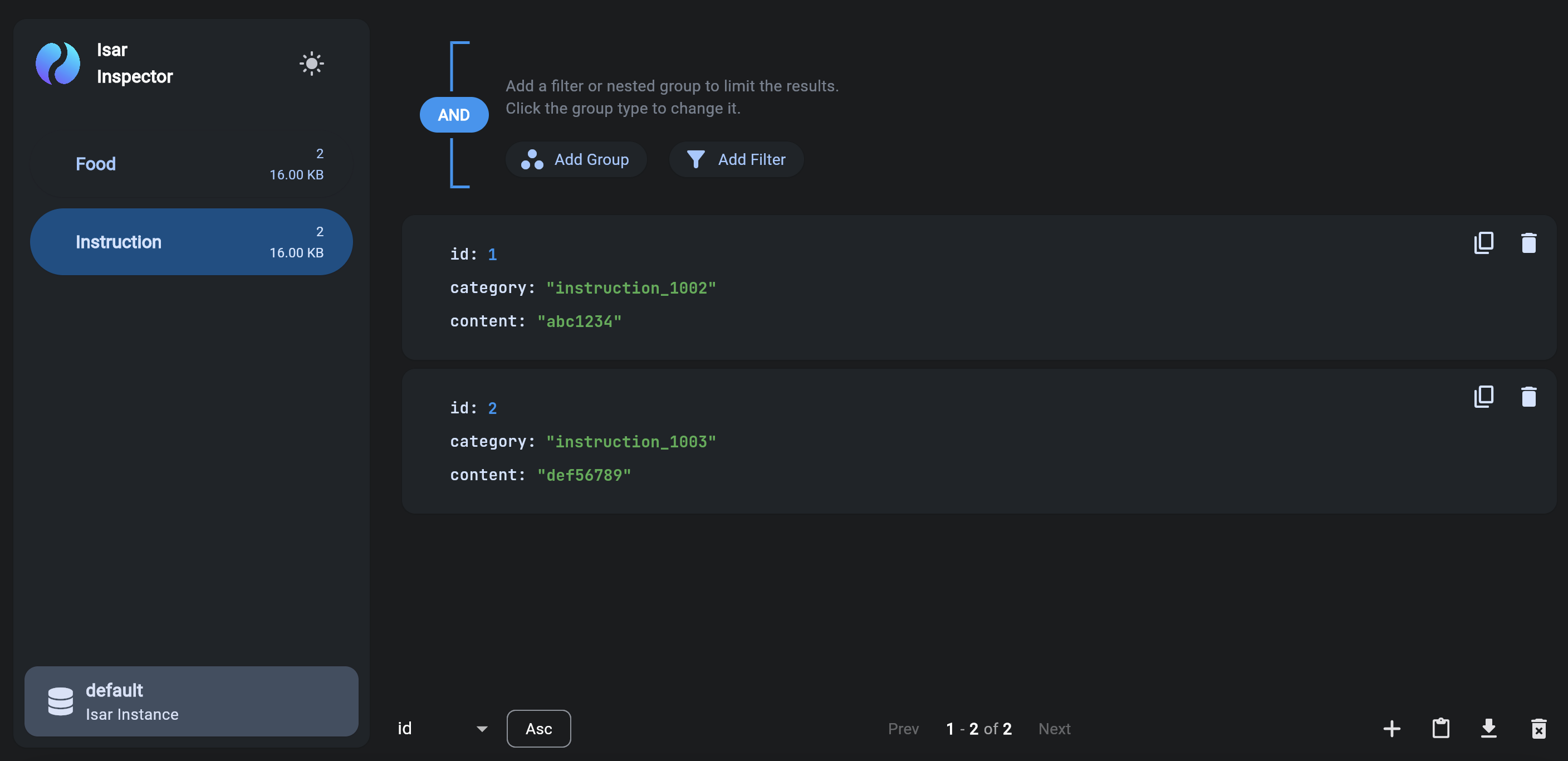
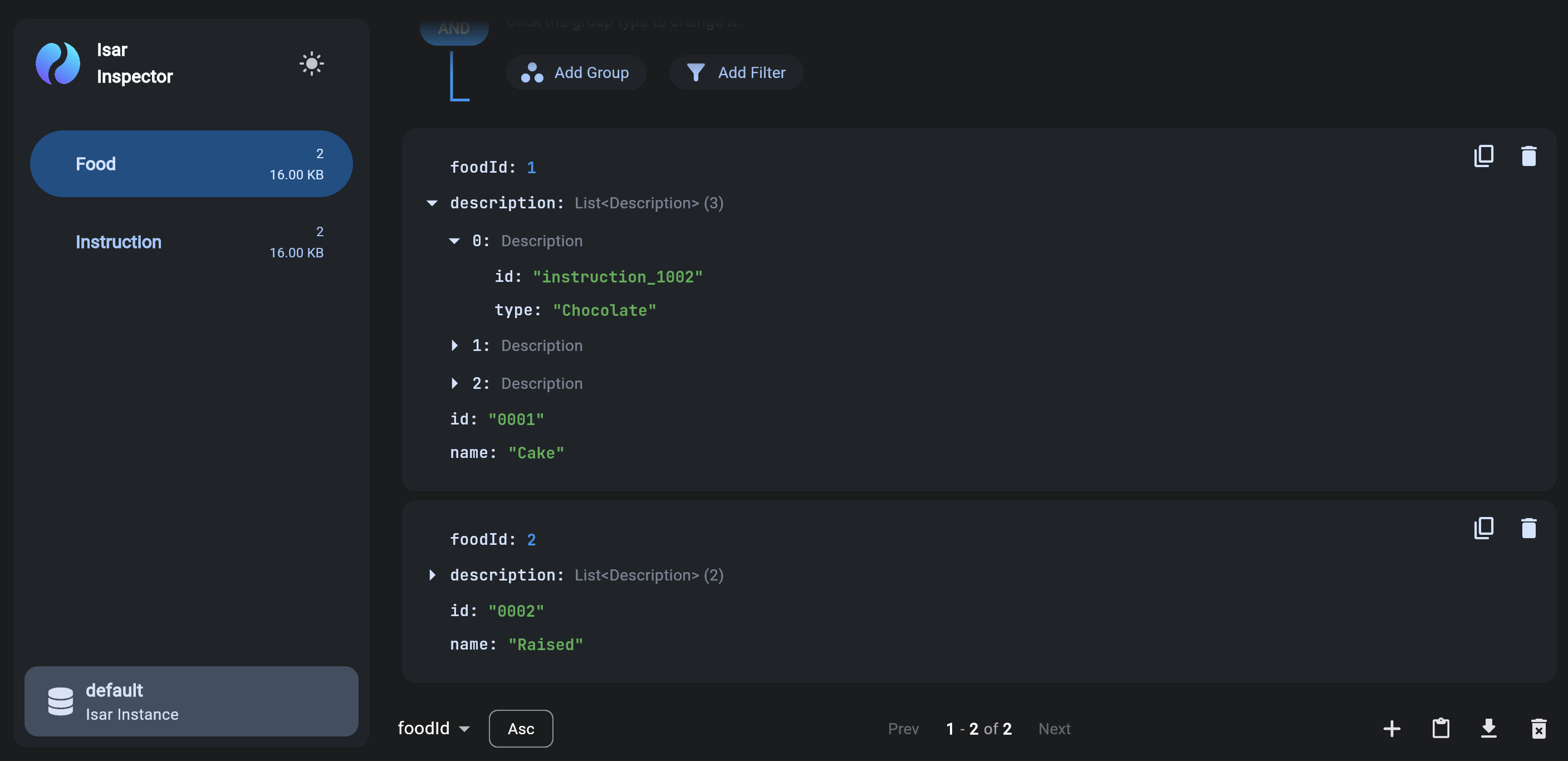
To view the data in the Isar database, use the Isar Inspector. You'll find the link on the terminal of your IDE when you run the application.
This is how my Isar Inspector looks like:
![enter image description here]()
![enter image description here]()
To display the information stored in the 2 collections respectively,
let's:
- Change MyApp class to a State class.
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
final Isar isar;
const MyApp({Key? key, required this.isar}) : super(key: key);
@override
State<MyApp> createState() => _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text("Isar Database"),
),
body: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
Align(
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: OutlinedButton(
onPressed: () {
importjson();
},
child: const Text("Import JSON"),
),
),
],
),
),
));
}
importjson() async {
await widget.isar.writeTxn(() async {
await widget.isar.clear();
});
importFood();
importInstructions();
}
importFood() async {
await widget.isar.writeTxn(() async {
await widget.isar.foods.importJson(response['food']!);
});
}
importInstructions() async {
await widget.isar.writeTxn(() async {
await widget.isar.instructions.importJson(response['instruction']!);
});
}
}
- Create a new function called exportjson() that will get data from Food collection.
Future<List<Food>> exportjson() async {
return await widget.isar.foods.where().findAll();
}
- In the design, we'll add a Text to refer to Exported JSON and a FutureBuilder that will help us handle the data that has been collected using exportjson() function
const Text(
"Exported JSON",
style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
FutureBuilder<List<Food>>(
future: exportjson(),
builder: (context, snapshot) {
List<Food> foodlist = snapshot.data ?? [];
if (foodlist.isNotEmpty) {
return Column(
children: [],
);
} else {
return const SizedBox.shrink();
}
})
- Let's build the childrens attribute for Column with what we have received from snapsot.data. We'll create the function below with argument of type List:
List<Widget> buildWidget(List<Food> f) {
List<Widget> x = [];
for (int i = 0; i < f.length; i++) {
x.add(SizedBox(
width: MediaQuery.of(context).size.width * 0.8,
child: Card(
child: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child:
Column(crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start, children: [
Text(f[i].name ?? ""),
const Text(
"Description",
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 11, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
]),
),
),
));
}
return x;
}
- Let's pass this function to the childrens attribute as shown below:
FutureBuilder<List<Food>>(
future: exportjson(),
builder: (context, snapshot) {
List<Food> foodlist = snapshot.data ?? [];
if (foodlist.isNotEmpty) {
return Column(
children: buildWidget(foodlist),
);
} else {
return const SizedBox.shrink();
}
})
The display will look like this:
![enter image description here]()
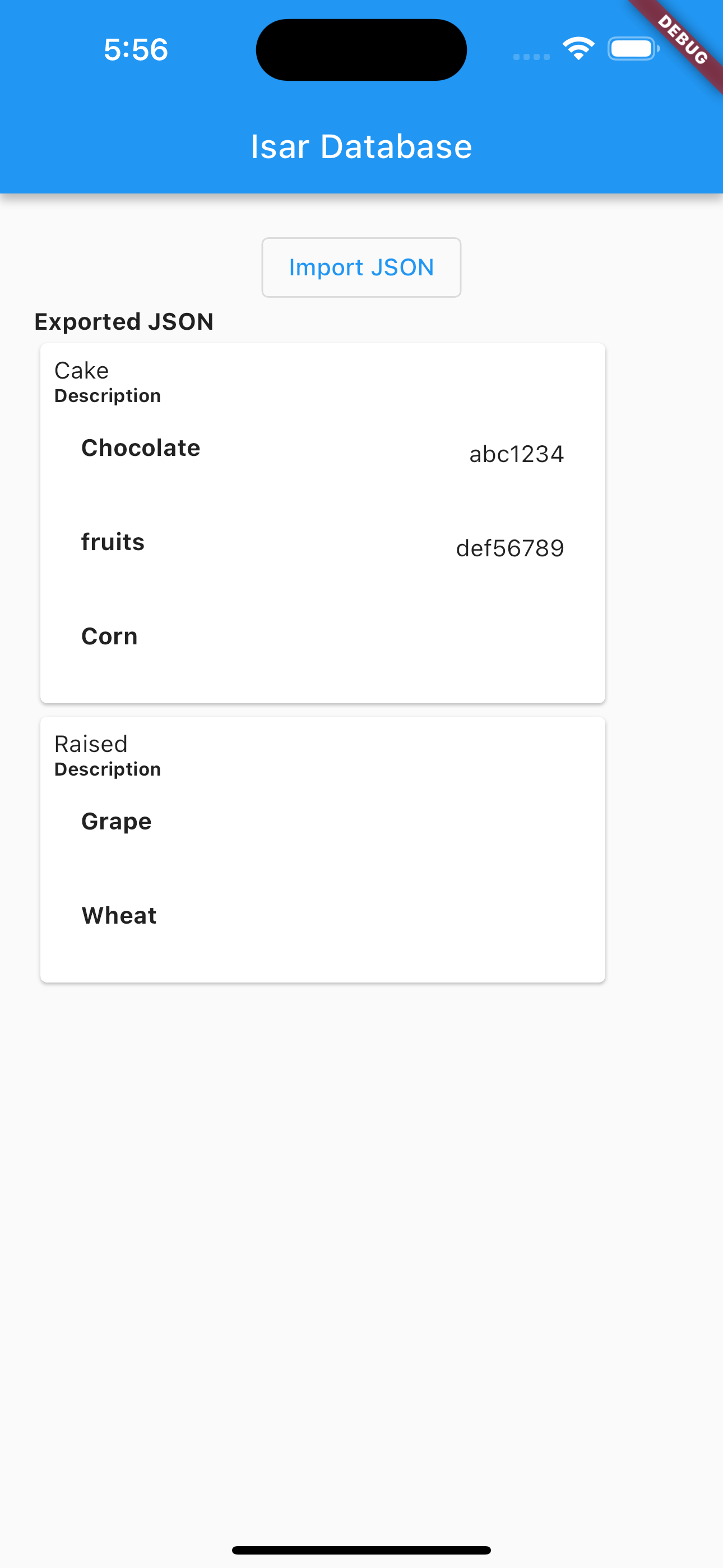
- Now, let's display description of each food using Instruction collection by creating another function that will query checking where category equals to the id of the description for the food, and then build the widgets for us.
Future<List<Widget>> buildDescription(List<Description> d) async {
List<Widget> y = [];
for (int i = 0; i < d.length; i++) {
Instruction? x = await widget.isar.instructions
.where()
.filter()
.categoryEqualTo(d[i].id)
.findFirst();
String content = x?.content ?? "";
y.add(ListTile(
leading: Text(
d[i].type!,
style: const TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
trailing: Text(content),
));
}
return y;
}
- We'll pass this function in the buildWidget() function like shown:
List<Widget> buildWidget(List<Food> f) {
List<Widget> x = [];
for (int i = 0; i < f.length; i++) {
List<Description> description = f[i].description ?? [];
x.add(SizedBox(
width: MediaQuery.of(context).size.width * 0.8,
child: Card(
child: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child:
Column(crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start, children: [
Text(f[i].name ?? ""),
const Text(
"Description",
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 11, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
FutureBuilder(
future: buildDescription(description),
builder: (context, snapshot) {
List<Widget> c = snapshot.data ?? [];
return Column(children: c);
})
]),
),
),
));
}
return x;
}
Now the screen will look as shown displaying description information of each food.
![enter image description here]()