I used with success the following Visual Studio 2013 extension: VisualMutator.Net. That's because other mutation tools needed Visual Studio 2005 in place or other uber obsolete software / frameworks / so on.
More here: http://visualmutator.github.io/web/
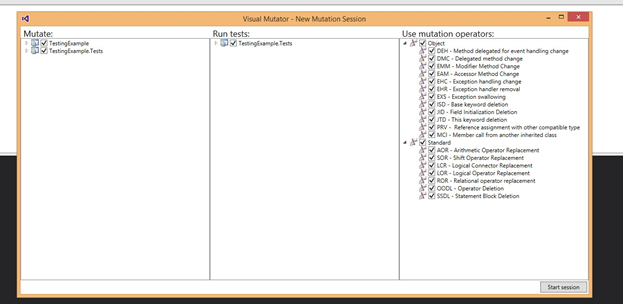
You will basically get a UI like the one below:
![Tests that can be runned]()
TestingExample.Tests will be mutated. Probably you already have your project structured Project & Project.Tests
You have access to the following list of mutans:
ISD (ISK) – Super/Base Keyword Deletion
Operator deletes a call for base class method in overloading method belonging to inheritance method.
DMC – Delegated Method Change
Operator changes a method of processing delegation into another one with similar signature.
DEH – Method Delegated for Event Handling Change
Operator changes a call adding or removing a method from error handling. EAM,
EMM – Accessors, Modifier Method Change
Operators change a call for class property into call for another property of the same type. EHR -
Exception Handler Removal
Operator removes catch block if there exists another catch or finally.
EHC – Exception Handling Change
Operator changes body of a catch block into throwing caught exception.
EXS – Exception Swallowing
Operator adds empty block catch(Exception e) so that no exception can leave current method.
JTI, JTD – This Keyword Insertion, Deletion
Operators add or remove this keyword if there exists local variable with the same name.
JID – Member Variable Initialization Deletion (Field Initialization Deletion) Operator deletes
initialisation of class's field with proper value.
MCI – Member Call from Another Inherited Class
Operator changes calling of a method on object into calling the same method on another object.
PRV - Reference Assignment with Other Compatible Type
Operator changes assigning certain object to references into assigning another compatible object.
Standard Operators:
AOR – Arithmetic Operator Replacement
Operator changes arithmetical operations (+, -, *, /, %) into another one from this group.
LOR – Logical Operator Replacement
Operator changes logical operations (&, |, ˆ) into another one from this group.
LCR – Logical Connector Replacement
Operator changes connector (,||) in logic expression into another one.
ROR – Relational Operator Replacement
Operator changes each relational operator (>, <, <=, >=, ==, !=) into another one from the same group.
SOR – Shift Operator Replacement
Operator changes logical shift (», «) into opposite one.
OODL – Operator Deletion
Operator creates two mutants from each operation such as +,-,>,<=,% etc. In one it removes operation
and what is on its left side, in the other one it removes operation and what is on its right side (e.g. from y=a+b; there will be following mutants : y=a; and y=b;).
SSDL – Statement Block Deletion
Operator removes statements and assignments, but not declarations (e.g. from int y=15; there will be following mutant: int y;).
And results are looking like the following:
Mutation score
![Mutation score]()
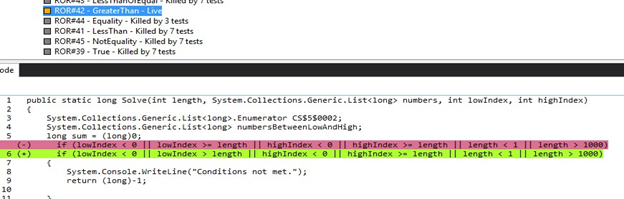
Not killed mutant
![Not killed mutant]()
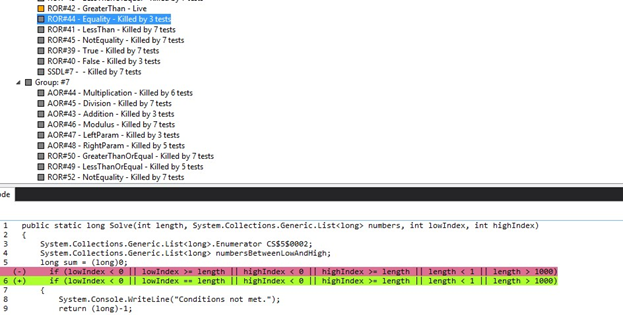
Killed mutant
![Killed mutant]()
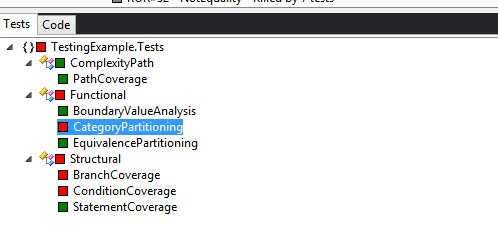
By the following tests
![Killed mutant by the following]()