seaborn.displot is a figure-level plot where the kind parameter specifies the approach. When kind='hist' the parameters for seaborn.histplot are available.
seaborn.axisgrid.FacetGrid.map expects dataframe column names, as such, to map the pdf onto seaborn.displot, the data needs to be in a dataframe.- An issue is that
x_pdf is calculated for each axes:
x0, x1 = p1.axes[0][0].get_xlim()- If the
axes are different for multiple Facets (sharex=False), then there's not a way to get xlim for each axes within .map.
- References:
- Tested in
python 3.8.11, pandas 1.3.2, matplotlib 3.4.2, seaborn 0.11.2
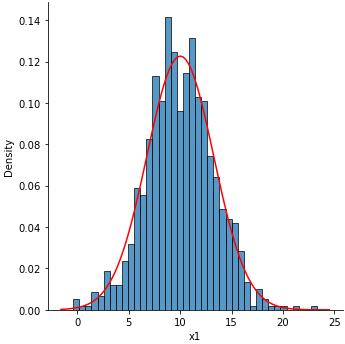
Single Facet
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
import scipy
# data
np.random.seed(365)
x1 = np.random.normal(10, 3.4, size=1000) # mean of 10
df = pd.DataFrame({'x1': x1})
# display(df.head(3))
x1
0 10.570932
1 11.779918
2 12.779077
# function for mapping the pdf
def map_pdf(x, **kwargs):
mu, std = scipy.stats.norm.fit(x)
x0, x1 = p1.axes[0][0].get_xlim() # axes for p1 is required to determine x_pdf
x_pdf = np.linspace(x0, x1, 100)
y_pdf = scipy.stats.norm.pdf(x_pdf, mu, std)
plt.plot(x_pdf, y_pdf, c='r')
p1 = sns.displot(data=df, x='x1', kind='hist', bins=40, stat='density')
p1.map(map_pdf, 'x1')
![enter image description here]()
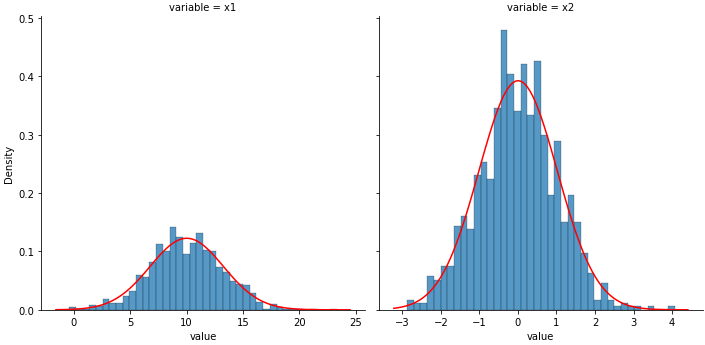
Single or Multiple Facets
- It's easier to iterate through each axes and add the pdf
# data
np.random.seed(365)
x1 = np.random.normal(10, 3.4, size=1000) # mean of 10
x2 = np.random.standard_normal(1000) # mean of 0
df = pd.DataFrame({'x1': x1, 'x2': x2}).melt() # create long dataframe
# display(df.head(3))
variable value
0 x1 10.570932
1 x1 11.779918
2 x1 12.779077
p1 = sns.displot(data=df, x='value', col='variable', kind='hist', bins=40, stat='density', common_bins=False,
common_norm=False, facet_kws={'sharey': True, 'sharex': False})
# extract and flatten the axes from the figure
axes = p1.axes.ravel()
# iterate through each axes
for ax in axes:
# extract the variable name
var = ax.get_title().split(' = ')[1]
# select the data for the variable
data = df[df.variable.eq(var)]
mu, std = scipy.stats.norm.fit(data['value'])
x0, x1 = ax.get_xlim()
x_pdf = np.linspace(x0, x1, 100)
y_pdf = scipy.stats.norm.pdf(x_pdf, mu, std)
ax.plot(x_pdf, y_pdf, c='r')
![enter image description here]()