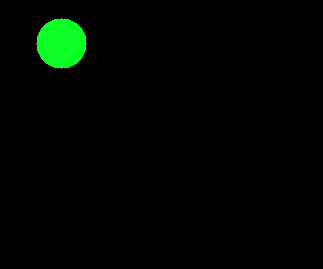
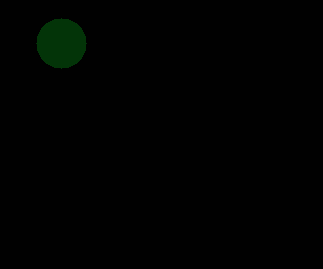
I can draw a line with OpenCV Python but I can't make the line transparent
def draw_from_pitch_to_image(image, reverse_output_points):
for i in range(0, len(reverse_output_points), 2):
x1, y1 = reverse_output_points[i]
x2, y2 = reverse_output_points[i + 1]
x1 = int(x1)
y1 = int(y1)
x2 = int(x2)
y2 = int(y2)
color = [255, 0, 0] if i < 1 else [0, 0, 255]
cv2.line(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
I changed the code but the line is still not transparent. I don't know why, could someone please help me to solve this problem?
def draw_from_pitch_to_image(image, reverse_output_points):
for i in range(0, len(reverse_output_points), 2):
x1, y1 = reverse_output_points[i]
x2, y2 = reverse_output_points[i + 1]
alpha = 0.4 # Transparency factor.
overlay = image.copy()
x1 = int(x1)
y1 = int(y1)
x2 = int(x2)
y2 = int(y2)
color = [255, 0, 0] if i < 1 else [0, 0, 255]
cv2.line(overlay, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
cv2.addWeighted(overlay, alpha, output, 1 - alpha, 0, output)