Now I got the solution of question, I am explaining it one by one.
As I want to translate my model names, model field names, some other texts available in modules and some static/dynamic texts present in my Django template.
Let's assume, I have the models.py and index.html as follows.
models.py
from django.db import models
class Student(models.Model):
first_name = models.CharField(max_length=100, null=True, blank=True, help_text="First name of student", verbose_name="First name")
last_name = models.CharField(max_length=100, null=True, blank=True, help_text="Last name of student" , verbose_name="Last name")
age = models.IntegerField(help_text="Age" , verbose_name="Age")
def __str__(self):
return "Student " + str(self.id) + " - " + self.first_name + " " + self.last_name + created_by_user % (self.userid.username)
class Meta:
verbose_name = "Student"
verbose_name_plural = "Students"
index.html
{% extends "base.html" %}
<h1> HOME PAGE </h1>
<h2> Django is nice </h2>
Now, I need to place translation texts in my modules and templates.
I want my Django application to support Arabic & English.
- Replace the code of
models.py and index.html as follows.
models.py
from django.db import models
from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _
class Student(models.Model):
first_name = models.CharField(max_length=100, null=True, blank=True, help_text = _("First name of student") , verbose_name =_("First name"))
last_name = models.CharField(max_length=100, null=True, blank=True, help_text = _("Last name of student") , verbose_name =_("Last name"))
age = models.IntegerField(help_text = _("Age") , verbose_name =_("Age"))
def __str__(self):
return "Student " + str(self.id) + " - " + self.first_name + " " + self.last_name + created_by_user % (self.userid.username)
class Meta:
verbose_name = _("Student")
verbose_name_plural = _("Students")
index.html
{% extends "base.html" %}
{% load i18n %}
<h1> {% trans "HOME PAGE" %} </h1>
<h2> {% trans "Django is nice" %} </h2>
In settings.py, add the following(In my case I created folder named locale inside BASE_DIR you can choose another location and specify the location in settings.py).
from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _
LOCALE_PATHS = (
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'locale'),
)
LANGUAGES = (
('ar', _('Arabic')),
('en', _('English')),
)
MULTILINGUAL_LANGUAGES = (
"en-us",
"ar-ae",
)
Run the makemessages command from any one of the 2 places based on the requirement as the command looks for the translation texts through all the child directories from which it is run.
a. Project's root directory where manage.py resides.
b. App's root directory where models.py, views.py resides.
django-admin.py makemessages -l ar
Click here to check the language codes
The above command will create a directory named ar inside locale directory with the following folder structure.
.
└── ar
└── LC_MESSAGES
└── django.po
In my case, django.po contains the following lines.
# SOME DESCRIPTIVE TITLE.
# Copyright (C) YEAR THE PACKAGE'S COPYRIGHT HOLDER
# This file is distributed under the same license as the PACKAGE package.
# FIRST AUTHOR <EMAIL@ADDRESS>, YEAR.
#
msgid ""
msgstr ""
"Project-Id-Version: \n"
"Report-Msgid-Bugs-To: \n"
"POT-Creation-Date: 2017-12-24 12:34+0530\n"
"PO-Revision-Date: 2017-12-24 11:56+0400\n"
"MIME-Version: 1.0\n"
"Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8\n"
"Content-Transfer-Encoding: 8bit\n"
"Plural-Forms: nplurals=6; plural=n==0 ? 0 : n==1 ? 1 : n==2 ? 2 : n%100>=3 "
"&& n%100<=10 ? 3 : n%100>=11 && n%100<=99 ? 4 : 5;\n"
"Last-Translator: \n"
"Language-Team: \n"
"X-Generator: Poedit 1.8.11\n"
#: student_activity_reporter_app/models.py:169
msgid "First name of student"
msgstr ""
#: student_activity_reporter_app/models.py:169
msgid "First name"
msgstr ""
#: student_activity_reporter_app/models.py:170
msgid "Last name of student"
msgstr ""
#: student_activity_reporter_app/models.py:170
msgid "Last name"
msgstr ""
#: student_activity_reporter_app/models.py:172
msgid "Age"
msgstr ""
#: student_activity_reporter_app/templates/student_activity_reporter_app/index.html:93
msgid "HOME"
msgstr ""
...
...
Now, fill the value of msgstr as the Arabic translation of the English string denoted by msgid as follows.
# SOME DESCRIPTIVE TITLE.
# Copyright (C) YEAR THE PACKAGE'S COPYRIGHT HOLDER
# This file is distributed under the same license as the PACKAGE package.
# FIRST AUTHOR <EMAIL@ADDRESS>, YEAR.
#
msgid ""
msgstr ""
"Project-Id-Version: \n"
"Report-Msgid-Bugs-To: \n"
"POT-Creation-Date: 2017-12-24 12:34+0530\n"
"PO-Revision-Date: 2017-12-24 11:56+0400\n"
"MIME-Version: 1.0\n"
"Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8\n"
"Content-Transfer-Encoding: 8bit\n"
"Plural-Forms: nplurals=6; plural=n==0 ? 0 : n==1 ? 1 : n==2 ? 2 : n%100>=3 "
"&& n%100<=10 ? 3 : n%100>=11 && n%100<=99 ? 4 : 5;\n"
"Last-Translator: \n"
"Language-Team: \n"
"X-Generator: Poedit 1.8.11\n"
#: student_activity_reporter_app/models.py:169
msgid "First name of student"
msgstr "الاسم الاول للمتهم"
#: student_activity_reporter_app/models.py:169
msgid "First name"
msgstr "الاسم الاول"
#: student_activity_reporter_app/models.py:170
msgid "Last name of student"
msgstr "اسم المتهم الأخير"
#: student_activity_reporter_app/models.py:170
msgid "Last name"
msgstr "اسم الأخير"
#: student_activity_reporter_app/models.py:172
msgid "Age"
msgstr "العمر"
#: student_activity_reporter_app/templates/student_activity_reporter_app/index.html:93
msgid "HOME"
msgstr "الصفحه الرئيسيه"
Now run the compilemessages from the same directory as mentioned above, it will generate django.mo file.
django-admin.py compilemessages
The directory structure of loacle directory will look like this.
.
└── ar
└── LC_MESSAGES
├── django.mo
└── django.po
Start the development server using
python manage.py runserver
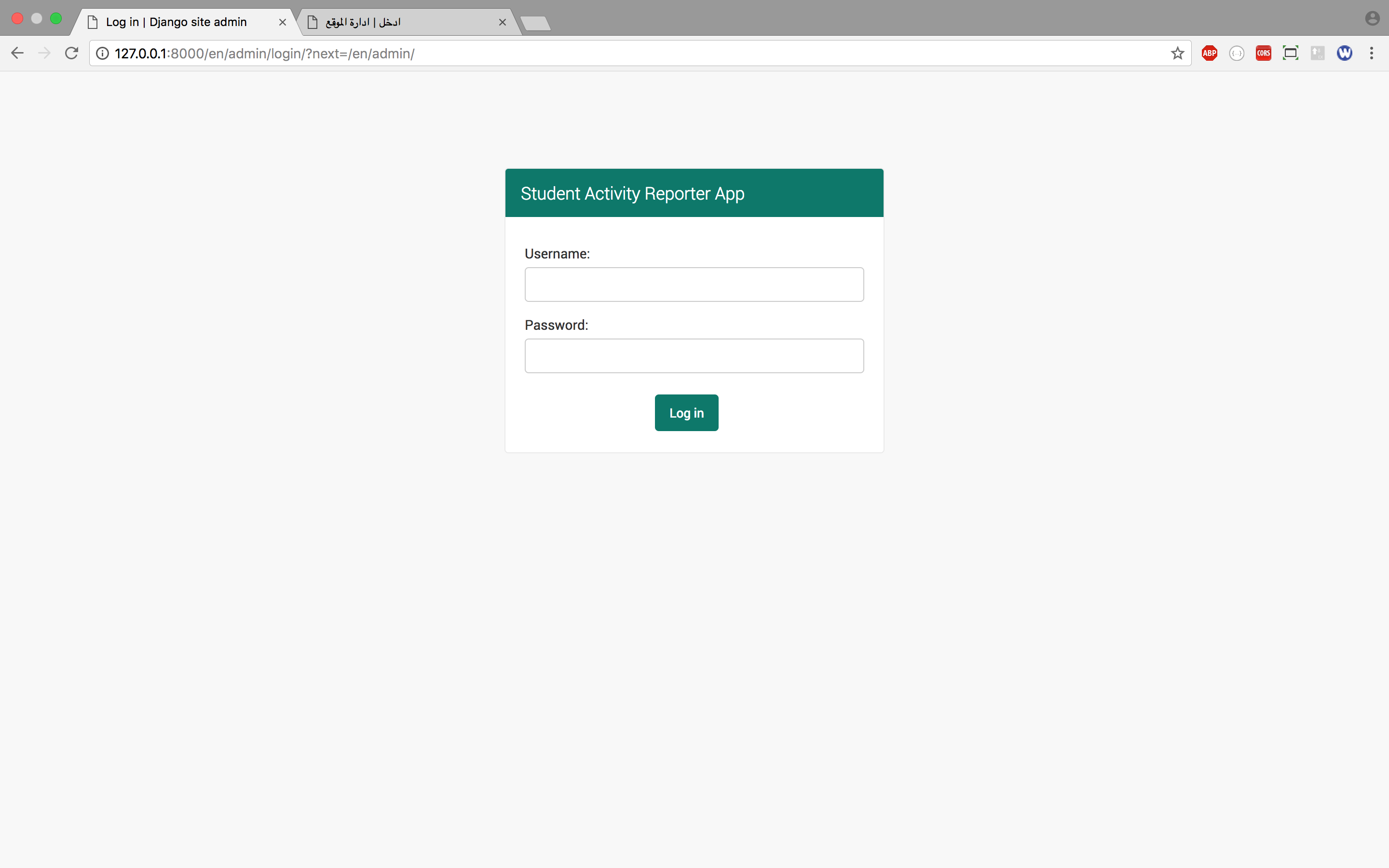
Visit http://127.0.0.1:8000/en/admin/ to view/access the English based Admin site. You will see the login page like below.
![English login page]()
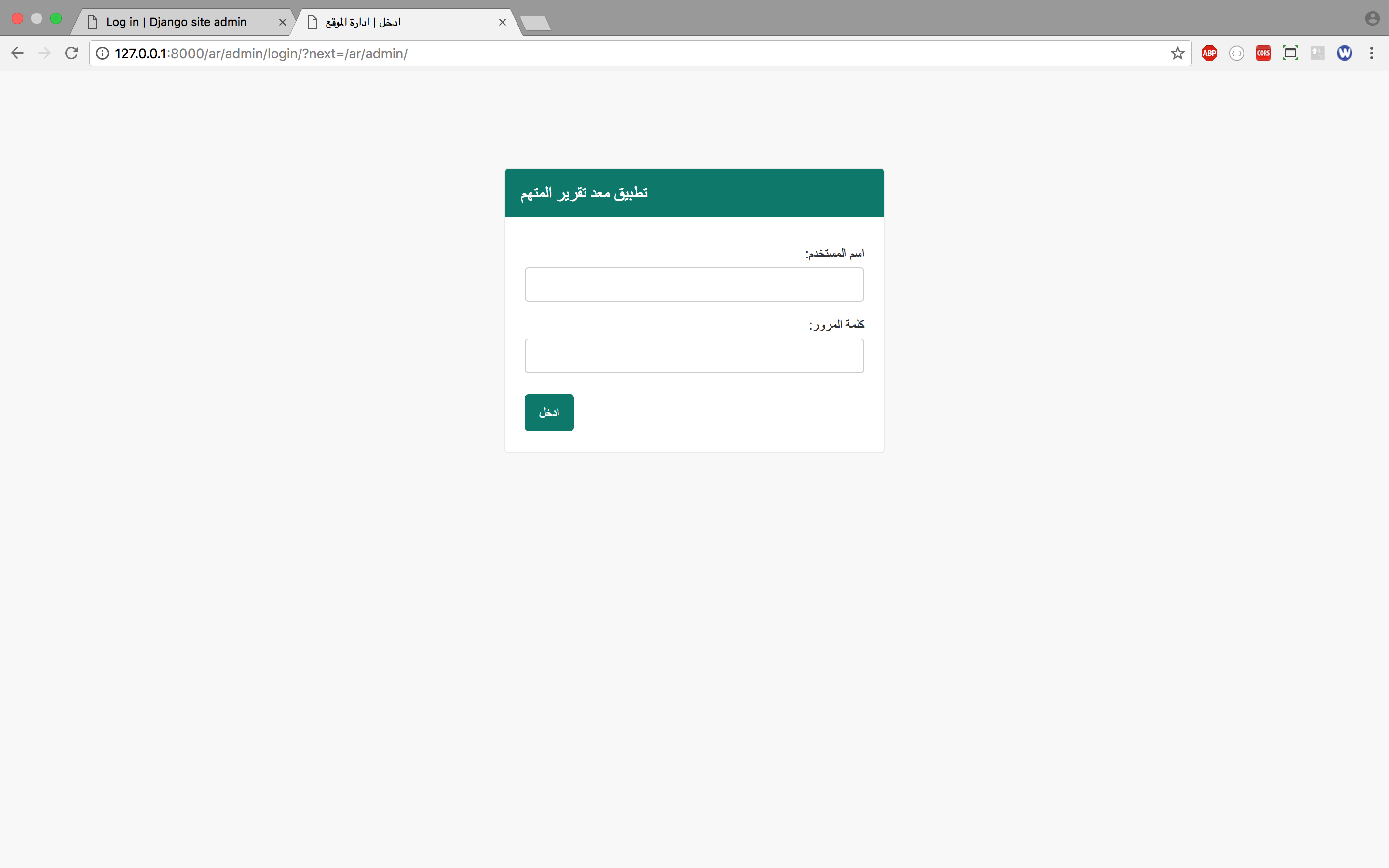
Visit http://127.0.0.1:8000/ar/admin/ to view/access the Arabic based Admin site. Now, you will see the login page like below.
![enter image description here]()
Add as many as translation texts to modules and templates, do proper configurations in settings.py, execute commands from proper place, choose proper language code and enjoy the multilingual support in your Django powered website.
References:
how to use django-admin.py makemessages --all
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/topics/i18n/translation/
Localization: How to Create Language Files