I developed a solution. Using Postman, I sent multipart/form-data containing multiple images, single and nested data.
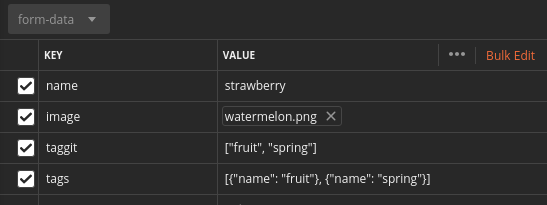
In my model file, I added the Tags model as ManyToManyField to be an example, and also django-taggit. form-data will be like in the picture.
![enter image description here]()
and models.py
class Product(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=20, blank=True)
tags = models.ManyToManyField(Tags)
taggit = TaggableManager(blank=True)
class ProductImage(models.Model):
product = models.ForeignKey(Product, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
image = models.ImageField(upload_to='image_path/', null=True, blank=True)
class Tags(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=15, blank=True)
First things first; the first data was not parsed correctly. As a solution to this and with the help of that answer, I created this custom parser:
class MultipartJsonParser(parsers.MultiPartParser):
def parse(self, stream, media_type=None, parser_context=None):
result = super().parse(
stream,
media_type=media_type,
parser_context=parser_context
)
data = {}
for key, value in result.data.items():
if type(value) != str:
data[key] = value
continue
if '{' in value or "[" in value:
try:
data[key] = json.loads(value)
except ValueError:
data[key] = value
else:
data[key] = value
return parsers.DataAndFiles(data, result.files)
Now we can parse our data with this parser and Django REST built-in JSONParser. Now it's time to build our viewsets.
class ProductViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = Product.objects.all()
serializer_class = ProductSerializer
parser_classes = [MultipartJsonParser, JSONParser]
def get_serializer_context(self):
context = super(ProductViewSet, self).get_serializer_context()
# appending extra data to context
if len(self.request.FILES) > 0:
context.update({
'included_images': self.request.FILES
})
return context
def create(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# Validating images with its own serializer, but not creating.
# The adding process must be through Serializer.
try:
image_serializer = ProductImageSerializer(data=request.FILES)
image_serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True)
except Exception:
raise NotAcceptable(
detail={
'message': 'Upload a valid image. The file you uploaded was either not '
'an image or a corrupted image.'}, code=406)
# the rest of method is about the product serialization(with extra context),
# validation and creation.
serializer = self.get_serializer(data=request.data)
serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True)
self.perform_create(serializer)
headers = self.get_success_headers(serializer.data)
return Response(serializer.data, status=status.HTTP_201_CREATED, headers=headers)
class ProductImageViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = ProductImage.objects.all()
serializer_class = ProductImageSerializer
class TagsViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = Tags.objects.all()
serializer_class = TagsSerializer
Let's examine here. As I mentioned in the comments, the image files will be included in request.FILES. For this reason, I first sent the data to the ProductImageSerializer and validated it. If a validation error occurs, the process will stop and the API will send an error message as a response. Then I sent the data to the ProductSerializer with the picture information I appended to the context in the get_serializer_context method.
We are done with the create method, other details are written on the code.
Finally, serializer.py
from django.forms import ImageField as DjangoImageField
class TagsSerializer(HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Tags
fields = ['url', 'pk', 'name']
class ProductImageSerializer(HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = ProductImage
fields = ['url', 'pk', 'product', 'image']
# attention!!! if you not use this bottom line,
# it will show error like "product required" and
# indirectly our validation at ProductViewSet will raise error.
extra_kwargs = {
'product': {'required': False}
}
# we created Object-level custom validation because validation not working correctly.
# when ProductImageSerializer get single image, everything just fine but
# when it get multiple image, serializer is just passing all the files.
def validate(self, attrs):
default_error_messages = {
'invalid_image':
'Upload a valid image. The file you uploaded was either not an image or a corrupted image.',
}
# in here we're verifying image with using django.forms; Pillow not necessary !!
for i in self.initial_data.getlist('image'):
django_field = DjangoImageField()
django_field.error_messages = default_error_messages
django_field.clean(i)
return attrs
class ProductSerializer(HyperlinkedModelSerializer, TaggitSerializer):
tags = TagsSerializer(allow_null=True, many=True, required=False)
# you can delete this line. If you delete it, it will appear as url in response.
productimage_set = ProductImageSerializer(allow_null=True, many=True, required=False)
taggit = TagListSerializerField(allow_null=True, required=False)
class Meta:
model = Product
fields = ['url', 'pk', 'name', 'tags', 'taggit', 'productimage_set']
def create(self, validated_data):
# create product
try:
product_obj = Product.objects.create(
name=validated_data['name']
)
except Exception:
raise NotAcceptable(detail={'message': 'The request is not acceptable.'}, code=406)
if 'included_images' in self.context: # checking if key is in context
images_data = self.context['included_images']
for i in images_data.getlist('image'):
ProductImage.objects.create(
product=product_obj,
image=i
)
# pop taggit and create
if 'taggit' in validated_data:
taggit_data = validated_data.pop('taggit')
for taggit_data in taggit_data:
taggit_obj, created = Tag.objects.get_or_create(name=taggit_data)
product_obj.taggit.add(taggit_obj)
# pop tags and create
if 'tags' in validated_data:
tags_data = validated_data.pop('tags')
for tags_data in tags_data:
for i in tags_data.items():
tags_obj, created = Tags.objects.get_or_create(name=i[1])
product_obj.tags.add(tags_obj)
return product_obj
So what happened here? Why did we create an extra validation for the image? Although I don't know why, ImageSerializer only makes the right validation for a single file. If you try to upload two files, you can even put a movie next to the picture, validation will not work. To prevent this, we validate the pictures in order using the built-in form of django; Change the format of .mp3 and make it .jpg, try to upload files of high size, none of them will work. The thing that makes the verification is pure django. Other details are in the code.
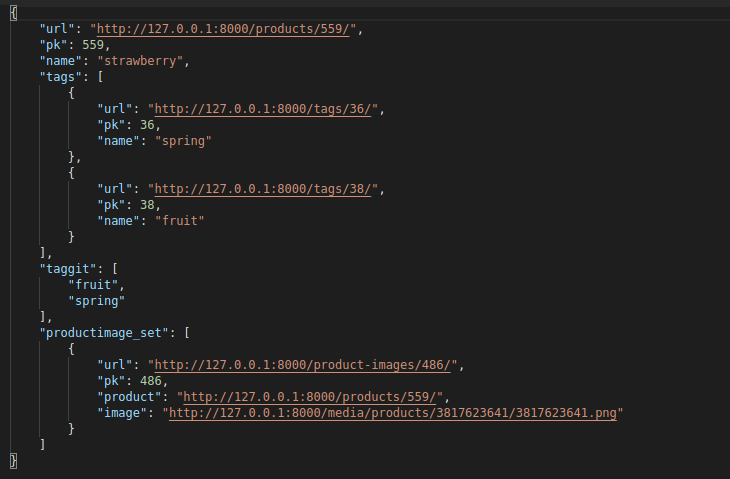
If you do everything as I stated, the response will be like this:
![enter image description here]()
I think this will make most Postman users happy. I hope it helps. If anything catches your attention, let's meet in comments.