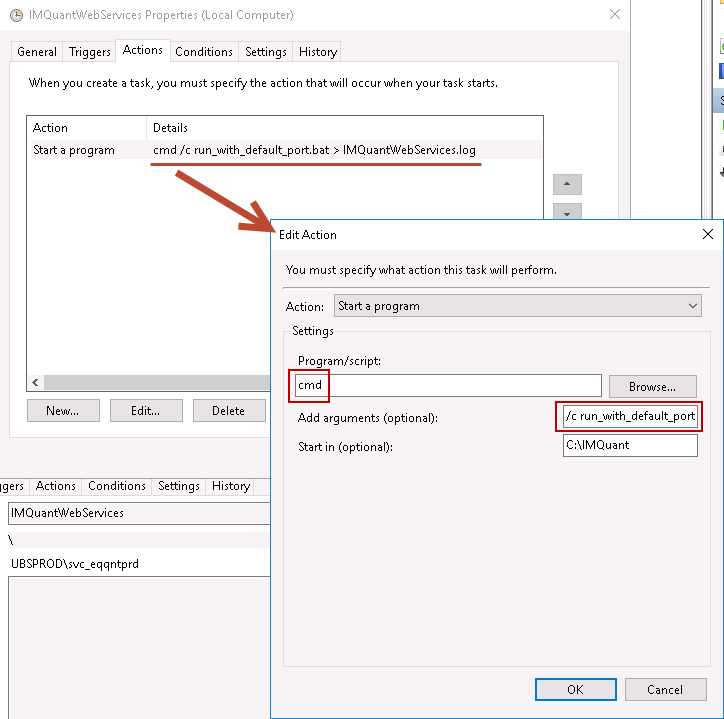
Use the cmd.exe command processor to build a timestamped file name to log your scheduled task's output
To build upon answers by others here, it may be that you want to create an output file that has the date and/or time embedded in the name of the file. You can use the cmd.exe command processor to do this for you.
Note: This technique takes the string output of internal Windows environment variables and slices them up based on character position. Because of this, the exact values supplied in the examples below may not be correct for the region of Windows you use. Also, with some regional settings, some components of the date or time may introduce a space into the constructed file name when their value is less than 10. To mitigate this issue, surround your file name with quotes so that any unintended spaces in the file name won't break the command-line you're constructing. Experiment and find what works best for your situation.
Be aware that PowerShell is more powerful than cmd.exe. One way it is more powerful is that it can deal with different Windows regions. But this answer is about solving this issue using cmd.exe, not PowerShell, so we continue.
Using cmd.exe
You can access different components of the date and time by slicing the internal environment variables %date% and %time%, as follows (again, the exact slicing values are dependent on the region configured in Windows):
- Year (4 digits):
%date:~10,4%
- Month (2 digits):
%date:~4,2%
- Day (2 digits):
%date:~7,2%
- Hour (2 digits):
%time:~0,2%
- Minute (2 digits):
%time:~3,2%
- Second (2 digits):
%time:~6,2%
Suppose you want your log file to be named using this date/time format: "Log_[yyyyMMdd]_[hhmmss].txt". You'd use the following:
Log_%date:~10,4%%date:~4,2%%date:~7,2%_%time:~0,2%%time:~3,2%%time:~6,2%.txt
To test this, run the following command line:
cmd.exe /c echo "Log_%date:~10,4%%date:~4,2%%date:~7,2%_%time:~0,2%%time:~3,2%%time:~6,2%.txt"
Putting it all together, to redirect both stdout and stderr from your script to a log file named with the current date and time, use might use the following as your command line:
cmd /c YourProgram.cmd > "Log_%date:~10,4%%date:~4,2%%date:~7,2%_%time:~0,2%%time:~3,2%%time:~6,2%.txt" 2>&1
Note the use of quotes around the file name to handle instances a date or time component may introduce a space character.
In my case, if the current date/time were 10/05/2017 9:05:34 AM, the above command-line would produce the following:
cmd /c YourProgram.cmd > "Log_20171005_ 90534.txt" 2>&1