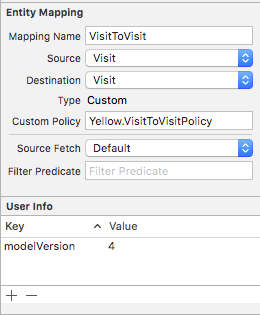
Based on the snippets from the previous answers, here's a more complete example implementation. In order to do this it seems like you need to do a fully manual migration.
Note: I haven't gotten this to work with the @FetchRequest decorator, but it is working with a basic MVVM setup. The part of the migration where I force update to get around WAL issues was causing issues with entities being loaded twice. Running a fetch request directly on a managed object context seems to work fine.
import CoreData
struct DataLayer {
static let shared = DataLayer()
let container: NSPersistentContainer
// The base directory for you app's documents
private var documentsUrl: URL {
let fileManager = FileManager.default
if let url = fileManager.containerURL(forSecurityApplicationGroupIdentifier: "your.group.here") {
return url
} else {
// Falling back to the regular core data location.
let urls = fileManager.urls(for: .documentDirectory, in: .userDomainMask)
return urls.first!
}
}
// The SQLite data store
private var dataStoreUrl: URL {
return documentsUrl.appendingPathComponent("YourDataStoreName")
}
init() {
container = NSPersistentContainer(name: "YourDataStoreName")
migrateIfNeeded()
// Prevent Core Data from trying to automatically migrate
container.persistentStoreDescriptions.first!.url = dataStoreUrl
container.persistentStoreDescriptions.first!.shouldMigrateStoreAutomatically = false
container.persistentStoreDescriptions.first!.shouldInferMappingModelAutomatically = false
// Load the new store just like you normally would
container.loadPersistentStores(completionHandler: { (storeDescription, error) in
if let error = error as NSError? {
print("Core Data failed to load: \(error.localizedDescription)")
}
})
container.viewContext.automaticallyMergesChangesFromParent = true
}
func getItems() -> [Item] {
let fetchRequest = NSFetchRequest<Item>(entityName: "Item")
fetchRequest.sortDescriptors = [NSSortDescriptor(key: "timestamp", ascending: true)]
do {
return try container.viewContext.fetch(fetchRequest)
} catch {
let nsError = error as NSError
print("Unresolved error \(nsError), \(nsError.userInfo)")
}
return []
}
/// Checks if the current data store is up to date and migrates to the newest version if needed
func migrateIfNeeded() {
// The managed object model we might need to migrate to
let finalManagedObjectModel = NSManagedObjectModel(contentsOf: Bundle.main.url(forResource: "Incremental", withExtension: "momd")!)!
// If the app hasn't ever been launched there might not be a data store at all
if !FileManager.default.fileExists(atPath: dataStoreUrl.path) {
print("No store to check")
return
}
// Get metadata from the source data store
guard let sourceMetadata = try? NSPersistentStoreCoordinator.metadataForPersistentStore(type: .sqlite, at: dataStoreUrl) else {
fatalError("Could not find metadata for current data store")
}
// If the current data store is compatable with the desired object model, no need to do anything
let compatible = finalManagedObjectModel.isConfiguration(withName: nil, compatibleWithStoreMetadata: sourceMetadata)
if compatible {
print("compatible - skipping migration")
return
}
// Get the object model of the current data store
let sourceModel = NSManagedObjectModel.mergedModel(from: [Bundle.main], forStoreMetadata: sourceMetadata)!
// Because iOS by default uses WAL to write new data to a SQLite database there's a chance not all data has been written to the
// main SQLite file. The following will force iOS to write all lingering data to the main file before migrating.
do {
var persistentStoreCoordinator: NSPersistentStoreCoordinator? = NSPersistentStoreCoordinator(managedObjectModel: sourceModel)
let options = [NSSQLitePragmasOption: ["journal_mode": "DELETE"]]
let store = try persistentStoreCoordinator!.addPersistentStore(type: .sqlite, at: dataStoreUrl, options: options)
try persistentStoreCoordinator!.remove(store)
persistentStoreCoordinator = nil
} catch let error {
fatalError("\(error)")
}
// Search for a mapping model from the current store version to the target version
// You could also attempt to infer a mapping model here
guard let mappingModel = NSMappingModel(from: [Bundle.main], forSourceModel: sourceModel, destinationModel: finalManagedObjectModel) else {
fatalError("Could not find mapping model")
}
// Fix the migration policies for the current target
mappingModel.entityMappings.forEach {
if let entityMigrationPolicyClassName = $0.entityMigrationPolicyClassName,
let namespace = Bundle.main.infoDictionary?["CFBundleExecutable"] as? String {
$0.entityMigrationPolicyClassName = "\(namespace).\(entityMigrationPolicyClassName)"
}
}
// Set up the migration manager and temporary data store
let migrationManager = NSMigrationManager(sourceModel: sourceModel, destinationModel: finalManagedObjectModel)
let tempDataStoreUrl = documentsUrl.appendingPathComponent("TemporaryIncremental.sqlite")
do {
// Migrate the old data store into the temporary one
try migrationManager.migrateStore(from: dataStoreUrl, type: .sqlite, options: nil, mapping: mappingModel, to: tempDataStoreUrl, type: .sqlite, options: nil)
// Delete the old data store and move the temporary into the original spot
try FileManager.default.removeItem(at: dataStoreUrl)
try FileManager.default.moveItem(at: tempDataStoreUrl, to: dataStoreUrl)
} catch let error {
fatalError("\(error)")
}
}
}