I am implementing a simple user authentication system using react js and node js api. This is what i am doing inside ComponentWillMount method :-
1.checking if the token exits (in localStorage)
2.if it doesn't exits then the value of state 'token' will stay blank
3.if it exists then checking if it's valid using an request to backend.
4.If the token is valid then state 'token' as localstorage.token
5.If the token is invalid then the value of state 'token' will stay blank
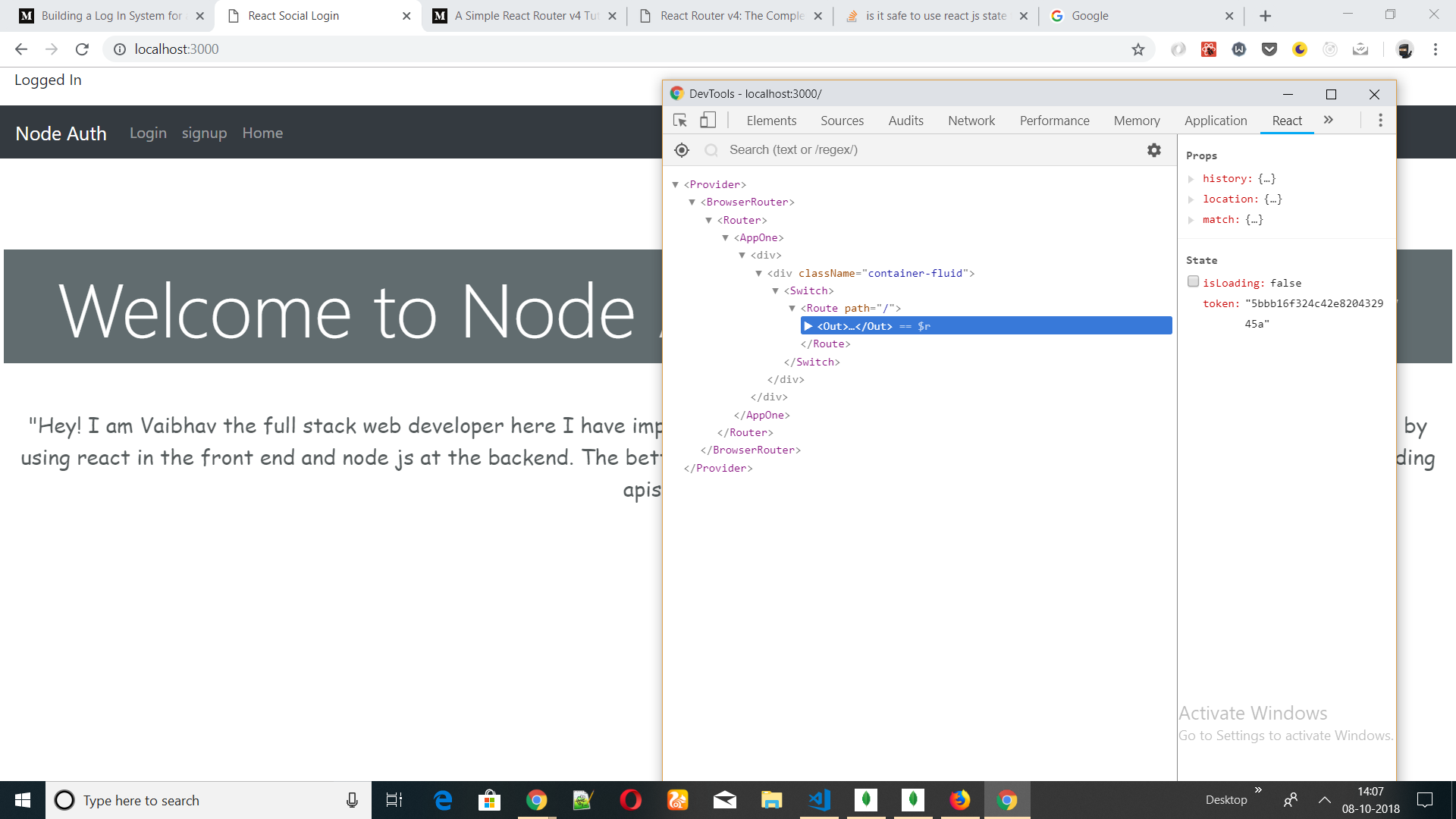
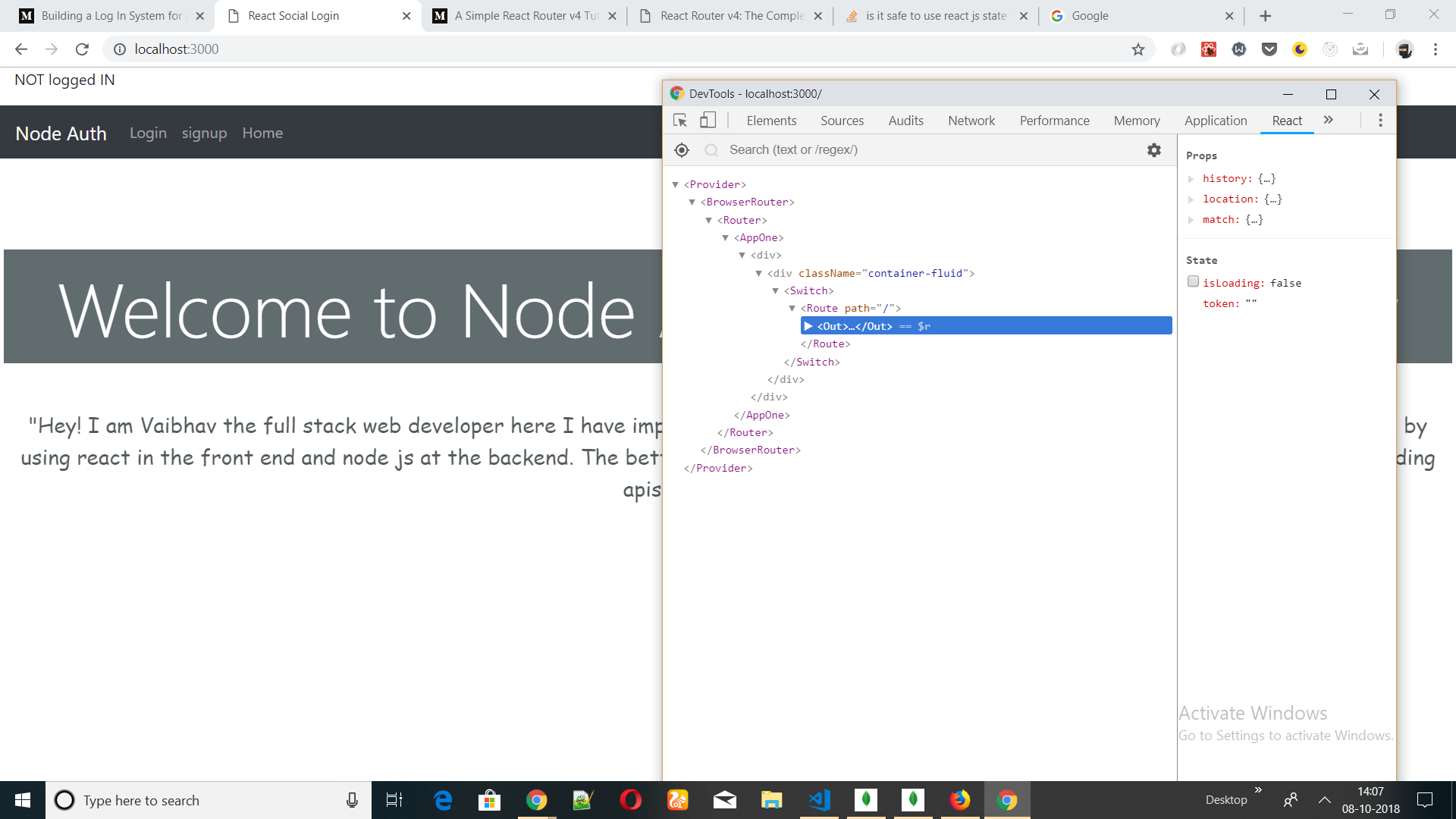
inside render method i have added conditional rendering based on the value of state 'token' i.e. if the state 'token' is blank then normal page will be rendered else it will be redirected to user's page.
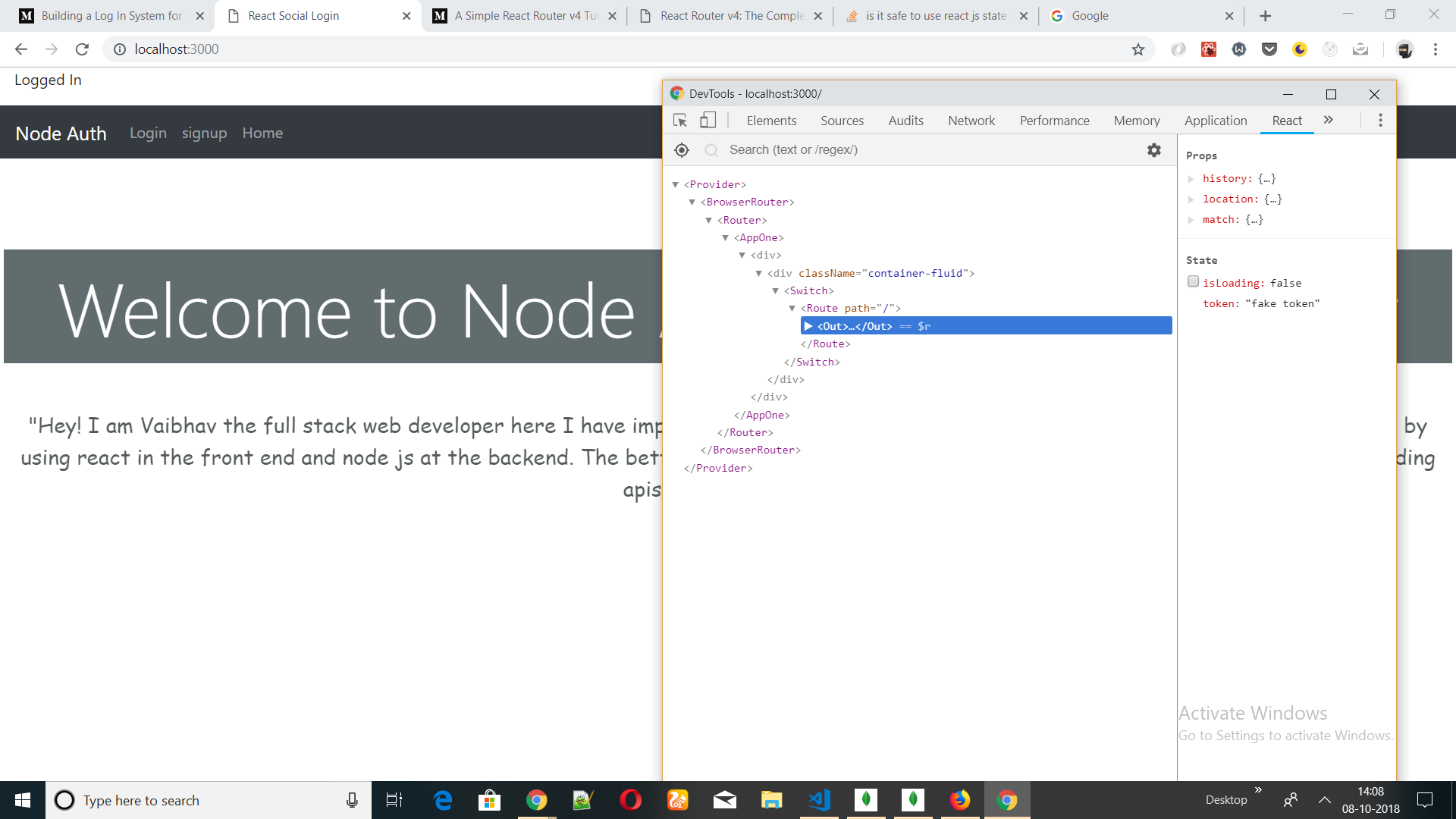
The problem is i can change the value of state 'token' using any react developer tool. And that is causing a loophole to login using a fake token.To avoid that i have to check for the validity of state 'token' everytime it is changed using one of the life cycle methods like componentDidUpdate shouldComponentUpdate . But as mentioned in the official documentation of react
shouldComponentUpdate only exists as a performance optimization. Do not rely on it to “prevent” a rendering, as this can lead to bugs.
Using componentDidUpdate isn't useful as it will be called after component will already be changed due to state change.
Using componentWillUpdate is mentioned as Unsafe in the official documentation
I am not sure how can i tackle this loophole. Here is the code for the component
import React,{Component} from 'react';
import {
BrowserRouter as Router,
Route,
Link,
Switch,
Redirect
} from 'react-router-dom';
import Home from './Home';
import Nav from './Nav';
import Login from './Login';
import Signup from './Signup';
class Out extends Component{
constructor(){
super();
this.state = {
token : '',
isLoading:false
}
this.isLoading = this.isLoading.bind(this);
}
logout(){
alert('logged out');
}
componentWillMount(){
let {match} = this.props;
this.navNoSessionRouteData = [
{to:`${match.url}login`,name:'Login',key:'r1'},
{to:`${match.url}signup`,name:'signup',key:'r2'},
{to:`${match.url}`,name:'Home',key:'r3'}
];
this.navNoSessionButtonData = [];
this.setState({
isLoading:true
});
const tokenVar = localStorage.getItem('token');
if(tokenVar == null){
console.log('not logged in');
this.setState({
isLoading:false
});
}else{
fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/account/verify?token='+tokenVar)
.then(res=>res.json())
.then(json=>{
if(json.success){
console.log('logged in');
this.setState({
token : tokenVar,
isLoading:false
});
}else{
this.setState({
isLoading:false,
});
}
});
}
}
isLoading(){
let {isLoading,token} = this.state;
if(isLoading === true){
return (
<p>Loading...</p>
);
}
else{
let {match} = this.props
console.log(token);
return(
<div>
{
(token)?<p>Logged In</p>:(<p>NOT logged IN</p>)
}
<div className = "row">
<Nav navRouteData = {this.navNoSessionRouteData} navButtonData = {this.navNoSessionButtonData}/>
</div>
<div className="row justify-content-center">
<Switch>
<Route exact = {true} path={`${match.path}`} component={Home} />
<Route path={`${match.path}login`} component={Login}/>
<Route path={`${match.path}signup`} component={Signup}/>
</Switch>
</div>
</div>
)
}
}
render(){
return(
<div>
{this.isLoading()}
</div>
)
}
}
export default Out;

/api/account/verify?token='+tokenVar. But I would require each sensitive api request to include a token from the user. If the token is invalid tell them so and give them a redirect to a login page where the token can be persisted locally. – Lockard