The EKS documentation says something about this.
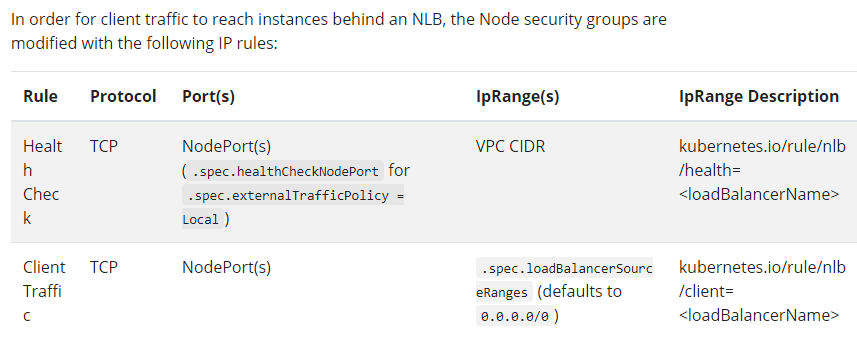
For each NLB that you create Amazon EKS adds one inbound rule to the
node's security group for client traffic and one rule for each load
balancer subnet in the VPC for health checks. Deployment of a service
of type LoadBalancer can fail if Amazon EKS attempts to create rules
that exceed the quota for the maximum number of rules allowed for a
security group. For more information, see Security groups in Amazon
VPC quotas in the Amazon VPC User Guide. Consider the following
options to minimize the chances of exceeding the maximum number of
rules for a security group.
Request an increase in your rules per security group quota. For more
information, see Requesting a quota increase in the Service Quotas
User Guide.
Use Create a network load balancer, rather than instance targets. With
IP targets, rules can potentially be shared for the same target ports.
Load balancer subnets can be manually specified with an annotation.
For more information, see Annotations on GitHub.
Use an Ingress, instead of a Service of type LoadBalancer to send
traffic to your service. The AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB)
requires fewer rules than NLBs. An ALB can also be shared across
multiple Ingresses. For more information, see Application load
balancing on Amazon EKS.
Deploy your clusters to multiple accounts.
If none of those options work for you, and you have also ALBs, you can minimize the rules for those ALB forcing them to use a specific security group instead of adding their rules to the node's security group. The annotation is service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-security-groups. Doing so, you replace several rules for just one, leaving more space for NLBs rules.