I'm trying to find the best possible combination that will maximize my sum value, but it has to be under 2 specific constraints, therefore I am assuming Linear programming will be the best fit.
The problem goes like this: Some educational world-event wish to gather the world's smartest teen students. Every state tested 100K students on the following exams:'MATH', 'ENGLISH', 'COMPUTERS', 'HISTORY','PHYSICS'.. and where graded 0-100 on EACH exam.
Every state was requested to send their best 10K from the tested 100K students for the event.
You, as the French representative, were requested to choose the top 10K students from the tested 100K student from your country. For that, you'll need to optimize the MAX VALUE from them in order to get the best possible TOTAL SCORE.
BUT there are 2 main constrains:
1- from the total 10K chosen students you need to allocate specific students that will be tested on the event on 1 specific subject only from the mentioned 5 subjects. the allocation needed is: ['MATH': 4000, 'ENGLISH':3000,'COMPUTERS':2000, 'HISTORY':750,'PHYSICS':250]
2- Each 'exam subject' score will have to be weighted differently.. for exp: 97 is Math worth more than 97 in History. the wheights are: ['MATH': 1.9, 'ENGLISH':1.7,'COMPUTERS':1.5, 'HISTORY':1.3,'PHYSICS':1.1]
MY SOLUTION: I tried to use the PULP (python) as an LP library and solved it correctly, but it took more than 2 HOURS of running. can you find a better (faster, simpler..) way to solve it? there are some NUMPY LP functions that could be used instead, maybe will be faster? it supposed to be a simple OPTIMIZATION problem be I made it too slow and complexed. --The solution needs to be in Python only please
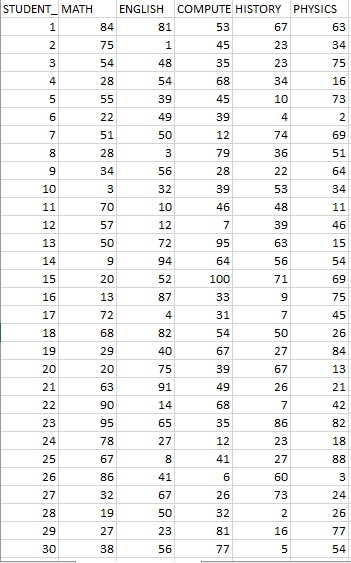
for example, let's look on a small scale at the same problem: there are 30 students and you need to choose only 15 students that will give us the best combination in relation to the following subject allocation demand. the allocation needed is- ['MATH': 5, 'ENGLISH':4,'COMPUTERS':3, 'HISTORY':2,'PHYSICS':1]
this is all the 30 students and their grades:
after running the algorithm, the output solution will be:
here is my full code for the ORIGINAL question (100K students):
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import pulp as p
import time
t0=time.time()
demand = [4000, 3000, 2000, 750,250]
weight = [1.9,1.7, 1.5, 1.3, 1.1]
original_data= pd.read_csv('GRADE_100K.csv') #created simple csv file with random scores
data_c=original_data.copy()
data_c.index = np.arange(1, len(data_c)+1)
data_c.columns
data_c=data_c[['STUDENT_ID', 'MATH', 'ENGLISH', 'COMPUTERS', 'HISTORY','PHYSICS']]
#DataFrame Shape
m=data_c.shape[1]
n=data_c.shape[0]
data=[]
sublist=[]
for j in range(0,n):
for i in range(1,m):
sublist.append(data_c.iloc[j,i])
data.append(sublist)
sublist=[]
def _get_num_students(data):
return len(data)
def _get_num_subjects(data):
return len(data[0])
def _get_weighted_data(data, weight):
return [
[a*b for a, b in zip(row, weight)]
for row in data
]
data = _get_weighted_data(data, weight)
num_students = _get_num_students(data)
num_subjects = _get_num_subjects(data)
# Create a LP Minimization problem
Lp_prob = p.LpProblem('Problem', p.LpMaximize)
# Create problem Variables
variables_matrix = [[0 for i in range(num_subjects)] for j in range(num_students)]
for i in range(0, num_students):
for j in range(0, num_subjects):
variables_matrix[i][j] = p.LpVariable(f"X({i+1},{j+1})", 0, 1, cat='Integer')
df_d=pd.DataFrame(data=data)
df_v=pd.DataFrame(data=variables_matrix)
ml=df_d.mul(df_v)
ml['coeff'] = ml.sum(axis=1)
coefficients=ml['coeff'].tolist()
# DEALING WITH TARGET FUNCTION VALUE
suming=0
k=0
sumsum=[]
for z in range(len(coefficients)):
suming +=coefficients[z]
if z % 2000==0:
sumsum.append(suming)
suming=0
if z<2000:
sumsum.append(suming)
sumsuming=0
for s in range(len(sumsum)):
sumsuming=sumsuming+sumsum[s]
Lp_prob += sumsuming
# DEALING WITH the 2 CONSTRAINS
# 1-subject constraints
con1_suming=0
for e in range(num_subjects):
L=df_v.iloc[:,e].to_list()
for t in range(len(L)):
con1_suming +=L[t]
Lp_prob += con1_suming <= demand[e]
con1_suming=0
# 2- students constraints
con2_suming=0
for e in range(num_students):
L=df_v.iloc[e,:].to_list()
for t in range(len(L)):
con2_suming +=L[t]
Lp_prob += con2_suming <= 1
con2_suming=0
print("time taken for TARGET+CONSTRAINS %8.8f seconds" % (time.time()-t0) )
t1=time.time()
status = Lp_prob.solve() # Solver
print("time taken for SOLVER %8.8f seconds" % (time.time()-t1) ) # 632 SECONDS
print(p.LpStatus[status]) # The solution status
print(p.value(Lp_prob.objective))
df_v=pd.DataFrame(data=variables_matrix)
# Printing the final solution
lst=[]
val=[]
for i in range(0, num_students):
lst.append([p.value(variables_matrix[i][j]) for j in range(0, num_subjects)])
val.append([sum([p.value(variables_matrix[i][j]) for j in range(0, num_subjects)]),i])
ones_places=[]
for i in range (0, len(val)):
if val[i][0]==1:
ones_places.append(i+1)
len(ones_places)
data_once=data_c[data_c['STUDENT_ID'].isin(ones_places)]
IDs=[]
for i in range(len(ones_places)):
IDs.append(data_once['STUDENT_ID'].to_list()[i])
course=[]
sub_course=[]
for i in range(len(lst)):
j=0
sub_course='x'
while j<len(lst[i]):
if lst[i][j]==1:
sub_course=j
j=j+1
course.append(sub_course)
coures_ones=[]
for i in range(len(course)):
if course[i]!= 'x':
coures_ones.append(course[i])
# adding the COURSE name to the final table
# NUMBER OF DICTIONARY KEYS based on number of COURSES
col=original_data.columns.values[1:].tolist()
dic = {0:col[0], 1:col[1], 2:col[2], 3:col[3], 4:col[4]}
cc_name=[dic.get(n, n) for n in coures_ones]
one_c=[]
if len(IDs)==len(cc_name):
for i in range(len(IDs)):
one_c.append([IDs[i],cc_name[i]])
prob=[]
if len(IDs)==len(cc_name):
for i in range(len(IDs)):
prob.append([IDs[i],cc_name[i], data_once.iloc[i][one_c[i][1]]])
scoring_table = pd.DataFrame(prob,columns=['STUDENT_ID','COURES','SCORE'])
scoring_table.sort_values(by=['COURES', 'SCORE'], ascending=[False, False], inplace=True)
scoring_table.index = np.arange(1, len(scoring_table)+1)
print(scoring_table)


sumas summary function) and step 2 : create the best possible groups [4k, 3k, 2k, 1k, 0.5k] (warning here they are duplicates) to maximise the score at each weighted exam for your country ? – Primrose