In practice, you'll want to store the board state in base-4 packed in unsigned longs, with each board row padded to an integral number of unsigned longs. This will give you the best memory locality, very fast access to board cells, but uses 26.2% more RAM than ternary packing.
To store the board state in a binary file, you can pack 5 ternary digits (five board cell states) into each 8-bit byte. This uses only 5.1% more memory than ternary packing, and is simple and robust to implement. In particular, this way you do not need to worry about byte order (endianness).
The problem with pure ternary packing is that each base-3 digit affects most of the binary digits representing the same numerical value. For example, 38 = 300000003 = 6561 = 11001101000012. This means that the only practical way to extract base-3 digits is via repeated division and modulus (by 3).
To describe a board of size N×M, the ternary packing and unpacking function will be essentially O(N2M2), and therefore slower and slower as the board size increases. You'll likely get better savings by using a compression library (say, liblzma) using less CPU time. For many board configurations, run-length encoding might also work well.
Here is an example implementation for boards of up to 16777215×16777215 cells (tested only up to 32768×32768 cells):
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <inttypes.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#define ULONG_BITS (CHAR_BIT * sizeof (unsigned long))
#define ULONG_CELLS (CHAR_BIT * sizeof (unsigned long) / 2)
struct board {
int rows;
int cols;
size_t stride;
unsigned long *data;
};
enum {
EMPTY = 0, /* calloc() clears the data to zeroes */
WHITE = 1,
BLACK = 2,
ERROR = 3
};
int board_init(struct board *const b, const int rows, const int cols)
{
const size_t stride = (cols + ULONG_CELLS - 1) / ULONG_CELLS;
const size_t ulongs = stride * (size_t)rows;
if (b) {
b->rows = 0;
b->cols = 0;
b->stride = 0;
b->data = NULL;
}
if (!b || rows < 1 || cols < 1)
return -1;
if ((size_t)(ulongs / stride) != (size_t)rows)
return -1;
b->data = calloc(ulongs, sizeof b->data[0]);
if (!b->data)
return -1;
b->rows = rows;
b->cols = cols;
b->stride = stride;
return 0;
}
static inline int get_cell(const struct board *const b, const int row, const int col)
{
if (!b || row < 0 || col < 0 || row >= b->rows || col >= b->cols)
return EMPTY;
else {
const size_t i = (size_t)col / ULONG_CELLS;
const size_t c = ((size_t)col % ULONG_CELLS) * 2;
const unsigned long w = b->data[b->stride * row + i];
return (w >> c) & 3;
}
}
static inline int set_cell(struct board *const b, const int row, const int col, const int value)
{
if (!b || row < 0 || col < 0 || row >= b->rows || col >= b->cols)
return EMPTY;
else {
const size_t i = (size_t)col / ULONG_CELLS;
const size_t c = ((size_t)col % ULONG_CELLS) * 2;
unsigned long *w = b->data + b->stride * row + i;
*w = ((*w) & (3uL << c)) | ((unsigned long)(value & 3) << c);
return value & 3;
}
}
static inline int write_u24(FILE *const out, const int value)
{
unsigned int u = value;
if (!out || value < 0 || value > 16777215 || ferror(out))
return -1;
if (fputc(u & 255, out) == EOF)
return -1;
else
u >>= 8;
if (fputc(u & 255, out) == EOF)
return -1;
else
u >>= 8;
if (fputc(u & 255, out) == EOF)
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
static inline int read_u24(FILE *const in, unsigned int *const to)
{
unsigned int result;
int c;
if (!in || ferror(in))
return -1;
c = fgetc(in);
if (c == EOF)
return -1;
else
result = c & 255;
c = fgetc(in);
if (c == EOF)
return -1;
else
result |= (c & 255) << 8;
c = fgetc(in);
if (c == EOF)
return -1;
else
result |= (c & 255) << 16;
if (to)
*to = result;
return 0;
}
int board_save(const struct board *const b, FILE *const out)
{
int row, col, cache, coeff;
if (!b || !out || ferror(out) || !b->stride ||
b->rows < 1 || b->rows > 16777215 ||
b->cols < 1 || b->cols > 16777215)
return -1;
if (write_u24(out, b->rows))
return -1;
if (write_u24(out, b->cols))
return -1;
/* Clear byte cache. */
cache = 0;
coeff = 1;
for (row = 0; row < b->rows; row++) {
for (col = 0; col < b->cols; col++) {
switch (get_cell(b, row, col)) {
case EMPTY: /* Saved as 0 */
break;
case WHITE: /* Saved as 1 */
cache += coeff;
break;
case BLACK: /* Saved as 2 */
cache += coeff + coeff;
break;
default: /* Invalid cell state. */
return -1;
}
if (coeff >= 81) {
if (fputc(cache, out) == EOF)
return -1;
cache = 0;
coeff = 1;
} else
coeff *= 3;
}
}
if (coeff > 1)
if (fputc(cache, out) == EOF)
return -1;
if (fflush(out))
return -1;
return 0;
}
int board_load(struct board *const b, FILE *in)
{
unsigned int rows, cols, row, col, cache, count;
int c;
if (b) {
b->rows = 0;
b->cols = 0;
b->stride = 0;
b->data = NULL;
}
if (!b || !in || ferror(in))
return -1;
if (read_u24(in, &rows) || rows < 1 || rows > 16777215)
return -1;
if (read_u24(in, &cols) || cols < 1 || cols > 16777215)
return -1;
if (board_init(b, rows, cols))
return -1;
/* Nothing cached at this point. */
cache = 0;
count = 0;
for (row = 0; row < rows; row++) {
for (col = 0; col < cols; col++) {
if (count < 1) {
c = fgetc(in);
if (c == EOF || c < 0 || c >= 243)
return -1;
cache = c;
count = 5;
}
switch (cache % 3) {
case 0: /* Leave as background. */
break;
case 1: /* White */
if (set_cell(b, row, col, WHITE) != WHITE)
return -1;
break;
case 2: /* Black */
if (set_cell(b, row, col, BLACK) != BLACK)
return -1;
break;
}
cache /= 3;
count--;
}
}
/* No errors. */
return 0;
}
/* Xorshift 64* pseudo-random number generator. */
static uint64_t prng_state = 1;
static inline uint64_t prng_randomize(void)
{
int rounds = 1024;
uint64_t state;
state = (uint64_t)time(NULL);
while (rounds-->0) {
state ^= state >> 12;
state ^= state << 25;
state ^= state >> 27;
}
if (!state)
state = 1;
prng_state = state;
return state;
}
static inline uint64_t prng_u64(void)
{
uint64_t state = prng_state;
state ^= state >> 12;
state ^= state << 25;
state ^= state >> 27;
prng_state = state;
return state * UINT64_C(2685821657736338717);
}
/* Uniform random ternary generator. */
static uint64_t ternary_cache = 0;
static int ternary_bits = 0;
static inline int prng_ternary(void)
{
int retval;
do {
if (ternary_bits < 2) {
ternary_cache = prng_u64();
ternary_bits = 64;
}
retval = ternary_cache & 3;
ternary_cache >>= 1;
ternary_bits -= 2;
} while (retval > 2);
return retval;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct board original, reloaded;
uint64_t correct, incorrect, count[3];
double percent;
FILE *file;
int rows, cols, row, col;
char dummy;
if (argc != 4) {
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s [ -h | --help ]\n", argv[0]);
fprintf(stderr, " %s FILENAME ROWS COLUMNS\n", argv[0]);
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This program generates a random ternary board,\n");
fprintf(stderr, "saves it to file FILENAME, reads it back, and\n");
fprintf(stderr, "verifies that the board state is intact.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
if (!argv[1][0]) {
fprintf(stderr, "No filename specified.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (sscanf(argv[2], "%d %c", &rows, &dummy) != 1 || rows < 1 || rows > 16777215) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: Invalid number of rows.\n", argv[2]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (sscanf(argv[3], "%d %c", &cols, &dummy) != 1 || cols < 1 || cols > 16777215) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: Invalid number of columns.\n", argv[2]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (board_init(&original, rows, cols)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot create a board with %d rows and %d columns.\n", rows, cols);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
fprintf(stderr, "Filling board with a random state; random seed is %" PRIu64 ".\n", prng_randomize());
percent = 100.0 / (double)rows / (double)cols;
count[0] = count[1] = count[2] = 0;
for (row = 0; row < rows; row++)
for (col = 0; col < cols; col++) {
int t = prng_ternary();
if (t < 0 || t > 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "prng_ternary() returned %d!\n", t);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
count[t]++;
set_cell(&original, row, col, t);
}
fprintf(stderr, " Empty: %" PRIu64 " cells, %.3f%%.\n", count[EMPTY], (double)count[EMPTY] * percent);
fprintf(stderr, " White: %" PRIu64 " cells, %.3f%%.\n", count[WHITE], (double)count[WHITE] * percent);
fprintf(stderr, " Black: %" PRIu64 " cells, %.3f%%.\n", count[BLACK], (double)count[BLACK] * percent);
file = fopen(argv[1], "wb");
if (!file) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: Cannot open file for writing.\n", argv[1]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
fprintf(stderr, "Saving to %s.\n", argv[1]);
if (board_save(&original, file)) {
fclose(file);
fprintf(stderr, "Write error.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (fclose(file)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Write error.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
fprintf(stderr, "Reloading game board.\n");
file = fopen(argv[1], "rb");
if (!file) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: Cannot open file for reading.\n", argv[1]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (board_load(&reloaded, file)) {
fclose(file);
fprintf(stderr, "Read error.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (fclose(file)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Read error.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (original.rows != reloaded.rows) {
fprintf(stderr, "Row count mismatches.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
} else
if (original.cols != reloaded.cols) {
fprintf(stderr, "Column count mismatches.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
fprintf(stderr, "Comparing board states.\n");
correct = 0;
incorrect = 0;
for (row = 0; row < rows; row++)
for (col = 0; col < cols; col++)
if (get_cell(&original, row, col) == get_cell(&reloaded, row, col))
correct++;
else
incorrect++;
if (incorrect) {
fprintf(stderr, "Found %" PRIu64 " mismatching cells (%.3f%%).\n", incorrect, (double)incorrect * percent);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (correct != (uint64_t)((uint64_t)rows * (uint64_t)cols)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Internal bug in the board comparison double loop.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
fprintf(stderr, "Verification successful; functions work as expected for a board with %d rows and %d columns.\n", rows, cols);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
The board_init() function initializes a board, board_save() saves a board state to a stream, including the board size, in portable binary format (each file will generate the same board on both big-endian and little-endian architectures), and board_load() will load a previously saved board from a stream. They all return 0 if success, nonzero if error.
The get_cell() and set_cell() functions are static inline accessor functions to examine and set the state of individual cells in a board.
As I initially suggested, this one uses 2 bits per cell in RAM (4 cells per byte), and 5 cells per byte when stored to a file.
The example program takes three command-line parameters: a file name, the number of rows, and the number of columns. It will generate a random state of that size, save it to the named file, read it back from the named file into a separate board, and finally compare the board states, to verify if the implemented functions seem to work correctly.

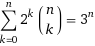
exp(), any small difference matters :-) – Scamperinput = (w, b)(wherewandbare what? 32/64 bit integers representing each colour's exclusive board?) andoutput =[no idea what you are expecting here] Or did you want a different way entirely to represent (w, b) in the first place? I'm really confused, and I've designed and prgrammed a bitboard engine for a Chess game before...:) – Raptureinput = (w, b), two bitboards for white and black.output = t, a tritboard. Example in my question isinput = (0b1010001, 0b0100100),output = 0t1210201(0tfor ternary). Do you see how output is directly derived from input? (It just has 2 at the positions of black pieces, and 1 at the positions of white.) Input and output are both integers, but input encodes board in base 2 and output in base 3. If you convert all of that to base 10, you getinput = (81, 36),output = 1315. Ideally, I would love to know a faster way to do this conversion than the baseline below. – Axletree