I've read these SO posts 1, 2, 3 which faced a similar problem. I'm trying to use a .klib in my KMM Android project. The Klib is built from library.h C header. Here's what I did:
I built the Kotlin Library
Using the following Gradle block in the KMM shared project:
kotlin {
...
androidNativeArm64 { // target
compilations.getByName("main") {
val mylib by cinterops.creating {
defFile(project.file("mylib.def"))
packageName("c.mylib")
// Options to be passed to compiler by cinterop tool.
compilerOpts("-I/home/me/CLionProjects/mylib/")
// Directories for header search (an analogue of the -I<path> compiler option).
includeDirs.allHeaders("/home/me/CLionProjects/mylib/")
// A shortcut for includeDirs.allHeaders.
includeDirs("/home/me/CLionProjects/mylib/")
}
}
binaries {
sharedLib() // https://kotlinlang.org/docs/mpp-build-native-binaries.html#declare-binaries
}
}
}
with mylib.def file
headers = /home/me/CLionProjects/mylib/library.h
headerFilter = /home/me/CLionProjects/mylib/*
package = c.mylib
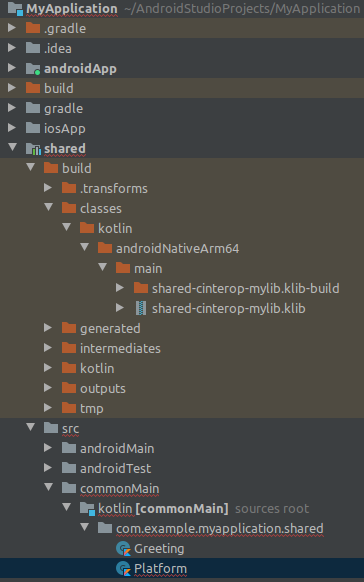
On building, the .klib and build folder appears in the classes directory of the shared project as shown below:
The red line under Platform is for the error:
Expected class 'Platform' has no actual declaration in module MyApplication.shared.androidNativeArm64Main for Native
but apparently that may just be a system glitch (not sure - the Alt+Enter solution to "create actual class..." doesn't seem to do anything). Assuming this is not a problem I continue...
I check the .klib details
Running .konan/.../bin/klib info mylib.klib I don't get c.mylib as the package name but com.example.myapplication:shared-cinterop-mylib instead (see below). I can live with that (although not sure why it isn't what I specified in Gradle)
Resolved to: /home/me/AndroidStudioProjects/MyApplication/shared/build/classes/kotlin/androidNativeArm64/main/shared-cinterop-mylib
Module name: <com.example.myapplication:shared-cinterop-mylib>
ABI version: 1.4.1
Compiler version: 1.4.10
Library version: null
Metadata version: 1.4.0
IR version: 1.0.0
Available targets: android_arm64
I tried including the package in my androidApp Gradle
I want to access the .klib inside my androidApp project. I tried both packages c.mylib and com.example.myapplication:shared-cinterop-mylib.
I tried adding implementation("com.example.myapplication:shared-cinterop-mylib") to my androidApp Gradle file, but got the error:
Could not determine the dependencies of task ':androidApp:lintVitalRelease'. Could not resolve all artifacts for configuration ':androidApp:debugCompileClasspath'. Could not find com.example.myapplication:shared-cinterop-mylib:. Required by: project :androidApp Possible solution:
- Declare repository providing the artifact, see the documentation at https://docs.gradle.org/current/userguide/declaring_repositories.html
I'm not sure if the hint would solve the problem, but I tried adding the file to the androidApp Gradle repositories { ... } block anyway using e.g.
maven {
url = uri("/home/me/AndroidStudioProjects/MyApplication/shared/build/classes/kotlin/androidNativeArm64/main/shared-cinterop-mylib.klib")
}
but I'm not sure that's the right way to add a file to a repository.
Question
Can anyone help me to get the package recognised in androidApp ? I'll keep trying.