I've been developing a game using SpriteKit and Swift but I seem to be having trouble determining what the real differences are between the GameViewController and any one of my SKScenes. I'm trying to understand the differences because I want to implement a GameCenter or local leaderboard into my game but in all the tutorials I find (like this one:Game Center Leaderboards! (Swift 2 in Xcode) ) they have all the logic in GameViewController as they are working with single view apps. I'm having trouble understanding the relation when I read the docs, so any help would be great. Ultimately, I want to be able to display and push data to and from GameCenter in one of my scenes such as GameOverScene. Thanks for any help!
Here is some good info to start with:
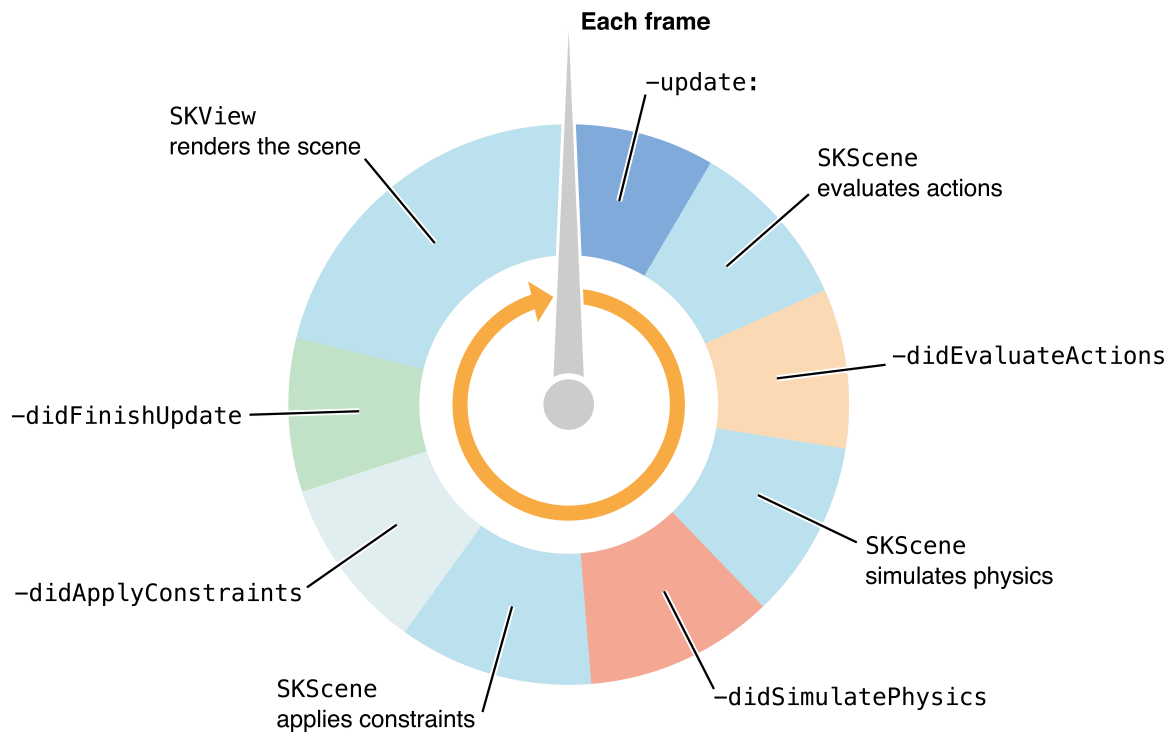
Diagram of what happens each frame in SK:
So you see, the SKScene is the class with all of the fun stuff like Nodes and Actions, and is where everything (important to you) happens. You can generate these scenes through the Editor, but then you probably need to make a new .swift file to go with it (as each scene can have its own logic).
The editor is just a 'shortcut' to initializing a bunch of stuff, and honestly, you can make complete games with little code (but you very quickly find out that you want more)
So in this code, where you declare GameScene or PauseScreen (which are basically just class declarations, that inherit from SKScene), you quickly find this line talking about something that ISNT a scene:
override func didMoveToView(view: SKView).. it's calling a SKView... what is that, and where did it come from?(Read about SKView here, and look at its inheritance):
We find this SKView declaration in the GameViewController file, (which is just a class), notice that it's the same as the regular iOS apps mostly, as it inherits UIViewController:
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
if let scene = GameScene(fileNamed:"GameScene") {
// Configure the view.
let skView = self.view as! SKView
skView.showsFPS = true
skView.showsNodeCount = true
/* Sprite Kit applies additional optimizations to improve rendering performance */
skView.ignoresSiblingOrder = true
/* Set the scale mode to scale to fit the window */
scene.scaleMode = .AspectFill
skView.presentScene(scene)
}
Again, that method is declared in GameViewController.swift, which is basically just this:
class GameViewController: UIViewController
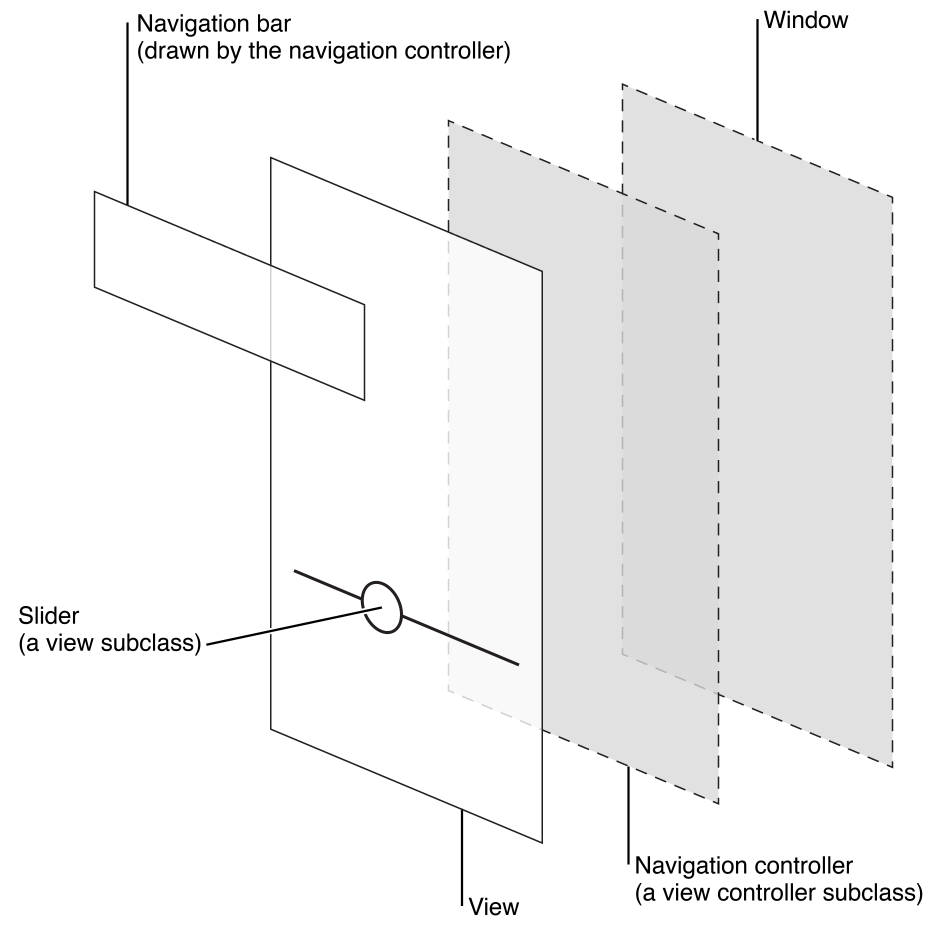
So how does all of this relate to iOS apps and SpriteKit? Well, they are all mashed on top of each other:
IOS app anatomy:
Basically, from right to left, you have the Window, which is (correct me if wrong) the AppDelegate, then the ViewController, then your View, which has all of the cool stuff in it (Storyboards sit inside of the View, just as SKScenes sit inside of the View.... Labels, Nodes, or Buttons, all sit inside of their respective classes ((the view)))
It's all a big sandwich of inheritance.
Check out the Apple websites for more info.
https://developer.apple.com/spritekit/
https://developer.apple.com/library/ios/documentation/SpriteKit/Reference/SpriteKitFramework_Ref/
Basically, everything is an Class inherited from a class inherited from a class and so on, so on... It can get messy. You can also see these inheritances in Xcode by CMD+clicking on them, which will jump you to the source file.
Goodluck with your studies and adventures in SpriteKit :)
You should only have a single GameViewController in your game. SKScenes are the scenes that the game transitions in between an to.
For example, the home menu screen? That's an SKScene. The main gameplay? That's an SKScene. The gameover screen? That's an SKScene.
The GameViewController initializes the entire view that the game will be maintained in, so the view. The SKScenes are just scenes that are placed on top of the view. You should be looking at a tutorial that uses SKScenes.
Here's how to make game center work as of the latest Swift 2.2.
Add this function anywhere inside the GameViewController class, and then just call it right after super.viewDidLoad().
func authenticateLocalPlayer() {
let localPlayer = GKLocalPlayer.localPlayer()
localPlayer.authenticateHandler = {(viewController, error) -> Void in
if (viewController != nil) {
self.presentViewController(viewController!, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
else {
print((GKLocalPlayer.localPlayer().authenticated))
}
}
}
Add the following functions in your SKScene class file. Don't forget to import GameKit. Just call showLeader() whenever you want the leaderboard to be displayed.
func showLeader() {
let viewControllerVar = self.view?.window?.rootViewController
let gKGCViewController = GKGameCenterViewController()
gKGCViewController.gameCenterDelegate = self
viewControllerVar?.presentViewController(gKGCViewController, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
func gameCenterViewControllerDidFinish(gameCenterViewController: GKGameCenterViewController) {
gameCenterViewController.dismissViewControllerAnimated(true, completion: nil)
}
And this is a sample I have of how the score is saved to game center.
func saveHighscore(gameScore: Int) {
print("Player has been authenticated.")
if GKLocalPlayer.localPlayer().authenticated {
let scoreReporter = GKScore(leaderboardIdentifier: "YOUR_LEADERBOARD_ID")
scoreReporter.value = Int64(gameScore)
let scoreArray: [GKScore] = [scoreReporter]
GKScore.reportScores(scoreArray, withCompletionHandler: {error -> Void in
if error != nil {
print("An error has occured: \(error)")
}
})
}
}
self refer to in the line gKGCViewController.gameCenterDelegate = self if this method is within my GameOverScene? I get the error Cannot assign value of type GameOverScene to type GKGameCenterControllerDelegate? ? –
Austenite saveHighScore in the viewdidload of the scene?? I also get this error: Attempting to load the view of a view controller while it is deallocating is not allowed and may result in undefined behavior (<UIAlertController: 0x1489d2190>) –
Austenite It all depends about how you are designing your app, and what technologies you want to use.
If you are looking to build an app in 100% Sprite Kit, then you treat your UIViewController as a shell that holds your Sprite Kit app. The only time you should be touching this is when you need to do things that the SpriteKit scene shouldn't be doing, like creating gesture controls and what not.
However, there are uses to having multiple view controllers with sprite kit elements. Perhaps you are making a business application, and decide to include a little game to go with it.
IMO the best way to think about it in terms of web design is think of your View controller as your HTML page, and think of your Scene as your flash/silverlight/unity/etc game player that you embed in the website. Sometimes you want that player to be full screen, some times you do not, it comes down to the design of the application. When in full screen, we do not need any other components, so the player can do all the work. But what if we attach a how to guide link on the page. We wouldn't want this in game, we want this outside of it. This link will then open up a new page, not associated with the old page, and has no use for the game player components.
Now for your situation with Game Center, it gets more complicated. Game Center was built before Sprite Kit came to existence, so all of its functionality is built on UIKit. But Game Center also allows for customization, so you do not have to use the UIKit features of it. Of course, you will have to do all of the work then in displaying the information inside of your scene with Sprite Kit objects.
To make life easiest for you, you would include all of the built in code needed into your View Controller, then what you do is create a delegate that the scene knows about, and assign your view controller to this delegate. Now Game Scene can access any element of that view controller that you allow, like presenting leader boards or passing up leader boards. Check out this tutorial in its entirety, it will help you learn all you will need to achieve what you want. https://www.raywenderlich.com/115300/swift-2-tutorial-part-3-tuples-protocols-delegates-and-table-views
In MVC the controller acts as a coordinator, a bit like the conductor in an orchestra. My preference is that scenes just do the one thing they were designed for i.e. implement game play. When a scene is completed, the final task is to notify the controller (using delegate pattern) that the scene is complete. It is then up to the controller to decide what happens next i.e. transition to next scene or game over.
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.