Ehcache talks about on-heap and off-heap memory. What is the difference? What JVM args are used to configure them?
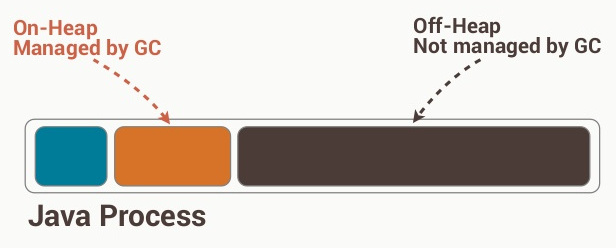
The on-heap store refers to objects that will be present in the Java heap (and also subject to GC). On the other hand, the off-heap store refers to (serialized) objects that are managed by EHCache, but stored outside the heap (and also not subject to GC). As the off-heap store continues to be managed in memory, it is slightly slower than the on-heap store, but still faster than the disk store.
The internal details involved in management and usage of the off-heap store aren't very evident in the link posted in the question, so it would be wise to check out the details of Terracotta BigMemory, which is used to manage the off-disk store. BigMemory (the off-heap store) is to be used to avoid the overhead of GC on a heap that is several Megabytes or Gigabytes large. BigMemory uses the memory address space of the JVM process, via direct ByteBuffers that are not subject to GC unlike other native Java objects.
from http://code.google.com/p/fast-serialization/wiki/QuickStartHeapOff
What is Heap-Offloading ?
Usually all non-temporary objects you allocate are managed by java's garbage collector. Although the VM does a decent job doing garbage collection, at a certain point the VM has to do a so called 'Full GC'. A full GC involves scanning the complete allocated Heap, which means GC pauses/slowdowns are proportional to an applications heap size. So don't trust any person telling you 'Memory is Cheap'. In java memory consumtion hurts performance. Additionally you may get notable pauses using heap sizes > 1 Gb. This can be nasty if you have any near-real-time stuff going on, in a cluster or grid a java process might get unresponsive and get dropped from the cluster.
However todays server applications (frequently built on top of bloaty frameworks ;-) ) easily require heaps far beyond 4Gb.
One solution to these memory requirements, is to 'offload' parts of the objects to the non-java heap (directly allocated from the OS). Fortunately java.nio provides classes to directly allocate/read and write 'unmanaged' chunks of memory (even memory mapped files).
So one can allocate large amounts of 'unmanaged' memory and use this to save objects there. In order to save arbitrary objects into unmanaged memory, the most viable solution is the use of Serialization. This means the application serializes objects into the offheap memory, later on the object can be read using deserialization.
The heap size managed by the java VM can be kept small, so GC pauses are in the millis, everybody is happy, job done.
It is clear, that the performance of such an off heap buffer depends mostly on the performance of the serialization implementation. Good news: for some reason FST-serialization is pretty fast :-).
Sample usage scenarios:
- Session cache in a server application. Use a memory mapped file to store gigabytes of (inactive) user sessions. Once the user logs into your application, you can quickly access user-related data without having to deal with a database.
- Caching of computational results (queries, html pages, ..) (only applicable if computation is slower than deserializing the result object ofc).
- very simple and fast persistance using memory mapped files
Edit: For some scenarios one might choose more sophisticated Garbage Collection algorithms such as ConcurrentMarkAndSweep or G1 to support larger heaps (but this also has its limits beyond 16GB heaps). There is also a commercial JVM with improved 'pauseless' GC (Azul) available.
The heap is the place in memory where your dynamically allocated objects live. If you used new then it's on the heap. That's as opposed to stack space, which is where the function stack lives. If you have a local variable then that reference is on the stack.
Java's heap is subject to garbage collection and the objects are usable directly.
EHCache's off-heap storage takes your regular object off the heap, serializes it, and stores it as bytes in a chunk of memory that EHCache manages. It's like storing it to disk but it's still in RAM. The objects are not directly usable in this state, they have to be deserialized first. Also not subject to garbage collection.
Not 100%; however, it sounds like the heap is an object or set of allocated space (on RAM) that is built into the functionality of the code either Java itself or more likely functionality from ehcache itself, and the off-heap Ram is there own system as well; however, it sounds like this is one magnitude slower as it is not as organized, meaning it may not use a heap (meaning one long set of space of ram), and instead uses different address spaces likely making it slightly less efficient.
Then of course the next tier lower is hard-drive space itself.
I don't use ehcache, so you may not want to trust me, but that what is what I gathered from their documentation.
The JVM doesn't know anything about off-heap memory. Ehcache implements an on-disk cache as well as an in-memory cache.
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.