This post builds upon this one.
I got a Pandas dataframe containing cities with their geo-coordinates (geodetic) as longitude and latitude.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame([{'city':"Berlin", 'lat':52.5243700, 'lng':13.4105300},
{'city':"Potsdam", 'lat':52.3988600, 'lng':13.0656600},
{'city':"Hamburg", 'lat':53.5753200, 'lng':10.0153400}]);
For each city I'm trying to find two other cities that are closest. Therefore I tried the scipy.spatial.KDTree. To do so, I had to convert the geodetic coordinates into 3D catesian coordinates (ECEF = earth-centered, earth-fixed):
from math import *
def to_Cartesian(lat, lng):
R = 6367 # radius of the Earth in kilometers
x = R * cos(lat) * cos(lng)
y = R * cos(lat) * sin(lng)
z = R * sin(lat)
return x, y, z
df['x'], df['y'], df['z'] = zip(*map(to_Cartesian, df['lat'], df['lng']))
df
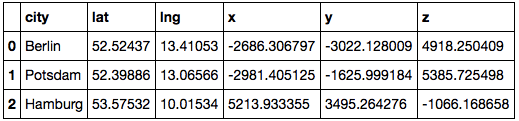
This give me this:
With this I can create the KDTree:
coordinates = list(zip(df['x'], df['y'], df['z']))
from scipy import spatial
tree = spatial.KDTree(coordinates)
tree.data
Now I'm testing it with Berlin,
tree.query(coordinates[0], 2)
which correctly gives me Berlin (itself) and Potsdam as the two cities from my list that are closest to Berlin.
Question: But I wonder what to do with the distance from that query? It says 1501 - but how can I convert this to meters or kilometers? The real distance between Berlin and Potsdam is 27km and not 1501km.
Remark: I know I could get longitude/latitude for both cities and calculate the haversine-distance. But would be cool that use the output from KDTree instead.
(array([ 0. , 1501.59637685]), array([0, 1]))
Any help is appreciated.