How does one create a Python friendly environment in Xcode 4, 5, 6 or 7?
I figured it out! The steps make it look like it will take more effort than it actually does.
These instructions are for creating a project from scratch. If you have existing Python scripts that you wish to include in this project, you will obviously need to slightly deviate from these instructions.
If you find that these instructions no longer work or are unclear due to changes in Xcode updates, please let me know. I will make the necessary corrections.
- Open Xcode. The instructions for either are the same.
- In the menu bar, click “File” → “New” → “New Project…”.
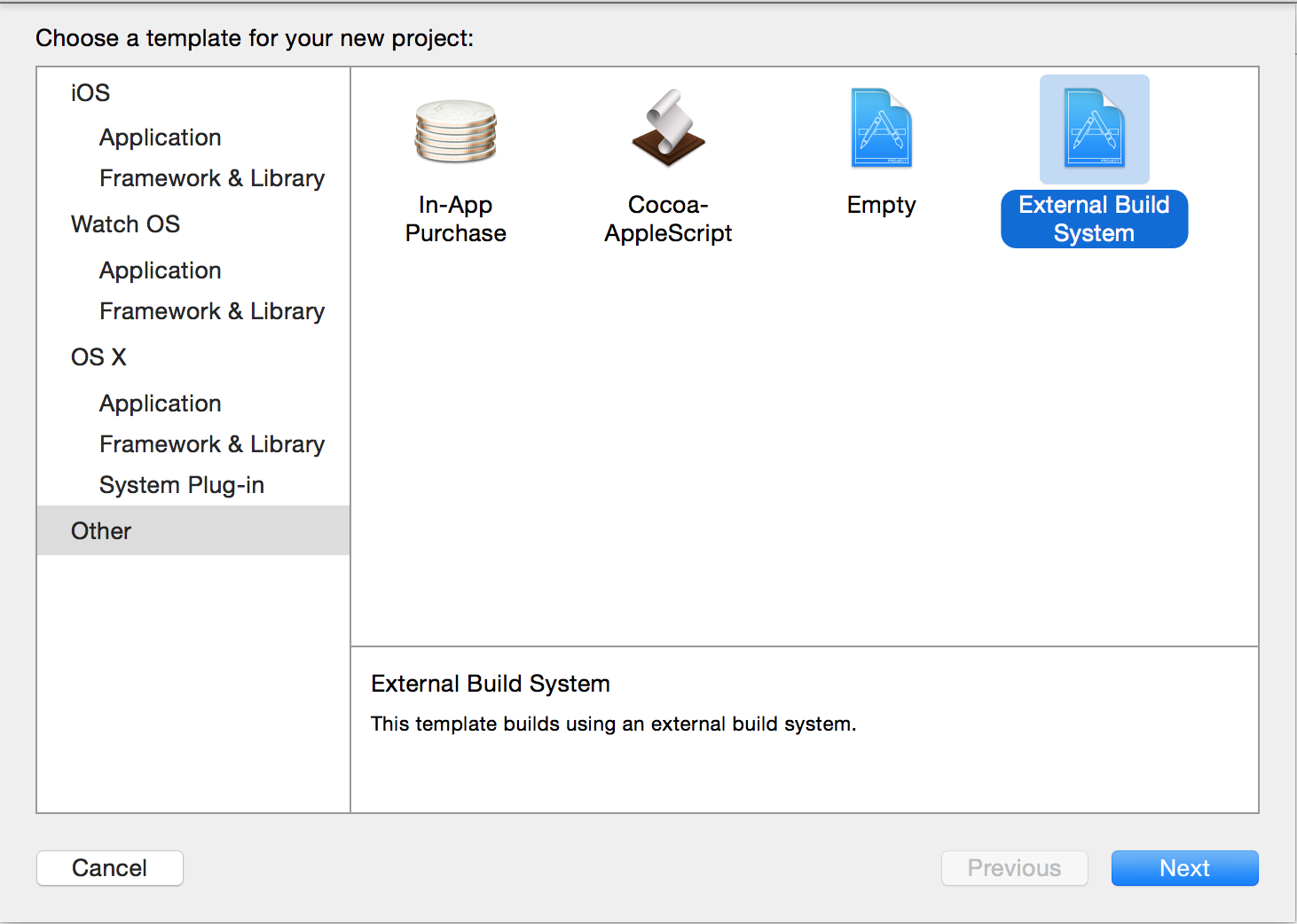
- Select “Other” in the left pane, then "External Build System" in the right page, and next click "Next".
- Enter the product name, organization name, or organization identifier.
- For the “Build Tool” field, type in /usr/local/bin/python3 for Python 3 or /usr/bin/python for Python 2 and then click “Next”. Note that this assumes you have the symbolic link (that is setup by default) that resolves to the Python executable. If you are unsure as to where your Python executables are, enter either of these commands into Terminal: which python3 and which python.
- Click “Next”.
- Choose where to save it and click “Create”.
- In the menu bar, click “File” → “New” → “New File…”.
- Select “Other” under “OS X”.
- Select “Empty” and click “Next”.
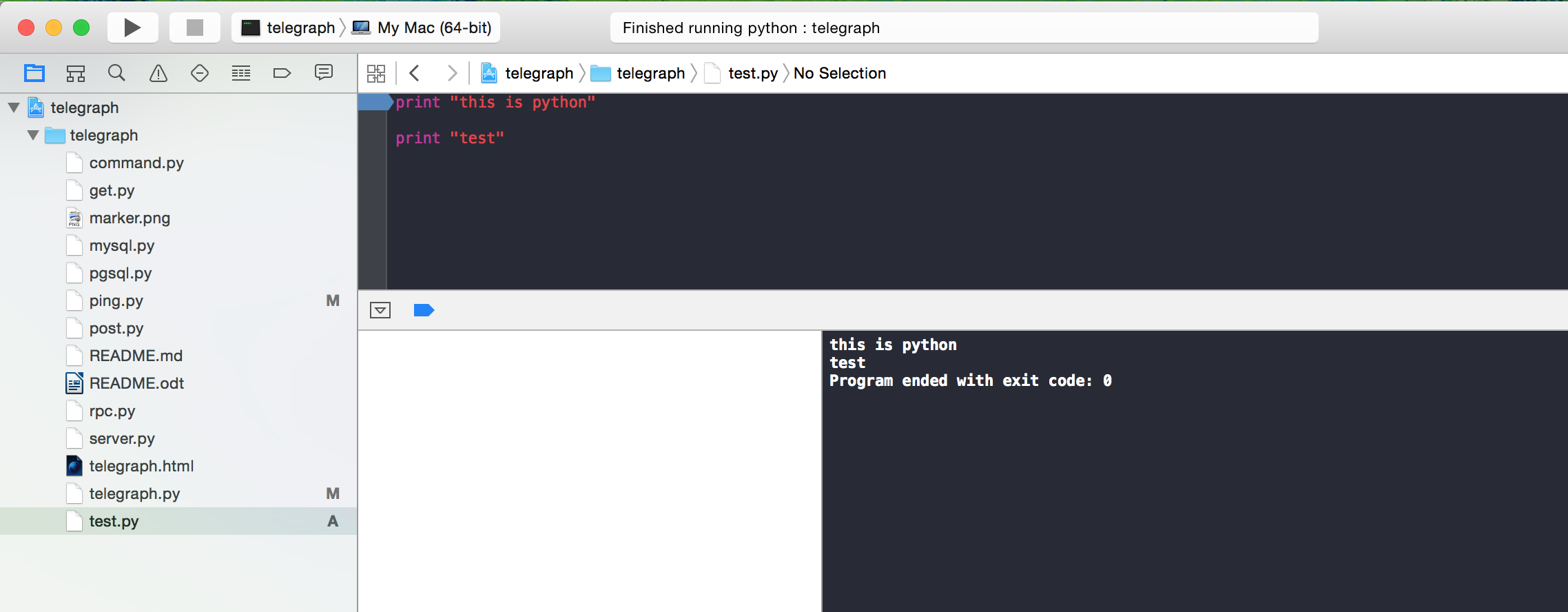
- Navigate to the project folder (it will not work, otherwise), enter the name of the Python file (including the “.py” extension), and click “Create”.
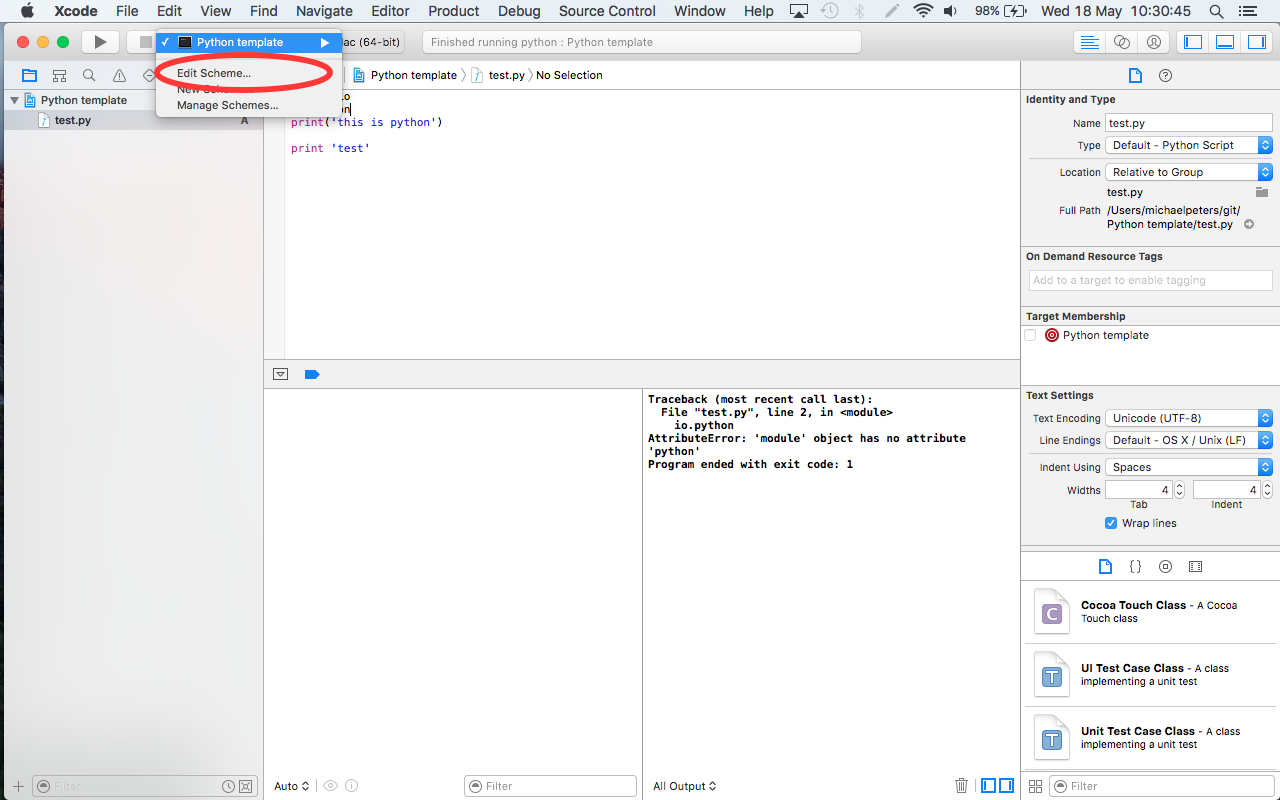
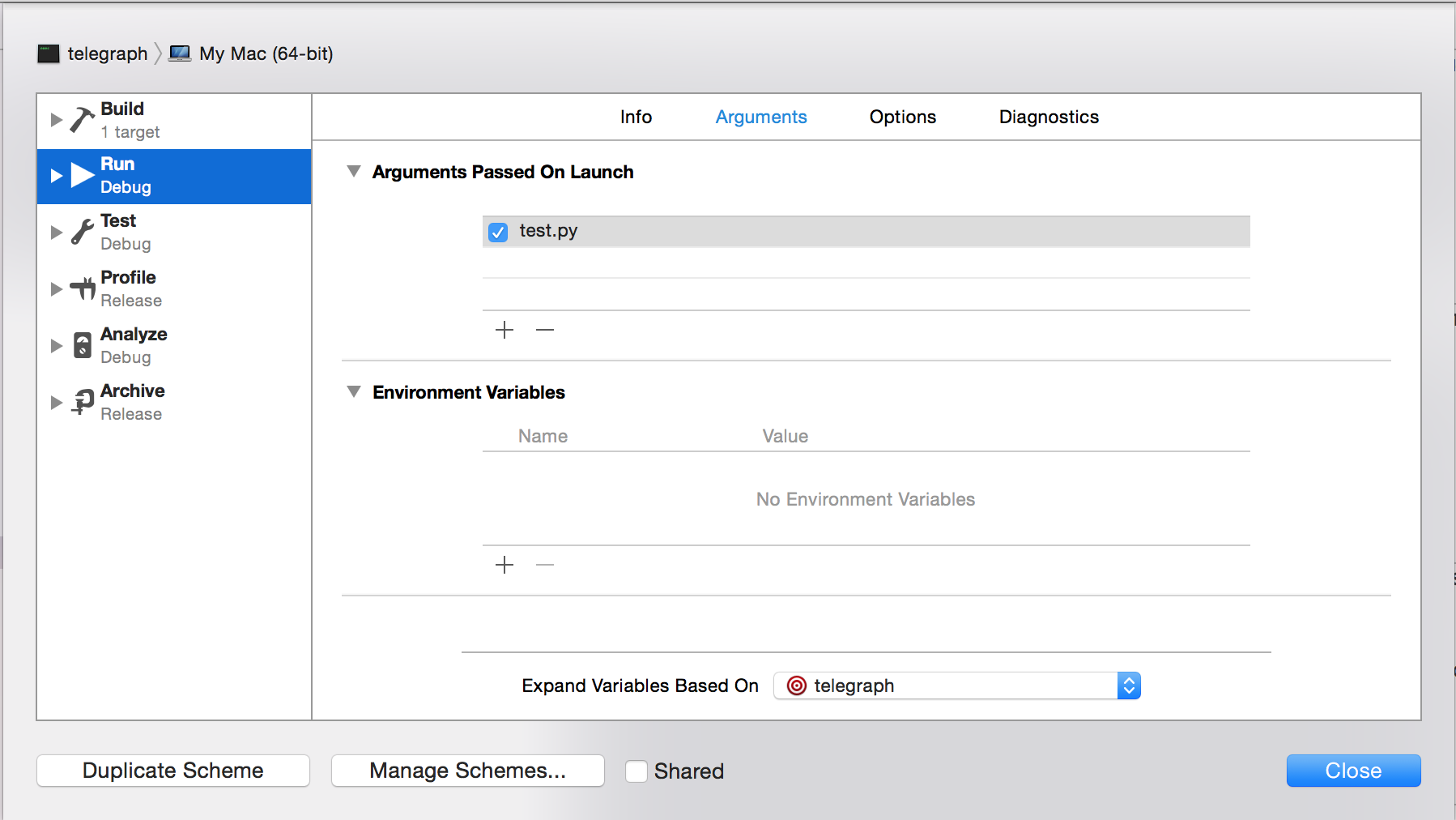
- In the menu bar, click “Product” → “Scheme” → “Edit Scheme…”.
- Click “Run” in the left pane.
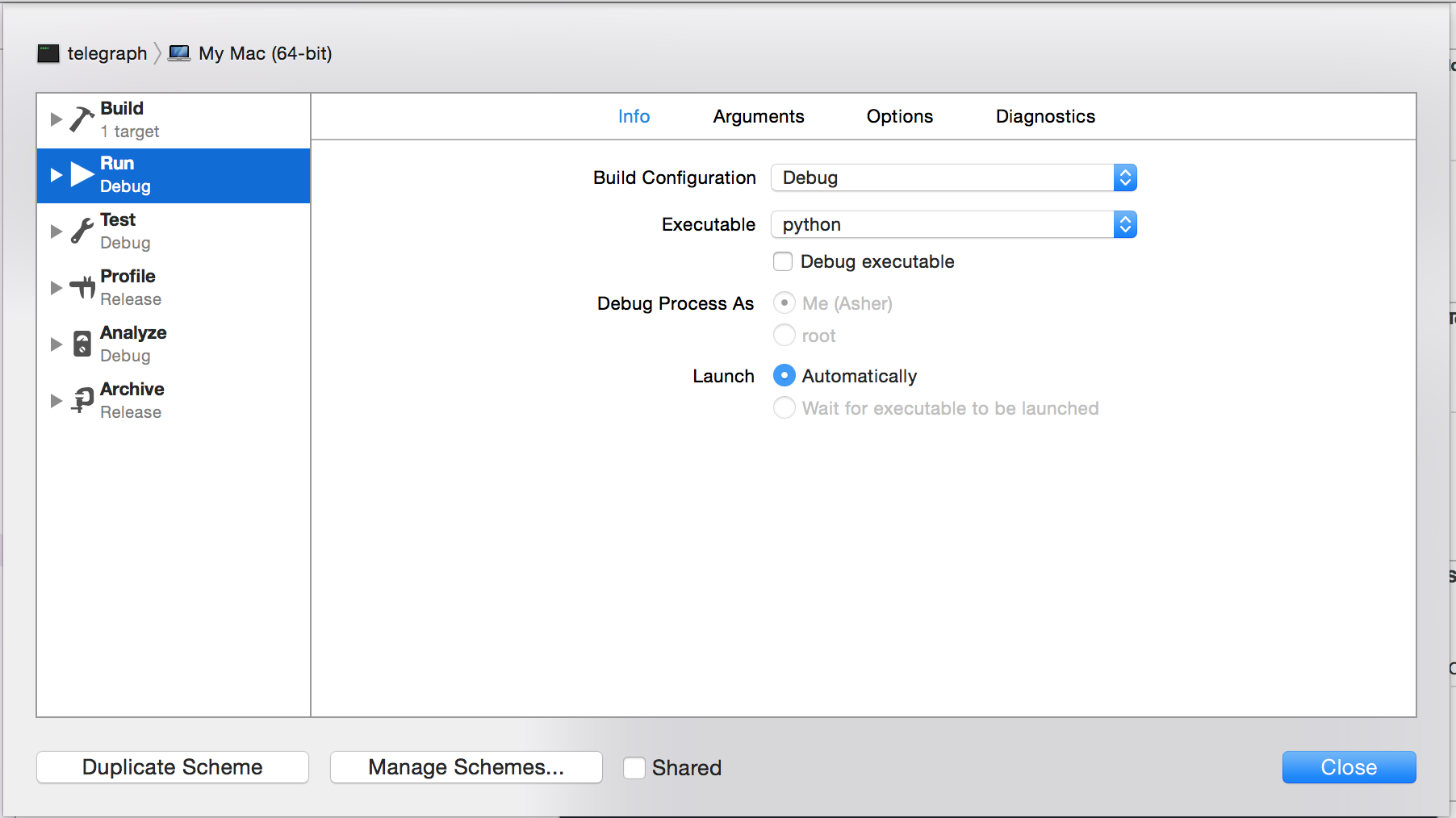
- In the “Info” tab, click the “Executable” field and then click “Other…”.
- Navigate to the executable from Step 5. You might need to use ⇧⌘G to type in the directory if it is hidden.
- Select the executable and click "Choose".
- Uncheck “Debug executable”. If you skip this step, Xcode will try to debug the Python executable itself. I am unaware of a way to integrate an external debugging tool into Xcode.
- Click the “+” icon under “Arguments Passed On Launch”. You might have to expand that section by clicking on the triangle pointing to the right.
- Type in $(SRCROOT)/ (or $(SOURCE_ROOT)/) and then the name of the Python file you want to test. Remember, the Python program must be in the project folder. Otherwise, you will have to type out the full path (or relative path if it's in a subfolder of the project folder) here. If there are spaces anywhere in the full path, you must include quotation marks at the beginning and end of this.
- Click “Close”.
Note that if you open the "Utilities" panel, with the "Show the File inspector" tab active, the file type is automatically set to "Default - Python script". Feel free to look through all the file type options it has, to gain an idea as to what all it is capable of doing. The method above can be applied to any interpreted language. As of right now, I have yet to figure out exactly how to get it to work with Java; then again, I haven't done too much research. Surely there is some documentation floating around on the web about all of this.
Running without administrative privileges:
If you do not have administrative privileges or are not in the Developer group, you can still use Xcode for Python programming (but you still won't be able to develop in languages that require compiling). Instead of using the play button, in the menu bar, click "Product" → "Perform Action" → "Run Without Building" or simply use the keyboard shortcut ^⌘R.
Other Notes:
To change the text encoding, line endings, and/or indentation settings, open the "Utilities" panel and click "Show the File inspector" tab active. There, you will find these settings.
For more information about Xcode's build settings, there is no better source than this. I'd be interested in hearing from somebody who got this to work with unsupported compiled languages. This process should work for any other interpreted language. Just be sure to change Step 5 and Step 16 accordingly.
pdb module as I have not needed it yet. Print statements have sufficed for me so far. I would imagine it would, though. You can use input() (or raw_input() in Python 2) so I imagine that it work as if you are running it in Terminal or something similar. –
Nainsook "Base Expansions On" field? –
Slipslop which command as noted in Step 6. –
Nainsook < filename as your last argument passed on launch. –
Nainsook < filename is a rather static approach... –
Ferula LaunchAction element in the scheme file (hidden within the project file itself) by setting selectedDebuggerIdentifier to the empty string, setting selectedLauncherIdentifier to "Xcode.IDEFoundation.Launcher.PosixSpawn", and adding <PathRunnable runnableDebuggingMode = "0" FilePath = "/usr/local/bin/python3"></PathRunnable> as a child element. –
Nainsook I've created Xcode 4 templates to simplify the steps provided by Tyler.
The result is Python Project Template for Xcode 4.
Now what you need to do is download the templates, move it to /Developer/Library/Xcode/Templates/Project Templates/Mac/Others/ and then new a Python project with Xcode 4.
It still needs manual Scheme setup (you can refer to steps 12–20 provided by Tyler.)
Procedure to get Python Working in XCode 7
Step 1: Setup your Project with a External Build System
Step 1.1: Edit the Project Scheme
Step 2: Specify Python as the executable for the project (shift-command-g) the path should be /usr/bin/python
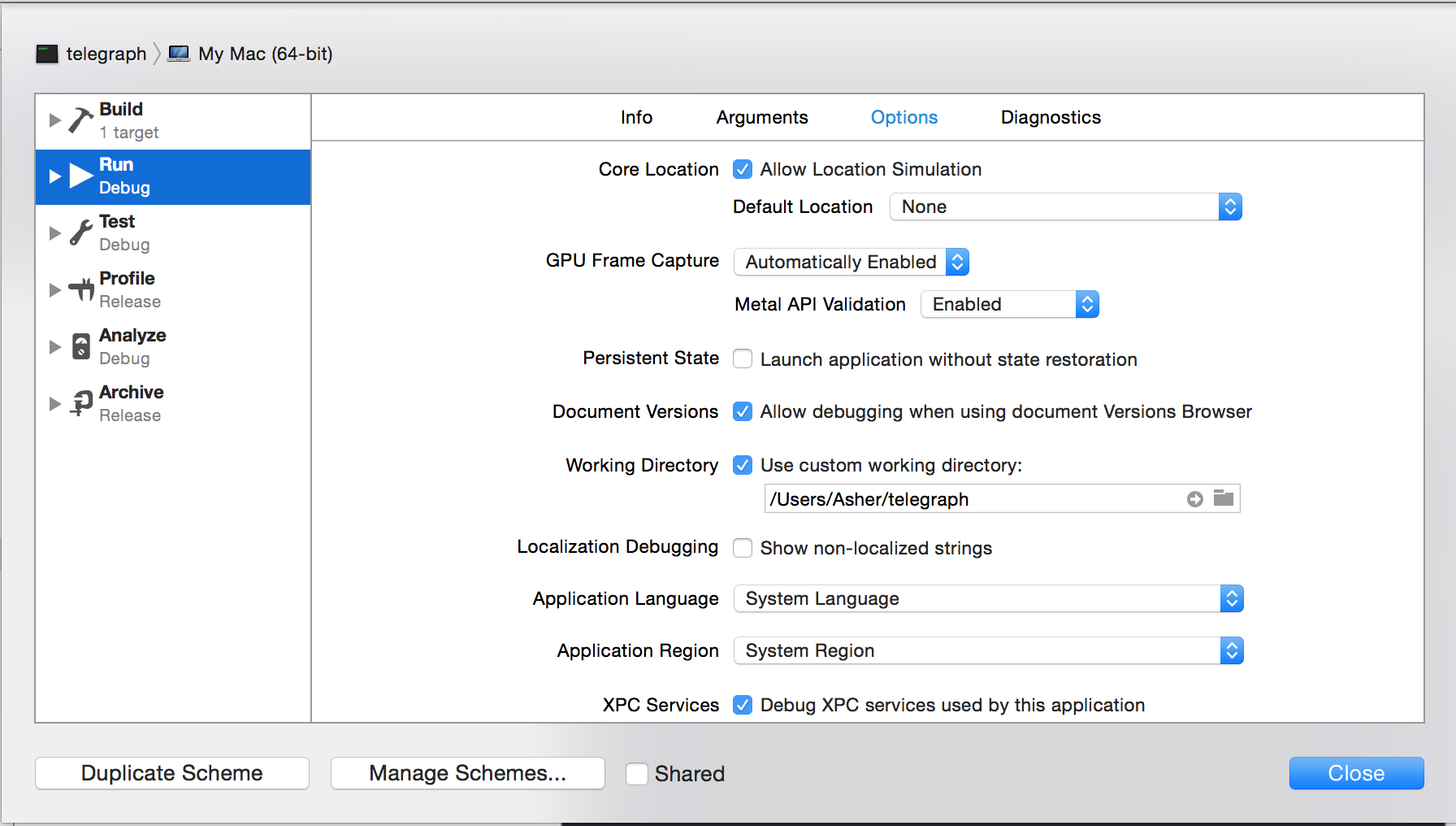
Step 3: Specify your custom working directory
Step 4: Specify your command line arguments to be the name of your python file. (in this example "test.py")
Step 5: Thankfully thats it!
(debugging can't be added until OSX supports a python debugger?)
which command in Terminal to get the exact location for the Build Tool. "which lua" for instance returns "/usr/local/bin/lua" on my system. –
Cleaves You should try PyDev plug in for Eclipse. I tried alot of editors/IDE's to use with python, but the only one i liked the most is the PyDev plugin for Eclipse. It has code completion, debugger and many other nice features. Plus both are free.
Another way, which I've been using for awhile in XCode3:
See steps 1-15 above.
- Choose /bin/bash as your executable
- For the "Debugger" field, select "None".
- In the "Arguments" tab, click the "Base Expansions On" field and select the target you created earlier.
- Click the "+" icon under "Arguments Passed On Launch". You may have to expand that section by clicking on the triangle pointing to the right.
- Type in "-l". This will tell bash to use your login environment (PYTHONPATH, etc..)
- Do step #19 again.
- Type in "-c '$(SOURCE_ROOT)/.py'"
- Click "OK".
- Start coding.
The nice thing about this way is it will use the same environment to develop in that you would use to run in outside of XCode (as setup from your bash .profile).
It's also generic enough to let you develop/run any type of file, not just python.
This Technical Note TN2328 from Apple Developer Library helped me a lot about Changes To Embedding Python Using Xcode 5.0.
This thread is old, but to chime in for Xcode Version 8.3.3, Tyler Crompton's method in the accepted answer still works (some of the names are very slightly different, but not enough to matter).
2 points where I struggled slightly:
Step 16: If the python executable you want is greyed out, right click it and select quick look. Then close the quick look window, and it should now be selectable.
Step 19: If this isn’t working for you, you can enter the name of just the python file in the Arguments tab, and then enter the project root directory explicitly in the Options tab under Working Directory--check the “Use custom working directory” box, and type in your project root directory in the field below it.
Try Editra It's free, has a lot of cool features and plug-ins, it runs on most platforms, and it is written in Python. I use it for all my non-XCode development at home and on Windows/Linux at work.
© 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.