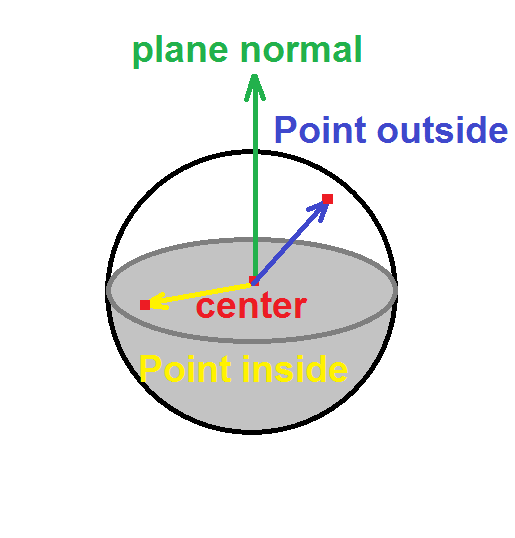
The simplest way is to cut your sphere by a plane.
![overview]()
If you have plane normal than any direction (point on sphere - sphere center) with the same direction to normal is cut off. Simply by this condition:
dot(point on sphere - sphere center , plane normal ) > 0.0
But do not forget to test both intersections of ray and sphere as the closest one can be on the other side of plane ...
I tried to implement this into mine GLSL Ray tracer:
And come up with this updated fragment shaders:
Vertex (no change):
//------------------------------------------------------------------
#version 420 core
//------------------------------------------------------------------
uniform float aspect;
uniform float focal_length;
uniform mat4x4 tm_eye;
layout(location=0) in vec2 pos;
out smooth vec2 txt_pos; // frag position on screen <-1,+1> for debug prints
out smooth vec3 ray_pos; // ray start position
out smooth vec3 ray_dir; // ray start direction
//------------------------------------------------------------------
void main(void)
{
vec4 p;
txt_pos=pos;
// perspective projection
p=tm_eye*vec4(pos.x/aspect,pos.y,0.0,1.0);
ray_pos=p.xyz;
p-=tm_eye*vec4(0.0,0.0,-focal_length,1.0);
ray_dir=normalize(p.xyz);
gl_Position=vec4(pos,0.0,1.0);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------
Fragment (added hemispheres):
//------------------------------------------------------------------
#version 420 core
//------------------------------------------------------------------
// Ray tracer ver: 1.000
//------------------------------------------------------------------
in smooth vec3 ray_pos; // ray start position
in smooth vec3 ray_dir; // ray start direction
uniform float n0; // refractive index of camera origin
uniform int fac_siz; // square texture x,y resolution size
uniform int fac_num; // number of valid floats in texture
uniform sampler2D fac_txr; // scene mesh data texture
out layout(location=0) vec4 frag_col;
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#define _reflect
#define _refract
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void main(void)
{
const vec3 light_dir=normalize(vec3(0.1,0.1,1.0));
const float light_iamb=0.1; // dot offset
const float light_idir=0.5; // directional light amplitude
const vec3 back_col=vec3(0.2,0.2,0.2); // background color
const float _zero=1e-6; // to avoid intrsection with start point of ray
const int _fac_triangles =0; // r,g,b,a, n, triangle count, { x0,y0,z0,x1,y1,z1,x2,y2,z2 }
const int _fac_spheres =1; // r,g,b,a, n, sphere count, { x,y,z,r }
const int _fac_hemispheres=2; // r,g,b,a, n, hemisphere count,{ x,y,z,r,nx,ny,nz }
// ray scene intersection
struct _ray
{
dvec3 pos,dir,nor;
vec3 col;
float refl,refr;// reflection,refraction intensity coeficients
float n0,n1; // refaction index (start,end)
double l; // ray length
int lvl,i0,i1; // recursion level, reflect, refract
};
const int _lvls=4;
const int _rays=(1<<_lvls)-1;
_ray ray[_rays]; int rays;
dvec3 v0,v1,v2,pos;
vec3 c;
float refr,refl,n1;
double tt,t,a;
int i0,ii,num,id;
// fac texture access
vec2 st; int i,j; float ds=1.0/float(fac_siz-1);
#define fac_get texture(fac_txr,st).r; st.s+=ds; i++; j++; if (j==fac_siz) { j=0; st.s=0.0; st.t+=ds; }
// enque start ray
ray[0].pos=ray_pos;
ray[0].dir=normalize(ray_dir);
ray[0].nor=vec3(0.0,0.0,0.0);
ray[0].refl=0.0;
ray[0].refr=0.0;
ray[0].n0=n0;
ray[0].n1=1.0;
ray[0].l =0.0;
ray[0].lvl=0;
ray[0].i0=-1;
ray[0].i1=-1;
rays=1;
// loop all enqued rays
for (i0=0;i0<rays;i0++)
{
// loop through all objects
// find closest forward intersection between them and ray[i0]
// strore it to ray[i0].(nor,col)
// strore it to pos,n1
t=tt=-1.0; ii=1; ray[i0].l=0.0;
ray[i0].col=back_col;
pos=ray[i0].pos; n1=n0;
for (st=vec2(0.0,0.0),i=j=0;i<fac_num;)
{
c.r=fac_get; // RGBA
c.g=fac_get;
c.b=fac_get;
refl=fac_get;
refr=fac_get;
n1=fac_get; // refraction index
a=fac_get; id=int(a); // object type
a=fac_get; num=int(a); // face count
if (id==_fac_triangles)
for (;num>0;num--)
{
v0.x=fac_get; v0.y=fac_get; v0.z=fac_get;
v1.x=fac_get; v1.y=fac_get; v1.z=fac_get;
v2.x=fac_get; v2.y=fac_get; v2.z=fac_get;
dvec3 e1,e2,n,p,q,r;
double t,u,v,det,idet;
//compute ray triangle intersection
e1=v1-v0;
e2=v2-v0;
// Calculate planes normal vector
p=cross(ray[i0].dir,e2);
det=dot(e1,p);
// Ray is parallel to plane
if (abs(det)<1e-8) continue;
idet=1.0/det;
r=ray[i0].pos-v0;
u=dot(r,p)*idet;
if ((u<0.0)||(u>1.0)) continue;
q=cross(r,e1);
v=dot(ray[i0].dir,q)*idet;
if ((v<0.0)||(u+v>1.0)) continue;
t=dot(e2,q)*idet;
if ((t>_zero)&&((t<=tt)||(ii!=0)))
{
ii=0; tt=t;
// store color,n ...
ray[i0].col=c;
ray[i0].refl=refl;
ray[i0].refr=refr;
// barycentric interpolate position
t=1.0-u-v;
pos=(v0*t)+(v1*u)+(v2*v);
// compute normal (store as dir for now)
e1=v1-v0;
e2=v2-v1;
ray[i0].nor=cross(e1,e2);
}
}
if (id==_fac_spheres)
for (;num>0;num--)
{
float r;
v0.x=fac_get; v0.y=fac_get; v0.z=fac_get; r=fac_get;
// compute l0 length of ray(p0,dp) to intersection with sphere(v0,r)
// where rr= r^-2
double aa,bb,cc,dd,l0,l1,rr;
dvec3 p0,dp;
p0=ray[i0].pos-v0; // set sphere center to (0,0,0)
dp=ray[i0].dir;
rr = 1.0/(r*r);
aa=2.0*rr*dot(dp,dp);
bb=2.0*rr*dot(p0,dp);
cc= rr*dot(p0,p0)-1.0;
dd=((bb*bb)-(2.0*aa*cc));
if (dd<0.0) continue;
dd=sqrt(dd);
l0=(-bb+dd)/aa;
l1=(-bb-dd)/aa;
if (l0<0.0) l0=l1;
if (l1<0.0) l1=l0;
t=min(l0,l1); if (t<=_zero) t=max(l0,l1);
if ((t>_zero)&&((t<=tt)||(ii!=0)))
{
ii=0; tt=t;
// store color,n ...
ray[i0].col=c;
ray[i0].refl=refl;
ray[i0].refr=refr;
// position,normal
pos=ray[i0].pos+(ray[i0].dir*t);
ray[i0].nor=pos-v0;
}
}
if (id==_fac_hemispheres)
for (;num>0;num--)
{
float r;
v0.x=fac_get; v0.y=fac_get; v0.z=fac_get; r=fac_get;
v1.x=fac_get; v1.y=fac_get; v1.z=fac_get;
// compute l0 length of ray(p0,dp) to intersection with sphere(v0,r)
// where rr= r^-2
double aa,bb,cc,dd,l0,l1,rr;
dvec3 p0,dp;
p0=ray[i0].pos-v0; // set sphere center to (0,0,0)
dp=ray[i0].dir;
rr = 1.0/(r*r);
aa=2.0*rr*dot(dp,dp);
bb=2.0*rr*dot(p0,dp);
cc= rr*dot(p0,p0)-1.0;
dd=((bb*bb)-(2.0*aa*cc));
if (dd<0.0) continue;
dd=sqrt(dd);
l0=(-bb+dd)/aa;
l1=(-bb-dd)/aa;
// test both hits-v0 against normal v1
v2=ray[i0].pos+(ray[i0].dir*l0)-v0; if (dot(v1,v2)>0.0) l0=-1.0;
v2=ray[i0].pos+(ray[i0].dir*l1)-v0; if (dot(v1,v2)>0.0) l1=-1.0;
if (l0<0.0) l0=l1;
if (l1<0.0) l1=l0;
t=min(l0,l1); if (t<=_zero) t=max(l0,l1);
if ((t>_zero)&&((t<=tt)||(ii!=0)))
{
ii=0; tt=t;
// store color,n ...
ray[i0].col=c;
ray[i0].refl=refl;
ray[i0].refr=refr;
// position,normal
pos=ray[i0].pos+(ray[i0].dir*t);
ray[i0].nor=pos-v0;
}
}
}
ray[i0].l=tt;
ray[i0].nor=normalize(ray[i0].nor);
// split ray from pos and ray[i0].nor
if ((ii==0)&&(ray[i0].lvl<_lvls-1))
{
t=dot(ray[i0].dir,ray[i0].nor);
// reflect
#ifdef _reflect
if ((ray[i0].refl>_zero)&&(t<_zero)) // do not reflect inside objects
{
ray[i0].i0=rays;
ray[rays]=ray[i0];
ray[rays].lvl++;
ray[rays].i0=-1;
ray[rays].i1=-1;
ray[rays].pos=pos;
ray[rays].dir=ray[rays].dir-(2.0*t*ray[rays].nor);
ray[rays].n0=ray[i0].n0;
ray[rays].n1=ray[i0].n0;
rays++;
}
#endif
// refract
#ifdef _refract
if (ray[i0].refr>_zero)
{
ray[i0].i1=rays;
ray[rays]=ray[i0];
ray[rays].lvl++;
ray[rays].i0=-1;
ray[rays].i1=-1;
ray[rays].pos=pos;
t=dot(ray[i0].dir,ray[i0].nor);
if (t>0.0) // exit object
{
ray[rays].n0=ray[i0].n0;
ray[rays].n1=n0;
if (i0==0) ray[i0].n1=n1;
v0=-ray[i0].nor; t=-t;
}
else{ // enter object
ray[rays].n0=n1;
ray[rays].n1=ray[i0].n0;
ray[i0 ].n1=n1;
v0=ray[i0].nor;
}
n1=ray[i0].n0/ray[i0].n1;
tt=1.0-(n1*n1*(1.0-t*t));
if (tt>=0.0)
{
ray[rays].dir=(ray[i0].dir*n1)-(v0*((n1*t)+sqrt(tt)));
rays++;
}
}
#endif
}
else if (i0>0) // ignore last ray if nothing hit
{
ray[i0]=ray[rays-1];
rays--; i0--;
}
}
// back track ray intersections and compute output color col
// lvl is sorted ascending so backtrack from end
for (i0=rays-1;i0>=0;i0--)
{
// directional + ambient light
t=abs(dot(ray[i0].nor,light_dir)*light_idir)+light_iamb;
t*=1.0-ray[i0].refl-ray[i0].refr;
ray[i0].col.rgb*=float(t);
// reflect
ii=ray[i0].i0;
if (ii>=0) ray[i0].col.rgb+=ray[ii].col.rgb*ray[i0].refl;
// refract
ii=ray[i0].i1;
if (ii>=0) ray[i0].col.rgb+=ray[ii].col.rgb*ray[i0].refr;
}
frag_col=vec4(ray[0].col,1.0);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
The Vertex shader just creates the Ray position and direction which is interpolated by GPU and then Fragment shader handles each ray (per pixel).
I use this scene:
// init mesh raytracer
ray.gl_init();
ray.beg();
// r g b rfl rfr n
ray.add_material(1.0,0.7,0.1,0.3,0.0,_n_glass); ray.add_hemisphere( 0.0, 0.0, 2.0,0.5, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
ray.add_material(1.0,1.0,1.0,0.3,0.0,_n_glass); ray.add_box ( 0.0, 0.0, 6.0,9.0,9.0,0.1);
ray.add_material(1.0,1.0,1.0,0.1,0.8,_n_glass); ray.add_sphere ( 0.0, 0.0, 0.5,0.5);
ray.add_material(1.0,0.1,0.1,0.3,0.0,_n_glass); ray.add_sphere (+2.0, 0.0, 2.0,0.5);
ray.add_material(0.1,1.0,0.1,0.3,0.0,_n_glass); ray.add_box (-2.0, 0.0, 2.0,0.5,0.5,0.5);
ray.add_material(0.1,0.1,1.0,0.3,0.0,_n_glass);
ray.add_tetrahedron
(
0.0, 0.0, 3.0,
-1.0,-1.0, 4.0,
+1.0,-1.0, 4.0,
0.0,+1.0, 4.0
);
ray.end();
containing single yellow hemisphere at (0.0, 0.0, 2.0) with radius r=0.5 and plane normal (0.0, 0.0, 1.0). Rotation of the object can by done simply by rotating the plane normal.
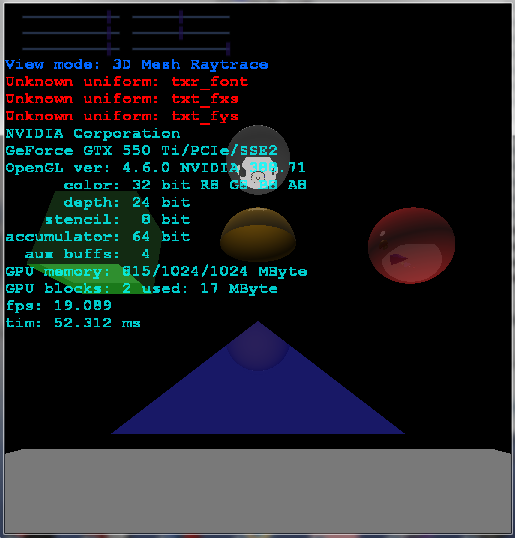
And this is preview:
![hemisphere]()
As you can see hemisphere is working by just cutting with a plane ... The only important code from above for you is this (see the *** comments):
if (id==_fac_hemispheres) // *** ignore
for (;num>0;num--) // *** ignore
{
float r;
// *** here v0 is center, v1 is plane normal and r is radius
v0.x=fac_get; v0.y=fac_get; v0.z=fac_get; r=fac_get;
v1.x=fac_get; v1.y=fac_get; v1.z=fac_get;
// *** this is ray/ellipsoid intersection returning l0,l1 ray distances for both hits
// compute l0 length of ray(p0,dp) to intersection with sphere(v0,r)
// where rr= r^-2
double aa,bb,cc,dd,l0,l1,rr;
dvec3 p0,dp;
p0=ray[i0].pos-v0; // set sphere center to (0,0,0)
dp=ray[i0].dir;
rr = 1.0/(r*r);
aa=2.0*rr*dot(dp,dp);
bb=2.0*rr*dot(p0,dp);
cc= rr*dot(p0,p0)-1.0;
dd=((bb*bb)-(2.0*aa*cc));
if (dd<0.0) continue;
dd=sqrt(dd);
l0=(-bb+dd)/aa;
l1=(-bb-dd)/aa;
// *** this thro away hits on wrong side of plane
// test both hits-v0 against normal v1
v2=ray[i0].pos+(ray[i0].dir*l0)-v0; if (dot(v1,v2)>0.0) l0=-1.0;
v2=ray[i0].pos+(ray[i0].dir*l1)-v0; if (dot(v1,v2)>0.0) l1=-1.0;
// *** this is just using closer valid hit
if (l0<0.0) l0=l1;
if (l1<0.0) l1=l0;
t=min(l0,l1); if (t<=_zero) t=max(l0,l1);
if ((t>_zero)&&((t<=tt)||(ii!=0)))
{
ii=0; tt=t;
// store color,n ...
ray[i0].col=c;
ray[i0].refl=refl;
ray[i0].refr=refr;
// position,normal
pos=ray[i0].pos+(ray[i0].dir*t);
ray[i0].nor=pos-v0;
}
}
I used mine ray and ellipsoid intersection accuracy improvement as it returns both hits not just the first one.
If you cross check the spheres and hemispheres you will see I just added these two lines:
v2=ray[i0].pos+(ray[i0].dir*l0)-v0; if (dot(v1,v2)>0.0) l0=-1.0;
v2=ray[i0].pos+(ray[i0].dir*l1)-v0; if (dot(v1,v2)>0.0) l1=-1.0;
which just converts ray distances to hit positions and computing the condition mentioned above...




dot(plane_normal,hit_normal)other option is to convert ray into object local coordinate system and just check the sign of one of the coordinates of hit position ... No code, no MCVE no valid problem description makes this unanswerable so +Close – Cenesthesia