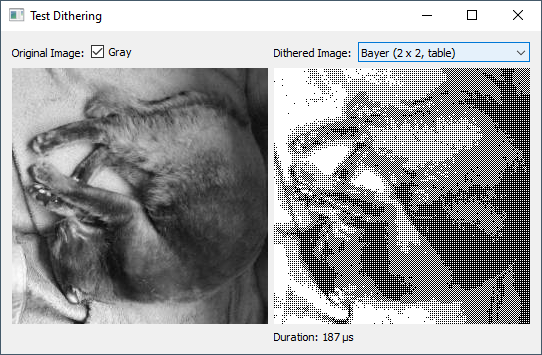
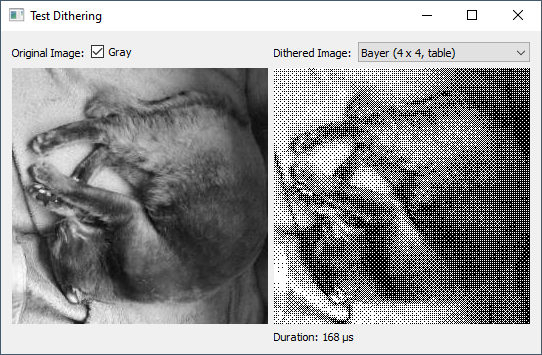
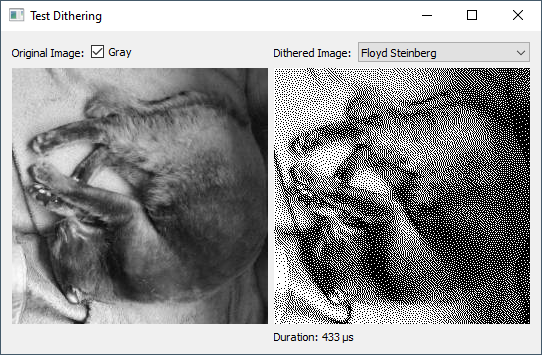
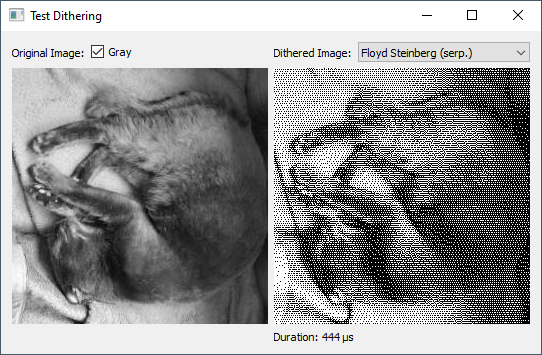
Prologue
I finally got around HW incompatibility between AT32UC3xxxxx and SSD1306 OLED I2C display (both have HW bugs making them incompatible) allowing me to use HW I2C at 400KBaud (~26.6ms per frame). So I decided to rewrite my old driver for this LCD to make advantage of the new speed by adding also filled surfaces (triangles,quads) instead of just lines and patterned lines (which I already implemented).
The problem is the display is 128x64 pixels but no colors or shades of gray just BW on/off
So in order to for example render rotating cube I need to distinguish the surfaces somehow. I was thinking about randomized filling pattern where surface is filled to some percentage instead of color.
Here my current code (Whole lib but without bugs its working as should):
LCD_SSD1306_I2C.h
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//--- SSD1306 I2C OLED LCD driver ver 2.000 ------------------------------------------------
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#ifndef _LCD_SSD1306_I2C_h
#define _LCD_SSD1306_I2C_h
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#define SSD1306_SETCONTRAST 0x81
#define SSD1306_DISPLAYALLON_RESUME 0xA4
#define SSD1306_DISPLAYALLON 0xA5
#define SSD1306_NORMALDISPLAY 0xA6
#define SSD1306_INVERTDISPLAY 0xA7
#define SSD1306_DISPLAYOFF 0xAE
#define SSD1306_DISPLAYON 0xAF
#define SSD1306_SETDISPLAYOFFSET 0xD3
#define SSD1306_SETCOMPINS 0xDA
#define SSD1306_SETVCOMDETECT 0xDB
#define SSD1306_SETDISPLAYCLOCKDIV 0xD5
#define SSD1306_SETPRECHARGE 0xD9
#define SSD1306_SETMULTIPLEX 0xA8
#define SSD1306_SETLOWCOLUMN 0x00
#define SSD1306_SETHIGHCOLUMN 0x10
#define SSD1306_SETSTARTLINE 0x40
#define SSD1306_MEMORYMODE 0x20
#define SSD1306_COLUMNADDR 0x21
#define SSD1306_PAGEADDR 0x22
#define SSD1306_COMSCANINC 0xC0
#define SSD1306_COMSCANDEC 0xC8
#define SSD1306_SEGREMAP 0xA0
#define SSD1306_CHARGEPUMP 0x8D
#define SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC 0x2
// Scrolling #defines
#define SSD1306_ACTIVATE_SCROLL 0x2F
#define SSD1306_DEACTIVATE_SCROLL 0x2E
#define SSD1306_SET_VERTICAL_SCROLL_AREA 0xA3
#define SSD1306_RIGHT_HORIZONTAL_SCROLL 0x26
#define SSD1306_LEFT_HORIZONTAL_SCROLL 0x27
#define SSD1306_VERTICAL_AND_RIGHT_HORIZONTAL_SCROLL 0x29
#define SSD1306_VERTICAL_AND_LEFT_HORIZONTAL_SCROLL 0x2A
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//#define I2C_send(adr,buf,siz){}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#ifndef _brv8_tab
#define _brv8_tab
static const U8 brv8[256] = // 8 bit bit reversal
{
0,128,64,192,32,160,96,224,16,144,80,208,48,176,112,240,8,136,72,200,40,168,104,232,24,152,
88,216,56,184,120,248,4,132,68,196,36,164,100,228,20,148,84,212,52,180,116,244,12,140,76,204,
44,172,108,236,28,156,92,220,60,188,124,252,2,130,66,194,34,162,98,226,18,146,82,210,50,178,
114,242,10,138,74,202,42,170,106,234,26,154,90,218,58,186,122,250,6,134,70,198,38,166,102,230,
22,150,86,214,54,182,118,246,14,142,78,206,46,174,110,238,30,158,94,222,62,190,126,254,1,129,
65,193,33,161,97,225,17,145,81,209,49,177,113,241,9,137,73,201,41,169,105,233,25,153,89,217,57,
185,121,249,5,133,69,197,37,165,101,229,21,149,85,213,53,181,117,245,13,141,77,205,45,173,109,
237,29,157,93,221,61,189,125,253,3,131,67,195,35,163,99,227,19,147,83,211,51,179,115,243,11,139,
75,203,43,171,107,235,27,155,91,219,59,187,123,251,7,135,71,199,39,167,103,231,23,151,87,215,55,
183,119,247,15,143,79,207,47,175,111,239,31,159,95,223,63,191,127,255
};
#endif
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
class LCD_SSD1306_I2C // max 96 lines
{
public:
// screen
int adr; // I2C adr
int xs,ys,sz; // resoluiton
U8 _scr[((128*96)>>3)+1]; // screen buffer
U8 *scr;
U8 *pyx[96]; // scan lines
// pattern
U32 pat,pat_m,pat_b; // binary pattern,max used bit mask,actual bit mask
// filling
U32 seed;
int bufl[96];
int bufr[96];
// system api
void init(int _adr,int _xs,int _ys); // initialize LCD: I2C_adr,xs,ys
void _command(U8 cmd); // *internal* do not cal it (sends command to LCD over I2C)
void rfsscr(); // copy actual screen buffer to LCD (by I2C)
// gfx rendering col = <0,1>
void clrscr(); // clear screen buffer
void rotate(int ang); // rotate 180 deg
void pixel(int x,int y,bool col); // set/res pixel
bool pixel(int x,int y); // get pixel
void line(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,bool col); // line
void triangle(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,bool col);// triangle
void quad(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int x3,int y3,bool col);
void rect(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,bool col); // rectangle using diagonal points
// patern rendering
void pat_set(char *s); // set binary pattern from bianry number string MSB renders first
void pat_beg(); // set pattern state to start of pattern
void pat_line(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,bool col);
void pat_triangle(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,bool col);
void pat_quad(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int x3,int y3,bool col);
void pat_rect(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,bool col);
// filled polygons col = <0,255>
void _fill_line(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1); // *internal* do not call it (render line into bufl/bufr)
void _fill_seed(); // *internal* do not call it (reset seed)
U8 _fill_rand(); // *internal* do not call it (get pseudo random number)
void fill_triangle(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,U8 col);
void fill_quad(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int x3,int y3,U8 col);
// text rendering
void prnchr(int x,int y,char c); // render char at x,y (y is rounded to multiple of 8)
void prntxt(int x,int y,const char *txt); // render text at x,y (y is rounded to multiple of 8)
};
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::_command(U8 cmd)
{
U8 buf[2]=
{
0x00, // 0x40 data/command
cmd,
};
I2C_send(adr,buf,2);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::init(int _adr,int _xs,int _ys)
{
int y;
adr=_adr;
xs=_xs;
ys=_ys;
sz=xs*(ys>>3);
const bool _external_Vcc=false;
// VRAM buffer
scr=_scr+1; // skip first Byte (VRAM/command selection)
for (y=0;y<ys;y++) pyx[y]=scr+((y>>3)*xs); // scanlines for fast direct pixel access
clrscr();
// Init sequence
U8 comPins = 0x02;
U8 contrast = 0x8F;
if((xs == 128) && (ys == 32)) { comPins = 0x02; contrast = 0x8F; }
else if((xs == 128) && (ys == 64)) { comPins = 0x12; contrast = (_external_Vcc) ? 0x9F : 0xCF; }
else if((xs == 96) && (ys == 16)) { comPins = 0x02; contrast = (_external_Vcc) ? 0x10 : 0xAF; }
else {} // Other screens
static U8 init0[27]=
{
0x00, // commands
SSD1306_DISPLAYOFF, // 0xAE
SSD1306_SETDISPLAYCLOCKDIV,0x80, // 0xD5
SSD1306_SETMULTIPLEX,ys-1, // 0xA8
SSD1306_SETDISPLAYOFFSET,0x00, // 0xD3 no offset
SSD1306_SETSTARTLINE | 0x0, // line 0
SSD1306_CHARGEPUMP,(_external_Vcc)?0x10:0x14, // 0x8D
SSD1306_MEMORYMODE,0x00, // 0x20 horizontal (scanlines)
SSD1306_SEGREMAP | 0x1,
SSD1306_COMSCANDEC,
SSD1306_SETCOMPINS,comPins,
SSD1306_SETCONTRAST,contrast,
SSD1306_SETPRECHARGE,(_external_Vcc)?0x22:0xF1, // 0xd9
SSD1306_SETVCOMDETECT,0x40, // 0xDB
SSD1306_DISPLAYALLON_RESUME, // 0xA4
SSD1306_NORMALDISPLAY, // 0xA6
SSD1306_DEACTIVATE_SCROLL,
SSD1306_DISPLAYON, // Main screen turn on
};
I2C_send(adr,init0,sizeof(init0));
// init default pattern
pat_set("111100100");
// clear filling buffers
for (y=0;y<96;y++)
{
bufl[y]=-1;
bufr[y]=-1;
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::clrscr()
{
for (int a=0;a<sz;a++) scr[a]=0x00;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::rotate(int ang)
{
U8 a0,a1;
int x0,y0,x1,y1;
if (ang==180)
for (y0=0,y1=ys-8;y0<y1;y0+=8,y1-=8)
for (x0=0,x1=xs-1;x0<xs;x0++,x1--)
{
a0=brv8[pyx[y0][x0]];
a1=brv8[pyx[y1][x1]];
pyx[y0][x0]=a1;
pyx[y1][x1]=a0;
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::rfsscr()
{
static const U8 init1[] =
{
0x00, // commands
SSD1306_MEMORYMODE,0, // horizontal addresing mode
SSD1306_COLUMNADDR,0,xs-1, // Column start/end address (0/127 reset)
SSD1306_PAGEADDR,0,(ys>>3)-1, // Page start/end address (0 reset)
};
I2C_send(adr,(U8*)init1,sizeof(init1));
_scr[0]=0x40; // 0x40 VRAM
// SW I2C can pass whole VRAM in single packet
// I2C_send(adr,_scr,sz+1);
// HW I2C must use packets up to 255 bytes so 128+1 (as TWIM0 on UC3 has 8 bit counter)
int i,n=128; U8 *p=_scr,a;
for (i=0;i<sz;i+=n){ a=p[0]; p[0]=0x40; I2C_send(adr,p,n+1); p[0]=a; p+=n; }
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::pixel(int x, int y,bool col)
{
// clip to screen
if ((x<0)||(x>=xs)||(y<0)||(y>=ys)) return;
// add or remove bit
if (col) pyx[y][x] |= (1<<(y&7));
else pyx[y][x] &= (255)^(1<<(y&7));
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool LCD_SSD1306_I2C::pixel(int x, int y)
{
// clip to screen
if ((x<0)||(x>=xs)||(y<0)||(y>=ys)) return false;
// get bit
return ((pyx[y][x]>>(y&7))&1);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::line(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,bool col)
{
int i,n,cx,cy,sx,sy;
// line DDA parameters
x1-=x0; sx=0; if (x1>0) sx=+1; if (x1<0) { sx=-1; x1=-x1; } if (x1) x1++; n=x1;
y1-=y0; sy=0; if (y1>0) sy=+1; if (y1<0) { sy=-1; y1=-y1; } if (y1) y1++; if (n<y1) n=y1;
// single pixel (not a line)
if (!n){ pixel(x0,y0,col); return; }
// ND DDA algo i is parameter
for (cx=cy=n,i=0;i<n;i++)
{
pixel(x0,y0,col);
cx-=x1; if (cx<=0){ cx+=n; x0+=sx; }
cy-=y1; if (cy<=0){ cy+=n; y0+=sy; }
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::pat_line(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,bool col)
{
bool ccc;
int i,n,cx,cy,sx,sy;
// line DDA parameters
x1-=x0; sx=0; if (x1>0) sx=+1; if (x1<0) { sx=-1; x1=-x1; } if (x1) x1++; n=x1;
y1-=y0; sy=0; if (y1>0) sy=+1; if (y1<0) { sy=-1; y1=-y1; } if (y1) y1++; if (n<y1) n=y1;
// single pixel (not a line)
if (!n){ pixel(x0,y0,col); return; }
// ND DDA algo i is parameter
for (cx=cy=n,i=0;i<n;i++)
{
ccc=(pat&pat_b); ccc^=(!col);
pat_b>>=1; if (!pat_b) pat_b=pat_m;
pixel(x0,y0,ccc);
cx-=x1; if (cx<=0){ cx+=n; x0+=sx; }
cy-=y1; if (cy<=0){ cy+=n; y0+=sy; }
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::_fill_line(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1)
{
int i,n,cx,cy,sx,sy,*buf;
// line DDA parameters
x1-=x0; sx=0; if (x1>0) sx=+1; if (x1<0) { sx=-1; x1=-x1; } if (x1) x1++; n=x1;
y1-=y0; sy=0; if (y1>0) sy=+1; if (y1<0) { sy=-1; y1=-y1; } if (y1) y1++; if (n<y1) n=y1;
// single pixel (not a line)
if (!n)
{
if ((y0>=0)&&(y0<ys))
{
bufl[y0]=x0;
bufr[y0]=x0;
}
return;
}
// target buffer depend on y direction
if (sy>0) buf=bufl; else buf=bufr;
// ND DDA algo i is parameter
for (cx=cy=n,i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if ((y0>=0)&&(y0<ys)) buf[y0]=x0;
cx-=x1; if (cx<=0){ cx+=n; x0+=sx; }
cy-=y1; if (cy<=0){ cy+=n; y0+=sy; }
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::_fill_seed()
{
seed=0x017A357E1;
// RandSeed=0x017A357E1;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
U8 LCD_SSD1306_I2C::_fill_rand()
{
U32 a,b,c;
a= seed &0x0FFFF;
b=(seed>>16)&0x0FFFF;
seed<<=11;
seed^=(a<<16);
seed&=0x0FFFF0000;
seed|=b+17;
return seed&255;
// return Random(256);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::triangle(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,bool col)
{
line(x0,y0,x1,y1,col);
line(x1,y1,x2,y2,col);
line(x2,y2,x0,y0,col);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::pat_triangle(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,bool col)
{
pat_line(x0,y0,x1,y1,col);
pat_line(x1,y1,x2,y2,col);
pat_line(x2,y2,x0,y0,col);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::fill_triangle(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,U8 col)
{
int x,y,X0,X1,Y0,Y1;
// y range to render
Y0=Y1=y0;
if (Y0>y1) Y0=y1;
if (Y1<y1) Y1=y1;
if (Y0>y2) Y0=y2;
if (Y1<y2) Y1=y2;
// clip to screen in y axis
if ((Y1<0)||(Y0>=ys)) return;
if (Y0< 0) Y0= 0;
if (Y1>=ys) Y1=ys-1;
// clear buffers
for (y=Y0;y<=Y1;y++)
{
bufl[y]=xs;
bufr[y]=-1;
}
// render circumference
_fill_line(x0,y0,x1,y1);
_fill_line(x1,y1,x2,y2);
_fill_line(x2,y2,x0,y0);
// fill horizontal lines
_fill_seed();
for (y=Y0;y<=Y1;y++)
{
// x range to render
X0=bufl[y];
X1=bufr[y];
if (X0>X1){ x=X0; X0=X1; X1=x; }
// clip to screen in y axis
if ((X1<0)||(X0>=xs)) continue;
if (X0< 0) X0= 0;
if (X1>=xs) X1=xs-1;
if (col== 0) for (x=X0;x<=X1;x++) pixel(x,y,0);
else if (col==255) for (x=X0;x<=X1;x++) pixel(x,y,1);
else for (x=X0;x<=X1;x++) pixel(x,y,(_fill_rand()<=col));
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::quad(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int x3,int y3,bool col)
{
line(x0,y0,x1,y1,col);
line(x1,y1,x2,y2,col);
line(x2,y2,x3,y3,col);
line(x3,y3,x0,y0,col);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::pat_quad(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int x3,int y3,bool col)
{
pat_line(x0,y0,x1,y1,col);
pat_line(x1,y1,x2,y2,col);
pat_line(x2,y2,x3,y3,col);
pat_line(x3,y3,x0,y0,col);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::fill_quad(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int x3,int y3,U8 col)
{
int x,y,X0,X1,Y0,Y1;
// y range to render
Y0=Y1=y0;
if (Y0>y1) Y0=y1;
if (Y1<y1) Y1=y1;
if (Y0>y2) Y0=y2;
if (Y1<y2) Y1=y2;
if (Y0>y3) Y0=y3;
if (Y1<y3) Y1=y3;
// clip to screen in y axis
if ((Y1<0)||(Y0>=ys)) return;
if (Y0< 0) Y0= 0;
if (Y1>=ys) Y1=ys-1;
// clear buffers
for (y=Y0;y<=Y1;y++)
{
bufl[y]=xs;
bufr[y]=-1;
}
// render circumference
_fill_line(x0,y0,x1,y1);
_fill_line(x1,y1,x2,y2);
_fill_line(x2,y2,x3,y3);
_fill_line(x3,y3,x0,y0);
// fill horizontal lines
_fill_seed();
for (y=Y0;y<=Y1;y++)
{
// x range to render
X0=bufl[y];
X1=bufr[y];
if (X0>X1){ x=X0; X0=X1; X1=x; }
// clip to screen in y axis
if ((X1<0)||(X0>=xs)) continue;
if (X0< 0) X0= 0;
if (X1>=xs) X1=xs-1;
if (col== 0) for (x=X0;x<=X1;x++) pixel(x,y,0);
else if (col==255) for (x=X0;x<=X1;x++) pixel(x,y,1);
else for (x=X0;x<=X1;x++) pixel(x,y,(_fill_rand()<=col));
}
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::rect(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,bool col)
{
line(x0,y0,x1,y0,col);
line(x1,y0,x1,y1,col);
line(x1,y1,x0,y1,col);
line(x0,y1,x0,y0,col);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::pat_rect(int x0,int y0,int x1,int y1,bool col)
{
pat_line(x0,y0,x1,y0,col);
pat_line(x1,y0,x1,y1,col);
pat_line(x1,y1,x0,y1,col);
pat_line(x0,y1,x0,y0,col);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::prnchr(int x,int y,char c)
{
y&=0xFFFFFFF8; // multiple of 8
if ((y<0)||(y>ys-8)) return;
int i,a;
a=c; a<<=3;
for (i=0;i<8;i++,x++,a++)
if ((x>=0)&&(x<xs))
pyx[y][x]=font[a];
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::prntxt(int x,int y,const char *txt)
{
for (;*txt;txt++,x+=8) prnchr(x,y,*txt);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::pat_set(char *s)
{
int i=1;
pat=0;
if (s!=NULL)
for (i=0;(*s)&&(i<32);s++,i++)
{
pat<<=1;
if (*s=='1') pat|=1;
}
if (!i) i=1;
pat_m=1<<(i-1);
pat_beg();
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LCD_SSD1306_I2C::pat_beg()
{
pat_b=pat_m;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#undef I2C_send
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#endif
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Its written for AVR32 studio 2.7 so on platforms where there is no U8/U16/U32 use unsigned int instead of the same (or bigger) bitwidth.
The code is not optimized and is deliberately written in manner it is (not for speed, I use this also on my lectures so students can grasp what I am doing)
Now when I render rotating cube (on win32 VCL test app on PC) using 2D filled quads using this technique:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include <vcl.h>
#include <math.h>
#pragma hdrstop
#include "win_main.h"
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#pragma package(smart_init)
#pragma resource "*.dfm"
TMain *Main;
const int sz=4; // LCD pixel size
int xs,ys; // LCD resolution * sz
int *psz; // screen pixel to LCD pixel
Graphics::TBitmap *bmp; // screen buffer
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
typedef BYTE U8; // here use data types you got like unsigned __int8_t ...
typedef WORD U16;
typedef DWORD U32;
void I2C_send(int adr,U8 *buf,int siz){}
//#include "font_8x8.h" // font file
static U8 font[256<<3]; // empty font instead (no printing used)
#include "LCD_SSD1306_I2C.h"
LCD_SSD1306_I2C lcd;
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
const float cube_pos[]=
{
// x y z //ix
-1.0,+1.0,-1.0, //0
+1.0,+1.0,-1.0, //1
+1.0,-1.0,-1.0, //2
-1.0,-1.0,-1.0, //3
-1.0,-1.0,+1.0, //4
+1.0,-1.0,+1.0, //5
+1.0,+1.0,+1.0, //6
-1.0,+1.0,+1.0, //7
-1.0,-1.0,-1.0, //3
+1.0,-1.0,-1.0, //2
+1.0,-1.0,+1.0, //5
-1.0,-1.0,+1.0, //4
+1.0,-1.0,-1.0, //2
+1.0,+1.0,-1.0, //1
+1.0,+1.0,+1.0, //6
+1.0,-1.0,+1.0, //5
+1.0,+1.0,-1.0, //1
-1.0,+1.0,-1.0, //0
-1.0,+1.0,+1.0, //7
+1.0,+1.0,+1.0, //6
-1.0,+1.0,-1.0, //0
-1.0,-1.0,-1.0, //3
-1.0,-1.0,+1.0, //4
-1.0,+1.0,+1.0, //7
};
const float cube_nor[]=
{
// nx ny nz //ix
0.0, 0.0,-1.0, //0
0.0, 0.0,-1.0, //1
0.0, 0.0,-1.0, //2
0.0, 0.0,-1.0, //3
0.0, 0.0,+1.0, //4
0.0, 0.0,+1.0, //5
0.0, 0.0,+1.0, //6
0.0, 0.0,+1.0, //7
0.0,-1.0, 0.0, //0
0.0,-1.0, 0.0, //1
0.0,-1.0, 0.0, //5
0.0,-1.0, 0.0, //4
+1.0, 0.0, 0.0, //1
+1.0, 0.0, 0.0, //2
+1.0, 0.0, 0.0, //6
+1.0, 0.0, 0.0, //5
0.0,+1.0, 0.0, //2
0.0,+1.0, 0.0, //3
0.0,+1.0, 0.0, //7
0.0,+1.0, 0.0, //6
-1.0, 0.0, 0.0, //3
-1.0, 0.0, 0.0, //0
-1.0, 0.0, 0.0, //4
-1.0, 0.0, 0.0, //7
};
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void matrix_mul_pos(float *c,const float *a,const float *b)
{
float q[3];
q[0]=(a[ 0]*b[0])+(a[ 4]*b[1])+(a[ 8]*b[2])+(a[12]);
q[1]=(a[ 1]*b[0])+(a[ 5]*b[1])+(a[ 9]*b[2])+(a[13]);
q[2]=(a[ 2]*b[0])+(a[ 6]*b[1])+(a[10]*b[2])+(a[14]);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) c[i]=q[i];
}
void matrix_mul_dir(float *c,const float *a,const float *b)
{
float q[3];
q[0]=(a[ 0]*b[0])+(a[ 4]*b[1])+(a[ 8]*b[2]);
q[1]=(a[ 1]*b[0])+(a[ 5]*b[1])+(a[ 9]*b[2]);
q[2]=(a[ 2]*b[0])+(a[ 6]*b[1])+(a[10]*b[2]);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) c[i]=q[i];
}
void matrix_mul_mat(float *c,float *a,float *b)
{
float q[16];
q[ 0]=(a[ 0]*b[ 0])+(a[ 1]*b[ 4])+(a[ 2]*b[ 8])+(a[ 3]*b[12]);
q[ 1]=(a[ 0]*b[ 1])+(a[ 1]*b[ 5])+(a[ 2]*b[ 9])+(a[ 3]*b[13]);
q[ 2]=(a[ 0]*b[ 2])+(a[ 1]*b[ 6])+(a[ 2]*b[10])+(a[ 3]*b[14]);
q[ 3]=(a[ 0]*b[ 3])+(a[ 1]*b[ 7])+(a[ 2]*b[11])+(a[ 3]*b[15]);
q[ 4]=(a[ 4]*b[ 0])+(a[ 5]*b[ 4])+(a[ 6]*b[ 8])+(a[ 7]*b[12]);
q[ 5]=(a[ 4]*b[ 1])+(a[ 5]*b[ 5])+(a[ 6]*b[ 9])+(a[ 7]*b[13]);
q[ 6]=(a[ 4]*b[ 2])+(a[ 5]*b[ 6])+(a[ 6]*b[10])+(a[ 7]*b[14]);
q[ 7]=(a[ 4]*b[ 3])+(a[ 5]*b[ 7])+(a[ 6]*b[11])+(a[ 7]*b[15]);
q[ 8]=(a[ 8]*b[ 0])+(a[ 9]*b[ 4])+(a[10]*b[ 8])+(a[11]*b[12]);
q[ 9]=(a[ 8]*b[ 1])+(a[ 9]*b[ 5])+(a[10]*b[ 9])+(a[11]*b[13]);
q[10]=(a[ 8]*b[ 2])+(a[ 9]*b[ 6])+(a[10]*b[10])+(a[11]*b[14]);
q[11]=(a[ 8]*b[ 3])+(a[ 9]*b[ 7])+(a[10]*b[11])+(a[11]*b[15]);
q[12]=(a[12]*b[ 0])+(a[13]*b[ 4])+(a[14]*b[ 8])+(a[15]*b[12]);
q[13]=(a[12]*b[ 1])+(a[13]*b[ 5])+(a[14]*b[ 9])+(a[15]*b[13]);
q[14]=(a[12]*b[ 2])+(a[13]*b[ 6])+(a[14]*b[10])+(a[15]*b[14]);
q[15]=(a[12]*b[ 3])+(a[13]*b[ 7])+(a[14]*b[11])+(a[15]*b[15]);
for(int i=0;i<16;i++) c[i]=q[i];
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
float deg=M_PI/180.0,angx=0.0,angy=0.0,angz=5.0*deg;
float view_FOVx=128.0*tan(30.0*deg)*0.5;
void obj2scr(int &x,int &y,const float *m,const float *pos)
{
float p[3],d;
x=0; y=0;
matrix_mul_pos(p,m,pos);
if (fabs(p[2])>1e-3) d=view_FOVx/p[2]; else d=0.0;
p[0]*=d; x=2.5*p[0]; x+=64;
p[1]*=d; y=2.5*p[1]; y+=32;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void TMain::draw()
{
int i,j,n,nz;
int x,y,x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3;
lcd.clrscr();
// modelview
float p[3],c,s,m[16],m0[16]=
{
1.0, 0.0, 0.0,0.0,
0.0, 1.0, 0.0,0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0,0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 7.0,1.0,
};
c=cos(angx); s=sin(angx);
float rx[16]= { 1, 0, 0, 0,
0, c, s, 0,
0,-s, c, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1 };
c=cos(angy); s=sin(angy);
float ry[16]= { c, 0, s, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0,
-s, 0, c, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1 };
c=cos(angz); s=sin(angz);
float rz[16]= { c, s, 0, 0,
-s, c, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1 };
matrix_mul_mat(m,rx,ry);
matrix_mul_mat(m,m,rz);
matrix_mul_mat(m,m,m0);
angx=fmod(angx+1.0*deg,2.0*M_PI);
angy=fmod(angy+5.0*deg,2.0*M_PI);
angz=fmod(angz+2.0*deg,2.0*M_PI);
n=6*4*3;
for (i=0;i<n;)
{
matrix_mul_dir(p,m,cube_nor+i);
nz=float(-255.0*p[2]*fabs(p[2]));
obj2scr(x0,y0,m,cube_pos+i); i+=3;
obj2scr(x1,y1,m,cube_pos+i); i+=3;
obj2scr(x2,y2,m,cube_pos+i); i+=3;
obj2scr(x3,y3,m,cube_pos+i); i+=3;
if (nz>0)
{
nz=100+((150*nz)>>8);
lcd.fill_quad(x0,y0,x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,nz);
}
}
lcd.rfsscr();
// copy LCD to Canvas to see result
if (1)
{
DWORD col[2]={0x00100018,0x00FFFFFF},*p;
int x,y,xx,yy;
for ( y=0,yy=psz[y];y<ys;y++,yy=psz[y])
for (p=(DWORD*)bmp->ScanLine[y],x=0,xx=psz[x];x<xs;x++,xx=psz[x])
p[x]=col[lcd.pixel(xx,yy)];
}
Canvas->Draw(0,0,bmp);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
__fastcall TMain::TMain(TComponent* Owner) : TForm(Owner)
{
lcd.init(0x3C,128,64);
bmp=new Graphics::TBitmap;
bmp->HandleType=bmDIB;
bmp->PixelFormat=pf32bit;
xs=lcd.xs*sz;
ys=lcd.ys*sz;
bmp->SetSize(xs,ys);
ClientWidth=xs;
ClientHeight=ys;
int i,n;
n=xs; if (n<ys) n=ys;
psz=new int[n+1];
for (i=0;i<n;i++) psz[i]=i/sz; psz[n]=0;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void __fastcall TMain::FormDestroy(TObject *Sender)
{
delete[] psz;
delete bmp;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void __fastcall TMain::tim_redrawTimer(TObject *Sender)
{
draw();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Just ignore the VCL stuff. The App has single timer which periodically redrawing screen. The lcd needs to be initialized first. The lcd uses I2C_send function to communicate by I2C so you have to implement it in order to use it with real LCD, If you just copy the screen into image or view (emulation) then empty function like I did will suffice. The same goes for printing texts it needs this font (it does not fit in here) so I used empty one (as the example does not print anything anyway).
I got this output (using the randomized shading filling and basic normal shading):
As you can see due to low resolution the cube is barely distinguishable I was hoping for something better.
So finally my question:
How to visually improve this kind of shading
I was thinking about some kind of hatching or predefined patterns more similar to Freescape engine output like this:

Do you have any ideas or pointers how to do this kind of 2D convex polygon filling?
The limitation is low resolution 128x64 1bpp image, low memory usage as target AVR32 UC3 platform have only (16+32+32) KBytes of RAM and in case someone would like to use AVR8 chips then only 2 KByte (you know Arduino use those).
Speed is not major concern as target platform has ~91 MIPS.
I am not very skilled with BW shading (back in the days I used mostly wireframe for BW output) so even hints from experienced users like:
- how many shades
16/32/256? - how big patterns
4x4/8x8/16x16? - how to generate the patterns (hardcoded, or some algo) ?
- how to deal with polygon movement to avoid noise/flickering (right now I reset Seed on each polygon)
might help me a lot.
Here a sample input image for testing: