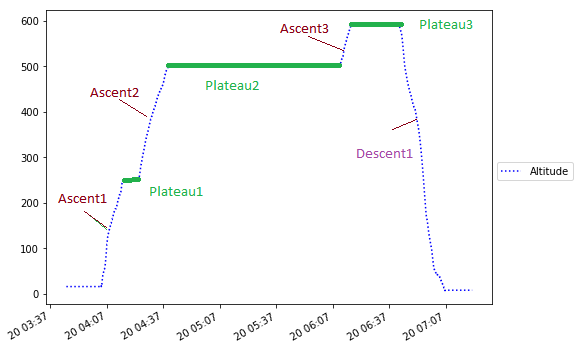
Analysing time series data of bike trails, I would like to know the time interval for each plateau ,ascent and descent.Sample csv file is uploaded here.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from datetime import datetime
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
df = pd.read_csv(r'C:\Data\Sample.csv', parse_dates=['dateTime'])
feature_used='Cycle_Alt'
print("Eliminating null values..")
df=df[df[feature_used].notnull()]
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
x=df['dateTime']
y=df['Cycle_Alt']
plt.plot(x,y,c='b',linestyle=':',label="Altitude")
plt.xticks(rotation='vertical')
plt.gcf().autofmt_xdate()
plt.legend(loc='best', bbox_to_anchor=(1, 0.5))
This plot provides me with a cross-profile like this.
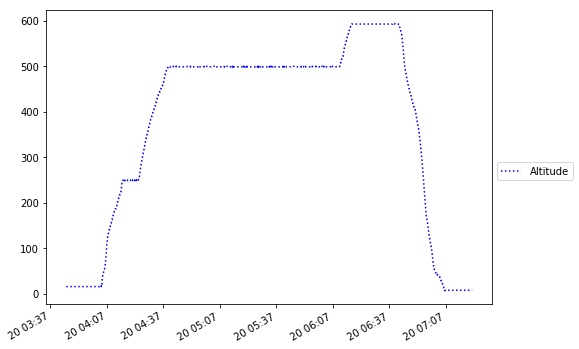
What could be done to classify the time-series data to detect each plateau ,ascent and descent, with the assumption that one may have more variables than presented in the sample.