Based on a feature mentioned in this answer to another question I have found a very generally applicable solution for placing labels on a bar chart.
Other solutions unfortunately do not work in many cases, because the spacing between label and bar is either given in absolute units of the bars or is scaled by the height of the bar. The former only works for a narrow range of values and the latter gives inconsistent spacing within one plot. Neither works well with logarithmic axes.
The solution I propose works independent of scale (i.e. for small and large numbers) and even correctly places labels for negative values and with logarithmic scales because it uses the visual unit points for offsets.
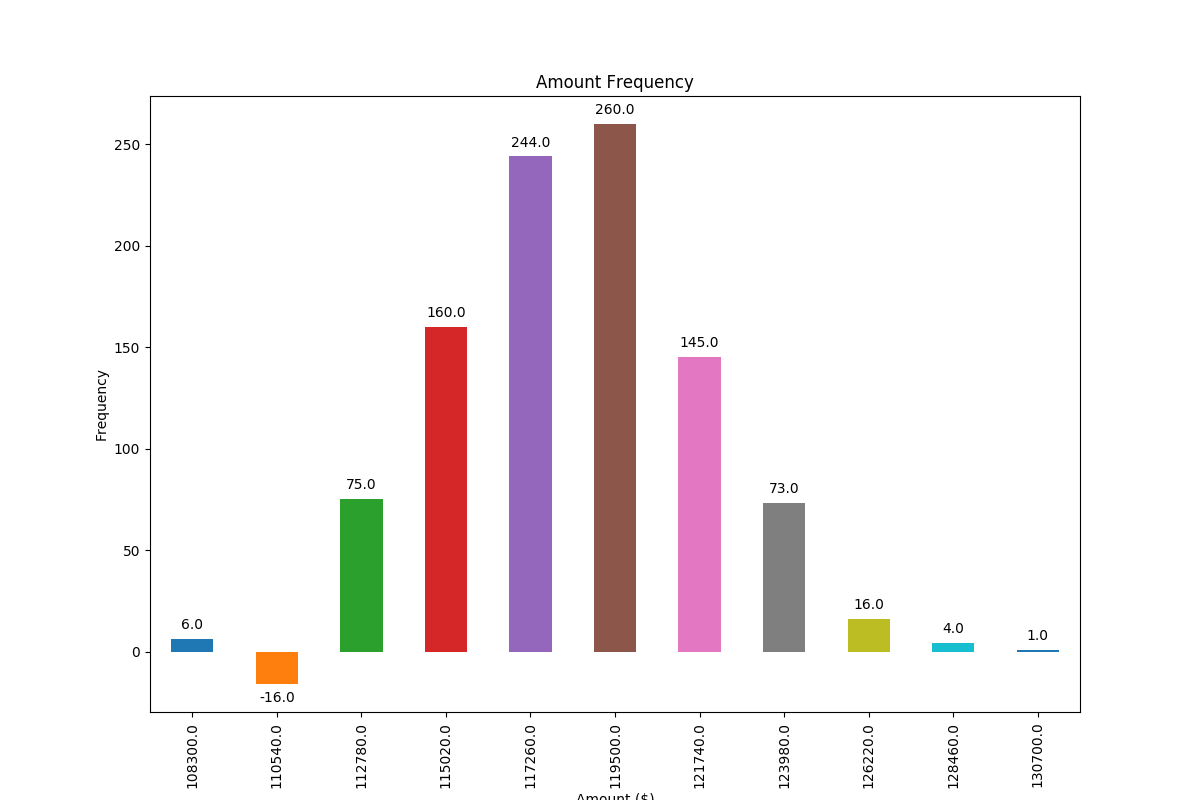
I have added a negative number to showcase the correct placement of labels in such a case.
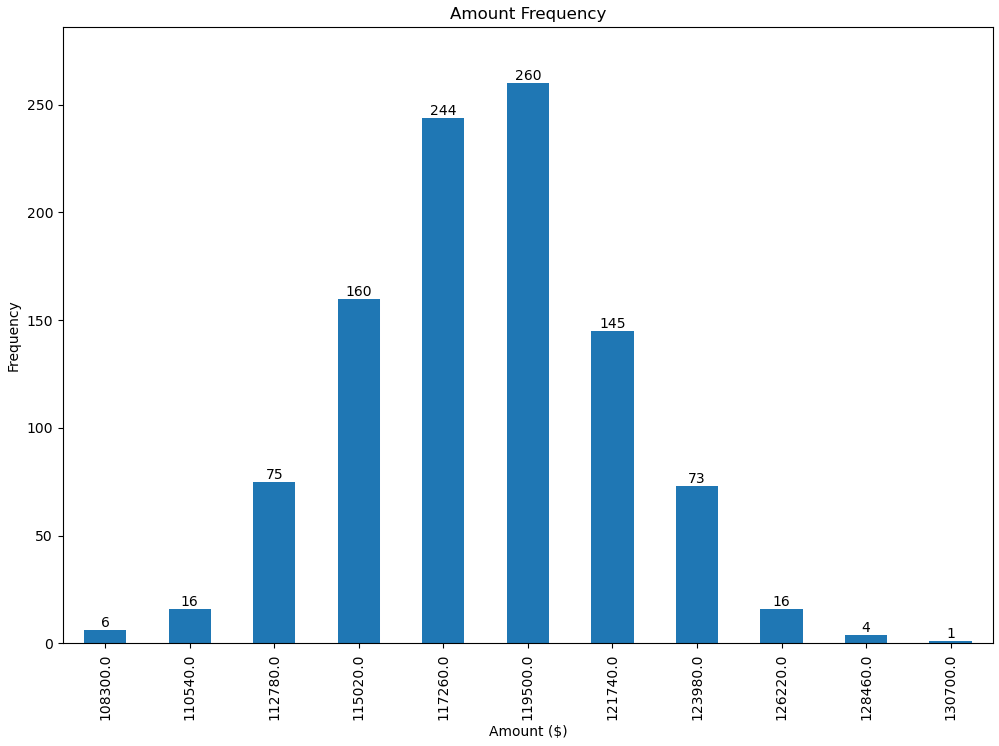
The value of the height of each bar is used as a label for it. Other labels can easily be used with Simon's for rect, label in zip(rects, labels) snippet.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Bring some raw data.
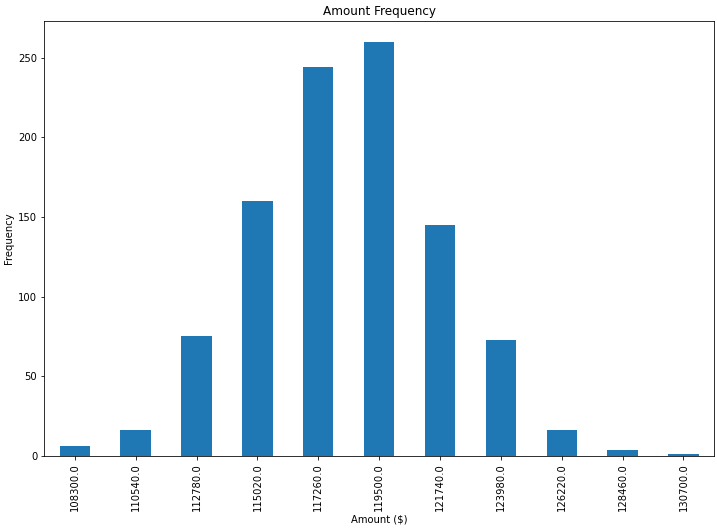
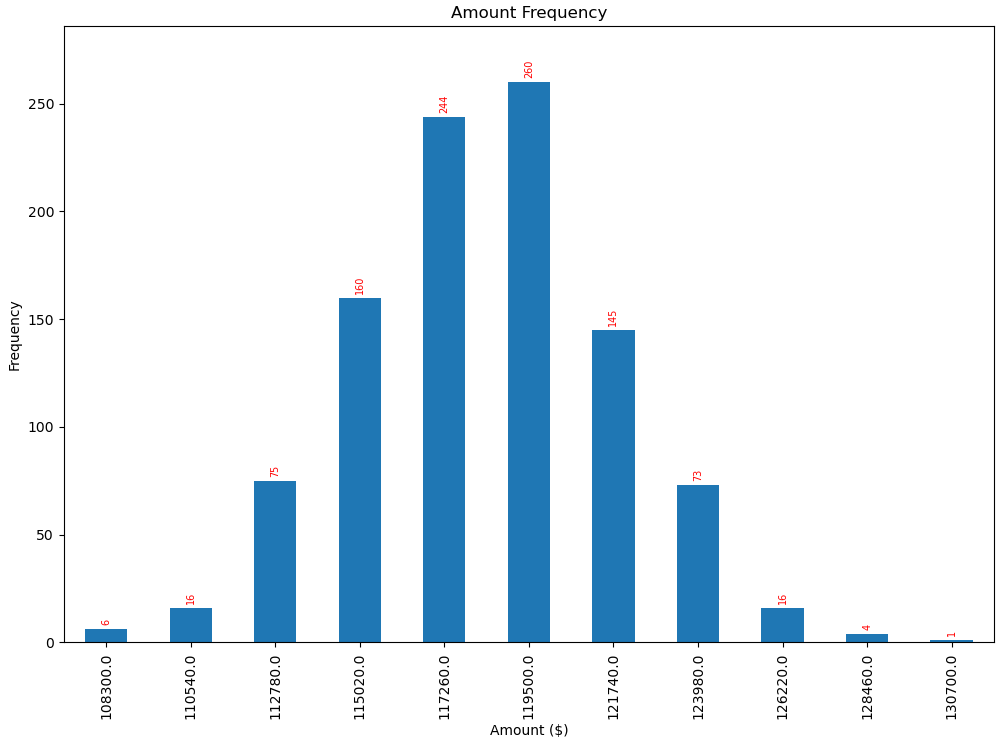
frequencies = [6, -16, 75, 160, 244, 260, 145, 73, 16, 4, 1]
# In my original code I create a series and run on that,
# so for consistency I create a series from the list.
freq_series = pd.Series.from_array(frequencies)
x_labels = [108300.0, 110540.0, 112780.0, 115020.0, 117260.0, 119500.0,
121740.0, 123980.0, 126220.0, 128460.0, 130700.0]
# Plot the figure.
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
ax = freq_series.plot(kind='bar')
ax.set_title('Amount Frequency')
ax.set_xlabel('Amount ($)')
ax.set_ylabel('Frequency')
ax.set_xticklabels(x_labels)
def add_value_labels(ax, spacing=5):
"""Add labels to the end of each bar in a bar chart.
Arguments:
ax (matplotlib.axes.Axes): The matplotlib object containing the axes
of the plot to annotate.
spacing (int): The distance between the labels and the bars.
"""
# For each bar: Place a label
for rect in ax.patches:
# Get X and Y placement of label from rect.
y_value = rect.get_height()
x_value = rect.get_x() + rect.get_width() / 2
# Number of points between bar and label. Change to your liking.
space = spacing
# Vertical alignment for positive values
va = 'bottom'
# If value of bar is negative: Place label below bar
if y_value < 0:
# Invert space to place label below
space *= -1
# Vertically align label at top
va = 'top'
# Use Y value as label and format number with one decimal place
label = "{:.1f}".format(y_value)
# Create annotation
ax.annotate(
label, # Use `label` as label
(x_value, y_value), # Place label at end of the bar
xytext=(0, space), # Vertically shift label by `space`
textcoords="offset points", # Interpret `xytext` as offset in points
ha='center', # Horizontally center label
va=va) # Vertically align label differently for
# positive and negative values.
# Call the function above. All the magic happens there.
add_value_labels(ax)
plt.savefig("image.png")
Edit: I have extracted the relevant functionality in a function, as suggested by barnhillec.
This produces the following output:
![Bar chart with automatically placed labels on each bar]()
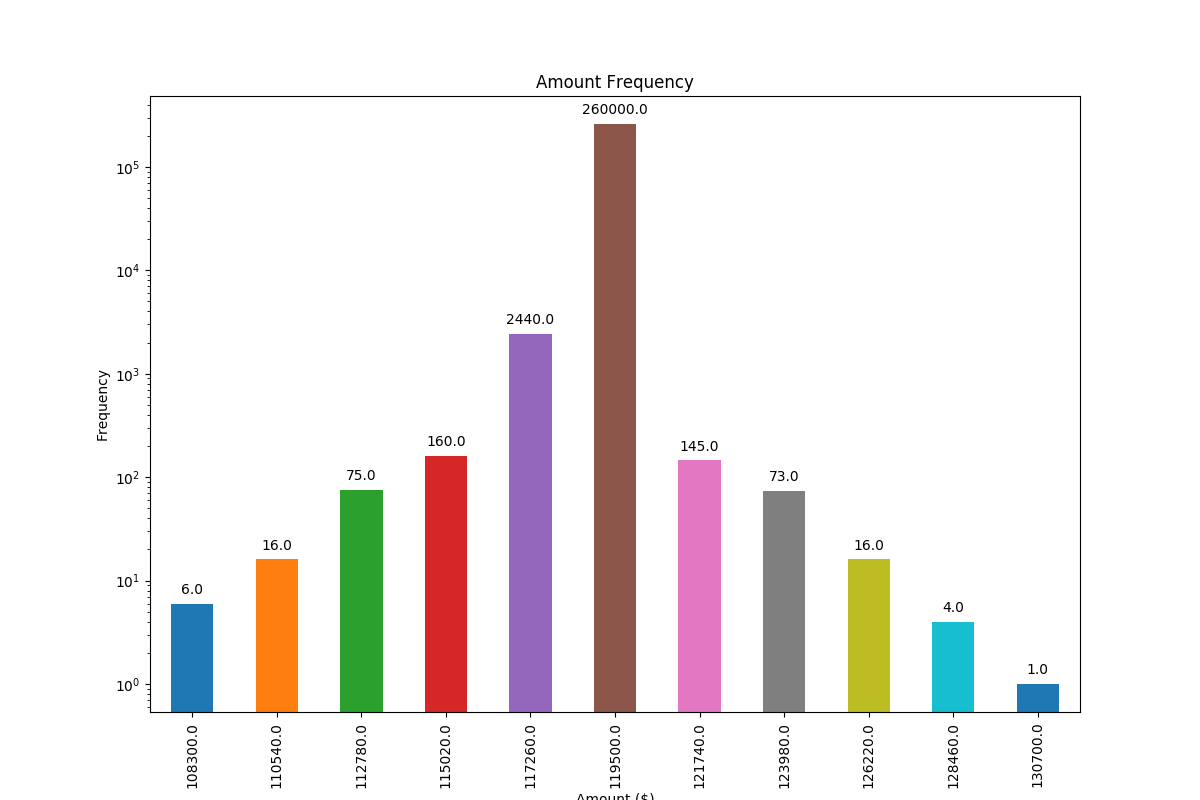
And with logarithmic scale (and some adjustment to the input data to showcase logarithmic scaling), this is the result:
![Bar chart with logarithmic scale with automatically placed labels on each bar]()



matplotlib >= 3.4.2use.bar_label, as shown in this answer. Applies topandasandseaborn, which usematplotlib. – Keeton