Which is the fastest algorithm to find out prime numbers using C++? I have used sieve's algorithm but I still want it to be faster!
A very fast implementation of the Sieve of Atkin is Dan Bernstein's primegen. This sieve is more efficient than the Sieve of Eratosthenes. His page has some benchmark information.
log log N Of course, this is so tiny it isn't going to matter much more than generic tuning. –
Clue If it has to be really fast you can include a list of primes:
http://www.bigprimes.net/archive/prime/
If you just have to know if a certain number is a prime number, there are various prime tests listed on wikipedia. They are probably the fastest method to determine if large numbers are primes, especially because they can tell you if a number is not a prime.
Until now, I believe that the fastest prime number testing algorithm is Strong Probable Prime (SPRP). I am quoting from Nvidia CUDA forums:
One of the more practical niche problems in number theory has to do with identification of prime numbers. Given N, how can you efficiently determine if it is prime or not? This is not just a thoeretical problem, it may be a real one needed in code, perhaps when you need to dynamically find a prime hash table size within certain ranges. If N is something on the order of 2^30, do you really want to do 30000 division tests to search for any factors? Obviously not.
The common practical solution to this problem is a simple test called an Euler probable prime test, and a more powerful generalization called a Strong Probable Prime (SPRP). This is a test that for an integer N can probabilistically classify it as prime or not, and repeated tests can increase the correctness probability. The slow part of the test itself mostly involves computing a value similar to A^(N-1) modulo N. Anyone implementing RSA public-key encryption variants has used this algorithm. It's useful both for huge integers (like 512 bits) as well as normal 32 or 64 bit ints.
The test can be changed from a probabilistic rejection into a definitive proof of primality by precomputing certain test input parameters which are known to always succeed for ranges of N. Unfortunately the discovery of these "best known tests" is effectively a search of a huge (in fact infinite) domain. In 1980, a first list of useful tests was created by Carl Pomerance (famous for being the one to factor RSA-129 with his Quadratic Seive algorithm.) Later Jaeschke improved the results significantly in 1993. In 2004, Zhang and Tang improved the theory and limits of the search domain. Greathouse and Livingstone have released the most modern results until now on the web, at http://math.crg4.com/primes.html, the best results of a huge search domain.
See here for more info: http://primes.utm.edu/prove/prove2_3.html and http://forums.nvidia.com/index.php?showtopic=70483
If you just need a way to generate very big prime numbers and don't care to generate all prime numbers < an integer n, you can use Lucas-Lehmer test to verify Mersenne prime numbers. A Mersenne prime number is in the form of 2^p -1. I think that Lucas-Lehmer test is the fastest algorithm discovered for Mersenne prime numbers.
And if you not only want to use the fastest algorithm but also the fastest hardware, try to implement it using Nvidia CUDA, write a kernel for CUDA and run it on GPU.
You can even earn some money if you discover large enough prime numbers, EFF is giving prizes from $50K to $250K: https://www.eff.org/awards/coop
There is a 100% mathematical test that will check if a number P is prime or composite, called AKS Primality Test.
The concept is simple: given a number P, if all the coefficients of (x-1)^P - (x^P-1) are divisible by P, then P is a prime number, otherwise it is a composite number.
For instance, given P = 3, would give the polynomial:
(x-1)^3 - (x^3 - 1)
= x^3 + 3x^2 - 3x - 1 - (x^3 - 1)
= 3x^2 - 3x
And the coefficients are both divisible by 3, therefore the number is prime.
And example where P = 4, which is NOT a prime would yield:
(x-1)^4 - (x^4-1)
= x^4 - 4x^3 + 6x^2 - 4x + 1 - (x^4 - 1)
= -4x^3 + 6x^2 - 4x
And here we can see that the coefficients 6 is not divisible by 4, therefore it is NOT prime.
The polynomial (x-1)^P will P+1 terms and can be found using combination. So, this test will run in O(n) runtime, so I don't know how useful this would be since you can simply iterate over i from 0 to p and test for the remainder.
x stands for? in (x-1)^P - (x^P-1). do you have a sample code for this? in C++ for determining if the integer is prime or not? –
Sashenka Is your problem to decide whether a particular number is prime? Then you need a primality test (easy). Or do you need all primes up to a given number? In that case prime sieves are good (easy, but require memory). Or do you need the prime factors of a number? This would require factorization (difficult for large numbers if you really want the most efficient methods). How large are the numbers you are looking at? 16 bits? 32 bits? bigger?
One clever and efficient way is to pre-compute tables of primes and keep them in a file using a bit-level encoding. The file is considered one long bit vector whereas bit n represents integer n. If n is prime, its bit is set to one and to zero otherwise. Lookup is very fast (you compute the byte offset and a bit mask) and does not require loading the file in memory.
Rabin-Miller is a standard probabilistic primality test. (you run it K times and the input number is either definitely composite, or it is probably prime with probability of error 4-K. (a few hundred iterations and it's almost certainly telling you the truth)
There is a non-probabilistic (deterministic) variant of Rabin Miller.
The Great Internet Mersenne Prime Search (GIMPS) which has found the world's record for largest proven prime (274,207,281 - 1 as of June 2017), uses several algorithms, but these are primes in special forms. However the GIMPS page above does include some general deterministic primality tests. They appear to indicate that which algorithm is "fastest" depends upon the size of the number to be tested. If your number fits in 64 bits then you probably shouldn't use a method intended to work on primes of several million digits.
It depends on your application. There are some considerations:
- Do you need just the information whether a few numbers are prime, do you need all prime numbers up to a certain limit, or do you need (potentially) all prime numbers?
- How big are the numbers you have to deal with?
The Miller-Rabin and analogue tests are only faster than a sieve for numbers over a certain size (somewhere around a few million, I believe). Below that, using a trial division (if you just have a few numbers) or a sieve is faster.
This is an implementation of the Sieve of Eratosthenes in Python I've been toying with.
def eratosthenes(maximum: int) -> list[int | None]:
"""
Find all the prime numbers between 2 and `maximum`.
Args:
maximum: The maximum number to check.
Returns:
A list of primes between 2 and `maximum`.
"""
if maximum < 2:
return []
# Discard even numbers by default.
sequence = dict.fromkeys(range(3, maximum+1, 2), True)
for num, is_prime in sequence.items():
# Already filtered, let's skip it.
if not is_prime:
continue
# Avoid marking the same number twice.
for num2 in range(num ** 2, maximum+1, num):
# Here, `num2` might contain an even number - skip it.
if num2 in sequence:
sequence[num2] = False
# Re-add 2 as prime and filter out the composite numbers.
return [2] + [num for num, is_prime in sequence.items() if is_prime]
The code appears to take roughly 16s for 10000000 numbers on a humble Samsung Galaxy A40.
Suggestions are welcome!
-> list[int]. An empty list (that you probably refer to with the None?) is still a list of int. –
Hate if num2 in sequence: by if num2 % 2:. This is significantly faster (and in my opinion better to read). –
Hate I found this solution pretty fast but it comes with consequences, So this is called Fermat's Little Theorem. If we take any number p and put that in (1^p)-1 or (2^p)-2...(n^p)-n likewise and the number we get is divisible by p then it's a prime number. Talking about consequences, it's not 100% right solution. There are some numbers like 341(not prime) it will pass the test with (2^341)-2 but fails on (3^341)-3, so it's called a composite number. We can have two or more checks to make sure they pass all of them. There is one more kind of number which are not prime but also pass all the test case:( 561, 1729 Ramanujan taxi no etc.
The good thing: With
(2^p)-2in first 25 billion numbers only 2183 fails this case.
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int isPrime(int p)
{
int tc = pow(2, p) - 2;
if (tc % p == 0)
{
cout << p << "is Prime ";
}
else
{
cout << p << "is Not Prime";
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int p;
cin >> p;
isPrime(p);
return 0;
}
Another Python implementation that is more straightforward and slightly faster* than the one in the answer of Death Mask Salesman:
import numpy as np
def prime_numbers(limit: int) -> list[int]:
"""Provide a list of all prime numbers <= the limit."""
is_prime = np.full((limit + 1, ), True)
is_prime[0:2] = False
for n in range(2, limit + 1):
if is_prime[n]:
is_prime[n**2::n] = False
return list(np.where(is_prime)[0])
You could further optimize by, e.g., excluding the 2, or by hard-coding even more prime numbers, but I wanted to keep it simple.
*exemplary runtime comparison (note: I used the optimized form of the other implementation, see my comment):
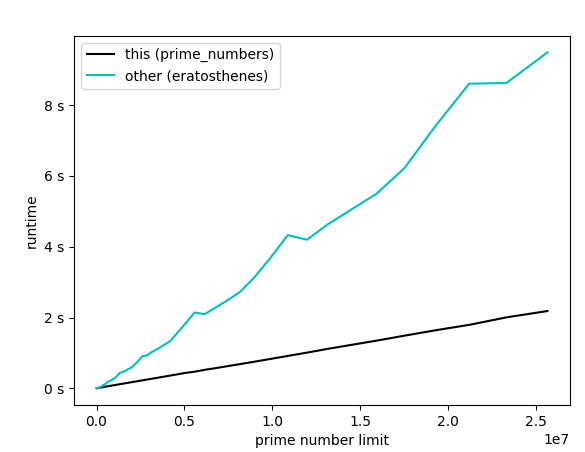
def erastothenes, while mine is def prime_numbers). –
Hate i wrote it today in C,compiled with tcc, figured out during preparation of compititive exams several years back. don't know if anyone already have wrote it alredy. it really fast(but you should decide whether it is fast or not). took one or two minuts to findout about 1,00,004 prime numbers between 10 and 1,00,00,000 on i7 processor with average 32% CPU use. as you know, only those can be prime which have last digit either 1,3,7 or 9 and to check if that number is prime or not, you have to divide that number by previously found prime numbers only. so first take group of four number = {1,3,7,9}, test it by dividing by known prime numbers, if reminder is non zero then number is prime, add it to prime number array. then add 10 to group so it becomes {11,13,17,19} and repeat the process.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int nums[4]={1,3,7,9};
int primes[100000];
primes[0]=2;
primes[1]=3;
primes[2]=5;
primes[3]=7;
int found = 4;
int got = 1;
int m=0;
int upto = 1000000;
for(int i=0;i<upto;i++){
//printf("iteration number: %d\n",i);
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
m = nums[j]+10;
//printf("m = %d\n",m);
nums[j] = m;
got = 1;
for(int k=0;k<found;k++){
//printf("testing with %d\n",primes[k]);
if(m%primes[k]==0){
got = 0;
//printf("%d failed for %d\n",m,primes[k]);
break;
}
}
if(got==1){
//printf("got new prime: %d\n",m);
primes[found]= m;
found++;
}
}
}
printf("found total %d prime numbers between 1 and %d",found,upto*10);
return 0;
}
I recently wrote this code to find the sum of numbers. It can be easily modified to find if a number is prime or not instead. Benchmarks are on top of the code.
// built on core-i2 e8400
// Benchmark from PowerShell
// Measure-Command { ExeName.exe }
// Days : 0
// Hours : 0
// Minutes : 0
// Seconds : 23
// Milliseconds : 516
// Ticks : 235162598
// TotalDays : 0.00027217893287037
// TotalHours : 0.00653229438888889
// TotalMinutes : 0.391937663333333
// TotalSeconds : 23.5162598
// TotalMilliseconds : 23516.2598
// built with latest MSVC
// cl /EHsc /std:c++latest main.cpp /O2 /fp:fast /Qpar
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
inline auto prime = [](std::uint64_t I, std::vector<std::uint64_t> &cache) -> std::uint64_t {
std::uint64_t root{static_cast<std::uint64_t>(std::sqrtl(I))};
for (std::size_t i{}; cache[i] <= root; ++i)
if (I % cache[i] == 0)
return 0;
cache.push_back(I);
return I;
};
inline auto prime_sum = [](std::uint64_t S) -> std::uint64_t {
std::uint64_t R{5};
std::vector<std::uint64_t> cache;
cache.reserve(S / 16);
cache.push_back(3);
for (std::uint64_t I{5}; I <= S; I += 8)
{
std::uint64_t U{I % 3};
if (U != 0)
R += prime(I, cache);
if (U != 1)
R += prime(I + 2, cache);
if (U != 2)
R += prime(I + 4, cache);
R += prime(I + 6, cache);
}
return R;
};
int main()
{
std::cout << prime_sum(63210123);
}
This is the fastest algorithm to find all prime numbers from 1 to n(on my pc it found all from 1 to 1000000 just for 0.004 seconds).
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
double FindPrime(bool* array, int size){
clock_t start;
double runtime;
for (int i = 2; i < size; i++)
array[i] = true;
start = clock();
for (int i = 2; i <= size; i++)
if (array[i])
for (int j = 2 * i; j < size; j += i)
array[j] = false;
runtime = (double)(clock() - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
return runtime;
}
int main() {
ofstream fout("prime.txt");
int n = 0;
cout << "Enter the upper limit of prime numbers searching algorithm:";
cin >> n;
bool* array = new bool[n + 1];
double duration = FindPrime(array, n + 1);
printf("\n%f seconds.\n", duration);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
if (array[i])
fout << i << endl;
fout.close();
return 0;
}
I always use this method for calculating primes numbers following with the sieve algorithm.
void primelist()
{
for(int i = 4; i < pr; i += 2) mark[ i ] = false;
for(int i = 3; i < pr; i += 2) mark[ i ] = true; mark[ 2 ] = true;
for(int i = 3, sq = sqrt( pr ); i < sq; i += 2)
if(mark[ i ])
for(int j = i << 1; j < pr; j += i) mark[ j ] = false;
prime[ 0 ] = 2; ind = 1;
for(int i = 3; i < pr; i += 2)
if(mark[ i ]) ind++; printf("%d\n", ind);
}
solution to find factors:
def divisors(integer):
result = set()
i = 2
j = integer/2
while(i <= j):
if integer % i == 0:
result.add(i)
#it dont need to
result.add(integer//i)
i += 1
j = integer//i
if len(result) > 0:
return f"not prime {sorted(result)}"
else:
return f"{integer} is prime"
--- Tests ---- import time
start_time = time.time()
print(divisors(180180180180))
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
--- 0.06314539909362793 seconds ---
start_time = time.time()
print(divs(180180180180180))
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
--- 1.5997519493103027 seconds ---
start_time = time.time()
print(divisors(1827))
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
--- 0.0 seconds ---
start_time = time.time()
print(divisors(104729))
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
--- 0.0 seconds ---
with this code:
def divs(integer):
result = set()
i = 2
j = integer / 2
loops = 0
while (i <= j):
if integer % i == 0:
print(f"loops:{loops}")
return f"{integer} is not a prime"
i += 1
j = integer // i
loops += 1
print(f"loops:{loops}")
return f"{integer} is prime"
--- Tests ---
start_time = time.time()
print(divs(180180180180180180180180))
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
--- 0.0 seconds ---
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
long long unsigned x,y,b,z,e,r,c;
scanf("%llu",&x);
if(x<2)return 0;
scanf("%llu",&y);
if(y<x)return 0;
if(x==2)printf("|2");
if(x%2==0)x+=1;
if(y%2==0)y-=1;
for(b=x;b<=y;b+=2)
{
z=b;e=0;
for(c=2;c*c<=z;c++)
{
if(z%c==0)e++;
if(e>0)z=3;
}
if(e==0)
{
printf("|%llu",z);
r+=1;
}
}
printf("|\n%llu outputs...\n",r);
scanf("%llu",&r);
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int set [1000000];
int main (){
for (int i=0; i<1000000; i++){
set [i] = 0;
}
int set_size= 1000;
set [set_size];
set [0] = 2;
set [1] = 3;
int Ps = 0;
int last = 2;
cout << 2 << " " << 3 << " ";
for (int n=1; n<10000; n++){
int t = 0;
Ps = (n%2)+1+(3*n);
for (int i=0; i==i; i++){
if (set [i] == 0) break;
if (Ps%set[i]==0){
t=1;
break;
}
}
if (t==0){
cout << Ps << " ";
set [last] = Ps;
last++;
}
}
//cout << last << endl;
cout << endl;
system ("pause");
return 0;
}
(n%2)+1+(3*n) is kind of nice though. :) –
Cothran I know it's somewhat later, but this could be useful to people arriving here from searches. Anyway, here's some JavaScript that relies on the fact that only prime factors need to be tested, so the earlier primes generated by the code are re-used as test factors for later ones. Of course, all even and mod 5 values are filtered out first. The result will be in the array P, and this code can crunch 10 million primes in under 1.5 seconds on an i7 PC (or 100 million in about 20). Rewritten in C it should be very fast.
var P = [1, 2], j, k, l = 3
for (k = 3 ; k < 10000000 ; k += 2)
{
loop: if (++l < 5)
{
for (j = 2 ; P[j] <= Math.sqrt(k) ; ++j)
if (k % P[j] == 0) break loop
P[P.length] = k
}
else l = 0
}
sqrt can be hoisted out of the loop and computed only once, while P[j]*P[j] must be computed at every iteration. I wouldn't presume one is faster than the other without testing. –
Counterpoison k % P[j] in the inner-most loop makes the algorithm one of slower ones. –
Humus #include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
int num,i,j,prime;
cout<<"Enter the upper limit :";
cin>>num;
cout<<"Prime numbers till "<<num<<" are :2, ";
for(i=3;i<=num;i++)
{
prime=1;
for(j=2;j<i;j++)
{
if(i%j==0)
{
prime=0;
break;
}
}
if(prime==1)
cout<<i<<", ";
}
}
break; it would be even slower, O(N^2), but that could be seen as a coding error already. saving and testing by primes is O(N^2/(log N)^2), and testing by primes below number's square root only, is O(N^1.5/(log N)^2). –
Cothran [n | n<-[2..], notElem(n) [j*k | j<-[2..(n-1)], k<-[2..(n-1)]]], or the absolute winner, let { isPrime(n) = n>1 && []==[i | i<-[2..n-1], isPrime(i) && rem(n)(i)==0] } in filter(isPrime) [2..] (in Haskell, sorry; using list comprehension syntax; rem is for remainder, %; [] is empty list). Compared to these two, the one here is all right (and by the way, equivalent to the last one, if one crucial - and simple - change is made). –
Cothran © 2022 - 2024 — McMap. All rights reserved.

int p[]= {2, 3};qualify as a "fastest algorithm to find out primes" ? – Bendicty